Residue Testing Market Size
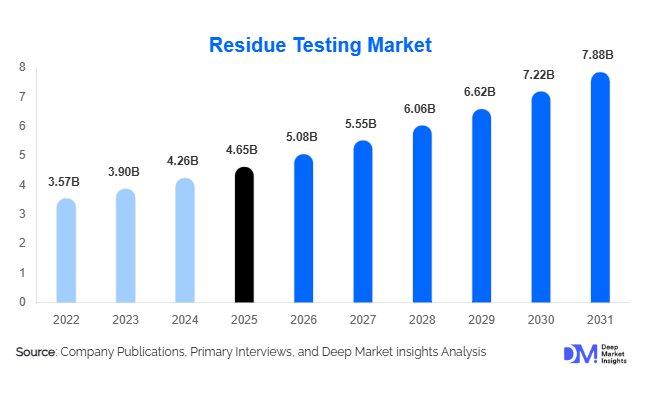
According to Deep Market Insights, the global residue testing market size was valued at USD 4.65 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 5.08 billion in 2026 to reach approximately USD 7.88 billion by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The residue testing market growth is primarily driven by tightening global food safety regulations, rising international trade of agricultural and food products, increasing consumer awareness regarding food quality, and the widespread adoption of advanced analytical testing technologies.
Key Market Insights
- Pesticide residue testing dominates the market, accounting for the largest share due to extensive pesticide usage in agriculture and stringent maximum residue limit (MRL) enforcement worldwide.
- Chromatography-based testing methods remain the gold standard, supported by regulatory acceptance and high accuracy in multi-residue detection.
- Europe leads the global market in value terms, driven by strict EU food safety frameworks and frequent surveillance programs.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, supported by expanding agricultural exports, rising domestic food safety enforcement, and rapid laboratory capacity expansion.
- Food manufacturers and processors are the largest end users, driven by mandatory compliance requirements before retail distribution.
- Rapid and on-site testing technologies are gaining traction as cost-effective pre-screening tools, especially among exporters and small producers.
What are the latest trends in the residue testing market?
Expansion of Multi-Residue and High-Throughput Testing
Residue testing laboratories are increasingly adopting multi-residue testing protocols that allow simultaneous detection of hundreds of compounds in a single analysis. This trend is driven by regulatory agencies expanding the list of monitored residues and lowering permissible limits. High-throughput LC-MS/MS systems, automation, and laboratory information management systems (LIMS) are improving efficiency, reducing turnaround time, and lowering per-sample costs. These advancements are enabling laboratories to handle rising testing volumes without proportionally increasing operational costs.
Growth of Rapid and On-Site Testing Solutions
Rapid residue testing kits and portable analyzers are gaining adoption as preliminary screening tools across farms, processing facilities, and export hubs. While confirmatory testing remains laboratory-based, on-site testing helps identify non-compliant batches early, reducing rejection risks and financial losses. This trend is particularly strong in emerging markets, where exporters are seeking faster compliance checks before shipment. The integration of digital reporting and cloud-based data sharing is further enhancing the usability of rapid testing solutions.
What are the key drivers in the residue testing market?
Stringent Global Food Safety Regulations
Governments and regulatory authorities worldwide are enforcing stricter food safety regulations to protect public health and ensure trade compliance. Lower MRL thresholds, expanded residue monitoring programs, and mandatory testing for both domestic consumption and exports are driving recurring demand for residue testing services. Regulatory harmonization with international standards such as Codex Alimentarius is further increasing testing frequency across supply chains.
Growth in International Food Trade
The rising global trade of agricultural commodities, seafood, meat, and processed foods has significantly increased the need for residue testing. Export-oriented producers must comply with the regulatory requirements of importing countries, often necessitating multiple rounds of testing. This driver is especially strong in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where agricultural exports are expanding rapidly.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Capital and Operational Costs
Advanced residue testing requires significant investment in sophisticated analytical instruments, skilled personnel, and accreditation processes. High capital expenditure and operating costs limit entry for smaller laboratories and can constrain capacity expansion in price-sensitive markets.
Pricing Pressure from Large Clients
Large food manufacturers and exporters often negotiate long-term contracts with testing laboratories, exerting pricing pressure and compressing margins. This creates challenges for smaller players that lack scale or technological differentiation.
What are the key opportunities in the residue testing industry?
Export-Oriented Testing Infrastructure in Emerging Economies
Emerging economies are rapidly expanding agricultural and food exports, creating strong demand for export-compliant residue testing facilities near production zones and ports. Establishing accredited laboratories focused on export certification presents a major opportunity for both global and regional players.
Integration of Digital Traceability and Data Platforms
The integration of residue testing data with digital traceability platforms offers significant value to food brands, retailers, and regulators. Digital solutions that link testing results with supply chain data are enhancing transparency, improving recall management, and strengthening brand trust.
Residue Type Insights
Pesticide residues represent the largest and most commercially critical segment of the residue testing market, accounting for approximately 38% of global market share in 2025. This dominance is primarily driven by the extensive and continuous use of agrochemicals across conventional agriculture, coupled with increasingly strict enforcement of maximum residue limits (MRLs) by regulatory authorities worldwide. The expansion of multi-residue testing mandates, particularly for fruits, vegetables, cereals, and oilseeds, has significantly increased testing volumes within this segment. Additionally, frequent updates to permitted pesticide lists and lower tolerance thresholds in export markets such as the EU and the U.S. are reinforcing recurring testing demand.
Veterinary drug residue testing constitutes the second-largest segment, supported by rising global production and consumption of meat, poultry, dairy, and aquaculture products. Increased scrutiny over antibiotic misuse, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and hormone residues has led to more rigorous monitoring programs, especially in export-oriented livestock industries. This segment benefits strongly from government surveillance initiatives and retailer-driven quality assurance programs. Mycotoxin residue testing is witnessing steady expansion due to climate-driven contamination risks in grains, cereals, nuts, and animal feed. Rising temperature variability, humidity, and storage challenges are increasing aflatoxin and ochratoxin incidences, particularly in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America. Meanwhile, heavy metal residue testing remains a critical segment driven by environmental pollution concerns, industrial contamination, and regulatory monitoring of water, soil, and food products, especially seafood and infant nutrition.
Technology Insights
Chromatography-based testing methods dominate the residue testing market, accounting for over 50% of total market revenue, and remain the preferred analytical approach globally. This leadership is driven by their unmatched accuracy, sensitivity, and ability to simultaneously detect multiple residues at trace levels. Technologies such as LC-MS/MS and GC-MS are widely accepted by regulatory agencies and are essential for confirmatory testing, making them indispensable for accredited laboratories and export certification. The continued dominance of chromatography is further reinforced by rising regulatory complexity, where laboratories must screen an expanding number of compounds within a single sample. Automation, high-throughput systems, and integrated laboratory information management systems (LIMS) are further strengthening the commercial viability of chromatography-based platforms.
Immunoassay-based methods, including ELISA and lateral flow assays, are widely used as cost-effective screening tools, particularly in high-volume testing environments and early-stage quality checks. These methods enable rapid decision-making before confirmatory analysis. Spectroscopy-based techniques, such as ICP-MS and atomic absorption spectroscopy, play a critical role in heavy metal residue detection, particularly for environmental and seafood testing. Rapid and biosensor-based testing technologies are emerging as complementary solutions, gaining adoption for on-site screening at farms, processing facilities, and export hubs. While they do not replace laboratory-based confirmatory testing, their ability to reduce rejection risks and turnaround time is driving steady uptake, especially in emerging markets.
End-Use Insights
Food manufacturers and processors represent the largest end-use segment in the residue testing market, driven by mandatory compliance requirements before retail distribution and export. Branded food producers, private-label manufacturers, and multinational processors rely heavily on routine residue testing to mitigate recall risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect brand reputation. Increasing retailer-led quality audits and supplier verification programs are further strengthening demand from this segment. Agricultural producers and exporters form the second-largest end-use segment, particularly in fresh produce, seafood, grains, and meat exports. Export-oriented testing is characterized by repeated batch testing, destination-specific compliance requirements, and third-party certification, resulting in high testing frequency and recurring revenue streams for laboratories.
Government and regulatory bodies continue to expand residue monitoring and surveillance programs as part of national food safety strategies. These programs drive large-volume, long-term testing contracts, often outsourced to accredited private laboratories. Contract research and testing laboratories play a central role in the market by providing specialized analytical capabilities, regulatory expertise, and scalable testing services to food producers, exporters, and government agencies alike.
| By Residue Type | By Technology | By End Use | By Sample Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Europe
Europe accounted for approximately 31% of the global residue testing market in 2025, making it the largest regional market by value. Growth in this region is primarily driven by the European Union’s stringent food safety regulations, low MRL thresholds, and comprehensive monitoring frameworks covering both domestic production and imports. Countries such as Germany, France, Italy, and Spain are key contributors due to their large food processing industries, high agricultural output, and advanced laboratory infrastructure. Frequent regulatory audits, strong enforcement mechanisms, and high consumer awareness regarding food safety further sustain high testing volumes across the region.
North America
North America held nearly 27% of the global market share, led predominantly by the United States. Regional growth is driven by strong regulatory enforcement, well-established food safety systems, and high consumption of processed and packaged foods. Mandatory testing programs enforced by food safety authorities, combined with retailer-driven quality standards, generate consistent demand. Canada contributes significantly through seafood, grain, and agricultural exports, where compliance with both domestic and international standards necessitates frequent residue testing.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, registering a CAGR exceeding 11%. Growth is driven by the rapid expansion of agricultural and food exports, rising domestic food safety enforcement, and increasing investment in laboratory infrastructure. China and India are major contributors, supported by regulatory reforms, export certification requirements, and heightened public scrutiny of food safety. Japan and Australia represent mature, high-value markets characterized by stringent standards and advanced analytical capabilities. Government initiatives to modernize food safety systems and align with global standards are accelerating regional demand.
Latin America
Latin America is witnessing steady growth, led by Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. The region’s expansion is driven by growing agricultural exports, particularly fruits, vegetables, meat, and seafood, to North America and Europe. Increasing regulatory alignment with international food safety standards and rising investment in export-oriented testing infrastructure are strengthening market growth. Climate-related contamination risks are also contributing to increased mycotoxin and pesticide residue testing demand.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa region is growing steadily, supported by a combination of food import dependence, export-driven testing in Africa, and increasing food safety investments in Gulf countries. GCC nations are strengthening food safety surveillance to ensure compliance with imported products, while African countries are expanding residue testing capacity to support agricultural exports. International aid programs, public-private partnerships, and investments in laboratory accreditation are further contributing to market development across the region.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Residue Testing Market
- SGS
- Eurofins Scientific
- Bureau Veritas
- Intertek Group
- ALS Limited
- TÜV SÜD
- TÜV Rheinland
- Mérieux NutriSciences
- NSF International
- AsureQuality
- Romer Labs
- Symbio Laboratories
- R J Hill Laboratories
- Tentamus Group
- FoodChain ID