Home Appliances Glass Market Size
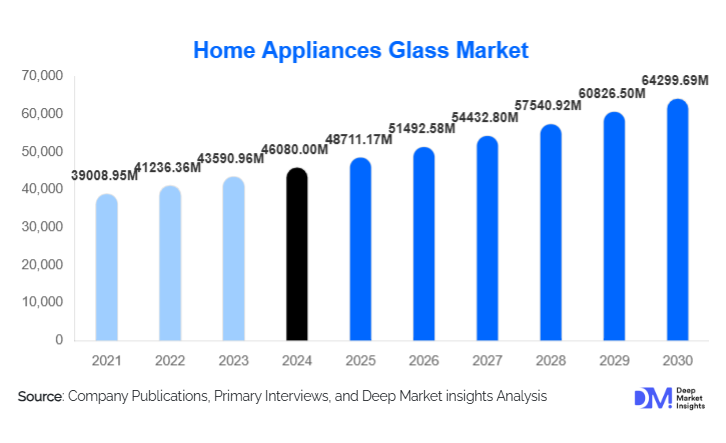
According to Deep Market Insights, the global home appliances glass market size was valued at USD 46,080.00 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 48,711.17 million in 2025 to reach USD 64,299.69 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 5.71% during the forecast period (2025–2030). Market growth is primarily driven by rising global demand for refrigerators, washing machines, ovens, cooktops, and microwaves, increasing consumer preference for premium glass-fronted and built-in appliances, and the integration of smart touch interfaces and advanced coatings that enhance both aesthetics and performance.
Key Market Insights
- Tempered soda–lime glass dominates the market, accounting for around 44% of global revenue in 2024 due to its broad use in refrigerator shelves, washing machine lids, microwave doors, and small appliances.
- Refrigerators and freezers are the largest application segment, representing roughly 30% of the market as multi-door and glass-rich designs become standard in many regions.
- Residential appliances drive nearly 78% of total demand, with rising penetration of dishwashers, automatic washing machines, and built-in ovens in emerging markets.
- OEM sales channels dominate with approximately 89% share, reflecting tightly integrated supply chains between glass processors and global appliance manufacturers.
- Asia-Pacific leads with about 41% of global market value, supported by strong manufacturing bases in China, India, South Korea, and Southeast Asia, and by rising domestic demand.
- Technology-intensive products such as glass-ceramic cooktops, coated oven doors, and digitally printed fascias are gaining share and supporting higher margins for specialized glass producers.
What are the latest trends in the home appliances glass market?
Smart User-Interface and Connected Appliance Glass
One of the most significant trends in the home appliances glass market is the shift toward smart user-interface glass for connected appliances. Ovens, refrigerators, and washing machines increasingly feature integrated displays, capacitive touch panels, and sensor windows behind sleek glass fronts. This requires high-clarity, scratch-resistant, and chemically strengthened glass that can accommodate embedded electronics while maintaining premium aesthetics. Manufacturers are developing multi-functional panels that combine display areas, touch-sensitive zones, and indicator lighting in a single glass surface. As smart home ecosystems expand and app-based control becomes commonplace, demand for advanced interface glass is expected to outpace that of standard clear glass, raising average value per unit across key appliance categories.
Premium Aesthetics, Coatings, and Digital Printing
Another major trend is the rapid adoption of premium surface finishes and decorative technologies. Consumers increasingly associate glass with modern, minimalist design, driving demand for black mirror oven doors, frameless glass refrigerator doors, and continuous glass-ceramic cooktops. To differentiate their products, appliance brands are specifying glass with anti-fingerprint, anti-glare, and easy-to-clean coatings. Digital and screen printing techniques are being used to embed control icons, brand logos, patterns, and color gradients directly into the glass, replacing traditional plastic overlays. These technologies enable highly customized, region-specific designs without changing mechanical components, giving OEMs greater flexibility and allowing glass processors to move up the value chain.
What are the key drivers in the home appliances glass market?
Urbanization, Rising Income, and Kitchen Modernization
The global expansion of the middle class, particularly in Asia and Latin America, is a foundational driver for the home appliances glass market. Rapid urbanization and the construction of new housing drive first-time purchases of refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, and ovens, all of which incorporate glass in shelves, doors, or control panels. In mature markets such as North America and Europe, growth is driven by replacement demand and kitchen remodeling. Homeowners are shifting from free-standing to built-in, design-coordinated kitchens where glass-front ovens, cooktops, and refrigerators act as visual focal points. This upgrade cycle not only increases unit volumes in certain categories but also raises the glass content and quality level per appliance.
Shift Toward Energy Efficiency and Safety Compliance
Stricter regulations on energy efficiency and product safety across major markets are directly boosting demand for high-performance glass solutions. In refrigerators and freezers, better-insulating glass doors help reduce thermal losses, supporting compliance with efficiency labeling schemes. In ovens, multi-layer and coated glass doors keep exterior surfaces cooler while improving heat retention, helping manufacturers meet eco-design and safety standards. Glass-ceramic cooktops withstand extreme temperature variations and thermal shocks, enabling the widespread adoption of induction and high-power electric cooking. As standards tighten and consumers become more aware of efficiency ratings, OEMs increasingly rely on advanced glass technologies to differentiate products and secure regulatory approvals.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Raw Material and Energy Cost Volatility
The home appliances glass industry is energy and raw material-intensive, relying heavily on silica sand, soda ash, and significant thermal energy for melting and tempering processes. Volatile energy prices and fluctuating raw material costs can compress margins for glass producers, especially when OEMs resist short-term price increases under long-term contracts. These cost pressures can delay capacity expansions, limit investment in new coating or printing lines, and encourage price-based competition in commoditized segments such as standard tempered panels. Smaller processors with less purchasing power and older, less efficient furnaces are particularly vulnerable to swings in gas and electricity prices.
Overcapacity and Price Pressure in Standard Glass Segments
In some regions, especially parts of Asia, historical investment in float glass and tempering lines has created pockets of overcapacity for standard clear tempered glass. This oversupply environment often results in aggressive price competition, short contract cycles, and commoditization, making it difficult for undifferentiated players to maintain healthy margins. For OEMs, this dynamic is beneficial in the short term but raises longer-term concerns around supplier consolidation and supply resilience for more specialized glass components. To overcome this restraint, many processors are shifting focus toward higher-spec products, such as coated, printed, or shaped glass, with more stable pricing and stronger OEM partnerships.
What are the key opportunities in the home appliances glass industry?
Advanced Interface, Sensor, and Display Integration
A major opportunity lies in the integration of displays, sensors, and touch controls into appliance glass. As connected appliances become standard, brands are looking to turn glass doors and fascias into interactive control hubs. This creates demand for specialized laminates that can accommodate OLED or LCDs, capacitive touch layers, and embedded LEDs while ensuring impact resistance and thermal stability. Glass manufacturers that invest in co-development with electronics suppliers and appliance OEMs can capture premium opportunities in smart ovens, refrigerators with display doors, and washer–dryer control panels. The higher value per square meter, combined with long-term platform commitments from OEMs, can significantly enhance revenue and margins.
Regional Manufacturing Hubs and Localized Premiumization
Another key opportunity is the growth of regional manufacturing hubs for both appliances and glass. Countries such as China, India, Turkey, Poland, Mexico, and Vietnam are emerging as global centers for appliance production, supported by incentives like “Make in India” and other local manufacturing policies. Establishing glass cutting, tempering, and coating facilities near these hubs reduces logistics costs, shortens lead times, and supports just-in-time delivery. At the same time, local consumers in these markets are trading up to more premium, glass-rich kitchen appliances, creating a dual revenue stream from exports and domestic sales. Companies that can offer localized designs, flexible batch sizes, and rapid prototyping around regional preferences are well-positioned to capture this opportunity.
Product Type Insights
By product type, tempered soda–lime glass holds the largest share, accounting for around 44% of the global market value in 2024. Its versatility, safety characteristics, and relatively low cost make it the default choice for refrigerator shelving, inner doors, washing machine lids, microwave doors, and many small appliances. Glass-ceramic represents a smaller but rapidly growing segment, driven by the popularity of flat cooktops and induction hobs that require high thermal resistance and stability. Borosilicate glass is favored for components that face temperature shocks and chemical exposure, including certain oven and microwave parts and specialty small appliances. Laminated and multi-layer safety glass is gaining traction in high-end refrigerator doors and premium oven doors, while coated, low-iron, and decorative glass contribute disproportionately to market value through advanced functional and aesthetic features.
Application Insights
Among applications, refrigerators and freezers form the largest segment, contributing roughly 30% of the home appliances glass market in 2024. Each unit incorporates multiple glass components, including shelves, crisper covers, bottle racks, and, in many premium models, glass-front doors. Ovens, ranges, and built-in cooktops represent another significant segment, driven by multi-layer oven doors and glass-ceramic cooktops. Microwaves and combination ovens rely on glass doors and viewing windows for safety and usability. Washing machines and dryers, especially front-load models, require large glass doors that double as design elements, while dishwashers, range hoods, splashbacks, and a variety of small appliances collectively add meaningful incremental demand. The trend toward built-in and integrated kitchen layouts, with aligned glass finishes across multiple appliances, is reinforcing growth across all major application segments.
Distribution Channel Insights
The home appliances glass market is overwhelmingly dominated by the OEM channel, which accounts for approximately 89% of global revenues. Glass processors supply directly to appliance manufacturers or through tier-1 component suppliers that integrate glass with metal frames, hinges, and seals. Long-term contracts, joint development of new designs, and strict quality and logistics requirements characterize this channel. The aftermarket and replacement segment makes up the remaining ~11% of the market and includes replacement shelves, doors, and panels sold through authorized service networks, third-party repair shops, and online platforms. While lower in volume, aftermarket glass can command higher unit prices due to smaller batch sizes and urgent replacement needs, especially for high-end appliances.
End-Use Insights
Residential household appliances are the primary end-use category, representing about 78% of market demand in 2024. This segment is expanding as household incomes rise, urban housing stock grows, and consumers upgrade from basic models to mid-range and premium appliances with larger glass surfaces and more complex finishes. In parallel, commercial foodservice and hospitality, including professional ovens, refrigerated display cases, beverage coolers, coffee machines, and dishwashers, constitute a smaller but faster-growing segment, supported by the proliferation of cafés, bakeries, supermarkets, and restaurant chains. Industrial and institutional appliances used in laundries, canteens, and healthcare facilities demand high-durability glass with stringent hygiene and safety specifications, adding a niche but high-value component to overall market demand.
Manufacturing Technology Insights
From a technology standpoint, the market is shaped by advancements in float glass cutting and tempering, bending and curving, molding and pressing, and coating and digital printing. Float glass lines supply the base material, which is then cut, edge-finished, drilled, and tempered to meet safety standards. Bending and curving technologies enable complex shapes required for oven doors, washer doors, and range hoods. Molding and pressing techniques support knobs, handles, and contoured components. The most dynamic area is coating and printing, where low-E, IR-reflective, anti-fingerprint, and easy-clean coatings are combined with screen or digital printing to achieve high-performance, brand-specific designs. Lamination and assembly processes are increasingly used for multi-layer structures, particularly in premium refrigerator and oven doors, further elevating technical complexity and value.
| By Glass Type | By Application | By End Use | By Manufacturing Technology | By Sales Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for roughly 22% of the home appliances glass market in 2024, with the United States representing the majority share and Canada contributing the remainder. The region is characterized by high appliance penetration and a strong replacement cycle, particularly in refrigerators, washers, dryers, and ranges. Consumers favor large-capacity appliances with premium glass-front designs, supporting higher average glass content per unit. North America is also one of the largest importers of finished appliances and glass products, drawing significant volumes of glass embedded in imported refrigerators, ovens, and microwaves. Demand growth is moderate but steady, supported by residential renovation activity and the adoption of smart, connected appliances.
Europe
Europe holds about 24% of the global market value, with major contributions from Germany, Italy, France, the U.K., and Spain. The region is strongly oriented toward built-in kitchens and energy-efficient appliances, which typically incorporate high-spec glass doors, glass-ceramic cooktops, and complex multi-layer oven glass. Stringent regulations on energy efficiency, safety, and eco-design encourage the adoption of advanced coatings and multi-pane structures. European consumers place a high value on design coherence across appliance brands and kitchen furniture, driving demand for coordinated glass finishes and colors. While overall appliance volume growth is modest, value growth is supported by premiumization and replacement of older, less efficient units.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the largest and fastest-growing region, accounting for around 41% of global home appliances glass demand in 2024. China alone represents roughly 20% of global demand, acting as both a major production hub and a large domestic market. India, Japan, South Korea, and Southeast Asian countries together add another substantial share. APAC benefits from a combination of rising household incomes, rapid urbanization, expanding housing stock, and strong export-oriented appliance manufacturing. Government initiatives promoting local manufacturing, such as India’s “Make in India,” further stimulate capacity investments in glass processing. The region’s market is expected to grow faster than the global average, with a particularly strong outlook for premium and smart appliances in urban centers.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for approximately 7% of the market, with Brazil and Mexico as the key countries. Brazil’s large population and growing middle class drive domestic demand for refrigerators, washing machines, and cookers, while Mexico functions as both a domestic market and an export base supplying North America. Appliance OEMs in the region are gradually shifting toward more glass-rich designs, although the rate of premiumization is slower than in Europe or North America. Economic volatility and currency fluctuations can temporarily impact appliance purchases and, consequently, glass demand, but long-term prospects remain positive as urbanization and electrification continue.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa (MEA) region holds about 6% of global market value, with demand concentrated in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar, alongside South Africa and select North African economies. Hot climates and reliance on refrigeration and cooling systems support sustained demand for refrigerators and freezers, many of which feature glass shelves and doors. The growth of modern retail, hotels, and restaurants is also driving demand for glass-fronted display refrigeration and professional kitchen appliances. From a growth perspective, MEA is among the faster-growing regions, although from a smaller base, as infrastructure development and rising disposable incomes translate into increased appliance adoption.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Top Manufacturers in the Home Appliances Glass Industry
- AGC Inc. (Asahi Glass)
- Saint-Gobain S.A.
- Schott AG
- Guardian Industries Holdings LLC
- Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd.
- EuroKera
- Corning Incorporated
- Xinyi Glass Holdings Ltd.
- CSG Holding Co., Ltd.
- China Glass Holdings Ltd.
- Qingdao Lansen Glass Technology Co., Ltd.
- Sanfeng Glass Co., Ltd.
- Taian Saintly Glass Co., Ltd.
- Kunshan Energy Glass Technology Co., Ltd.
- Vetrerie Riunite Group
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, Whirlpool of India introduced the Ice Magic Pro glass door refrigerator range, featuring premium glass-front designs, Microblock antibacterial technology, and claims of up to seven days of “garden freshness” plus extended milk preservation during power cuts for Indian households.
- In June 2024, Haier India launched its Phoenix series of direct-cool glass door refrigerators, promoted as one of the widest glass-door DC line-ups in the Indian market, with decorative glass fascias aimed at style-conscious consumers in the 185–190 litre segment.
- In May 2024, LG Electronics expanded its InstaView refrigerators with MoodUP into Europe, bringing colour-changing LED glass doors and knock-to-see-inside viewing panels to markets such as France, and positioning the range as both a design element and a connected appliance controlled via the ThinQ app.
- In January 2025, LG announced the Smart InstaView French Door Refrigerator featuring a 36-inch transparent OLED display embedded in the upper right glass door, enabling users to see contents, view widgets and media, and overlay digital information directly on the transparent panel.
- In September 2024, Siemens presented its premium iQ500 inductionAir Plus cooktop at IFA, using SCHOTT CERAN Miradur glass-ceramic with the “diamondProtect” scratch-resistant coating to deliver a highly durable, glossy glass surface for high-end built-in hobs.