Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Market Size
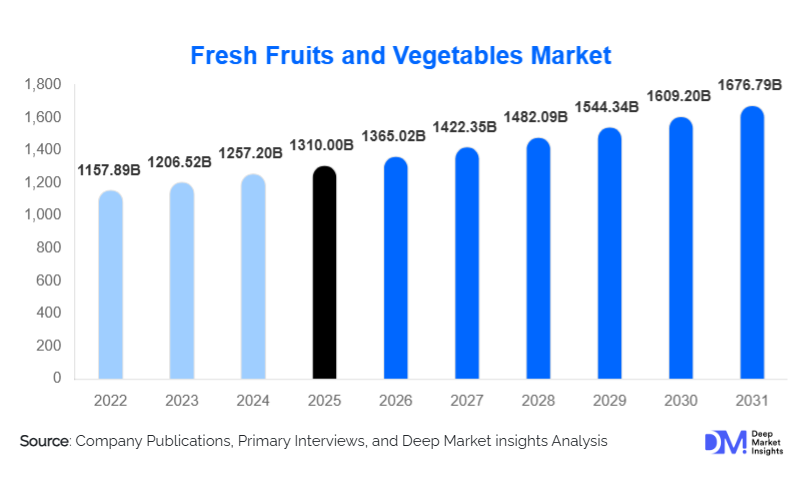
According to Deep Market Insights, the global fresh fruits and vegetables market size was valued at USD 1,310.00 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 1,365.02 billion in 2026 to reach USD 1,676.79 billion by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 4.2% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The fresh fruits and vegetables market growth is primarily driven by rising health consciousness, increasing consumption of plant-based diets, expansion of organized retail and e-commerce channels, and improvements in cold chain and logistics infrastructure globally.
Key Market Insights
- Vegetables dominate global consumption, accounting for more than half of the total market value due to their role as daily dietary staples across emerging and developed economies.
- Asia Pacific leads global demand, supported by population density, strong domestic production, and cultural preference for fresh food consumption.
- Supermarkets and hypermarkets remain the leading distribution channel, benefiting from better supply chain integration, quality control, and private-label expansion.
- Organic produce is the fastest-growing natural segment, driven by rising consumer awareness around food safety, sustainability, and chemical-free farming.
- E-commerce and direct-to-consumer models are reshaping procurement, improving price transparency and year-round availability of fresh produce.
- Cold-chain modernization and post-harvest loss reduction are becoming critical competitive differentiators for producers and exporters.
What are the latest trends in the fresh fruits and vegetables market?
Rising Demand for Organic and Clean-Label Produce
Consumer preferences are increasingly shifting toward organic and clean-label fruits and vegetables, driven by health awareness and concerns over pesticide residues. Organic produce is witnessing higher adoption in North America and Europe, while urban centers in the Asia Pacific are emerging as high-growth markets. Retailers are expanding shelf space for certified organic fruits and vegetables, often commanding price premiums of 20–40% over conventional produce. Traceability, eco-certifications, and sustainable farming practices are becoming essential for brand differentiation.
Digitalization and Cold Chain Integration
Technology integration across the fresh produce value chain is accelerating. Digital procurement platforms, blockchain-enabled traceability, IoT-based cold storage monitoring, and AI-driven demand forecasting are improving efficiency and reducing waste. Cold chain investments are enabling longer shelf life and higher export volumes, particularly for berries, leafy greens, and tropical fruits. These advancements are improving market access for producers and ensuring consistent quality for retailers and end consumers.
What are the key drivers in the fresh fruits and vegetables market?
Growing Health and Nutrition Awareness
Rising incidence of lifestyle diseases and global health campaigns promoting fruit- and vegetable-rich diets are significantly boosting consumption. Fresh produce is increasingly viewed as essential for preventive healthcare, driving sustained household demand and institutional procurement by schools and hospitals.
Urbanization and Modern Retail Expansion
Rapid urbanization and the growth of organized retail formats have improved accessibility to diverse fresh produce. Supermarkets, hypermarkets, and online grocery platforms offer standardized quality, competitive pricing, and convenience, strengthening demand across urban and semi-urban regions.
Global Trade and Export Growth
Advancements in logistics and trade agreements have increased cross-border trade of fresh produce. Import-dependent regions rely heavily on exports to ensure year-round availability, supporting global market expansion.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Post-Harvest Losses
Inadequate storage and transportation infrastructure in developing economies leads to significant post-harvest losses, reducing effective supply and impacting farmer profitability. These inefficiencies constrain market growth and price stability.
Climate and Seasonal Volatility
Fresh produce production is highly sensitive to weather patterns and climate change. Extreme temperatures, droughts, and floods disrupt yields and increase price volatility, posing challenges for supply consistency.
What are the key opportunities in the fresh fruits and vegetables industry?
Cold Chain and Infrastructure Development
Investments in cold storage, refrigerated transport, and packhouse infrastructure present major growth opportunities. Improved post-harvest handling can significantly reduce losses, enhance export competitiveness, and stabilize pricing.
Value-Added and Ready-to-Eat Fresh Produce
Demand for pre-cut, washed, and ready-to-eat fruits and vegetables is rising, particularly among urban consumers and foodservice operators. This segment offers higher margins and longer shelf life, creating opportunities for product innovation.
Product Type Insights
Fresh vegetables dominate the global market, accounting for approximately 55% of the total market value in 2025. Their leading position is primarily driven by daily consumption patterns, affordability, and nutritional awareness among consumers worldwide. Leafy greens, tubers, and cruciferous vegetables are staples in households across both developed and emerging markets, while technological advancements in cultivation, cold-chain storage, and distribution have improved year-round availability, further supporting this segment. Fresh fruits constitute roughly 35% of the market, with rising consumer preference for citrus fruits, berries, and tropical varieties, especially in urban and high-income regions. Organic produce, although smaller in overall share, is the fastest-growing segment, propelled by premiumization, sustainability trends, and increasing willingness of consumers to pay a price premium for chemical-free, eco-friendly produce.
End-Use Insights
Household consumption remains the dominant end-use segment, representing nearly 60% of global demand. This is fueled by increasing health consciousness, preference for home-cooked meals, and incorporation of fresh produce into daily diets. The foodservice sector accounts for approximately 25% of demand, benefiting from the recovery of restaurants, quick-service restaurants (QSRs), and cafes, where fresh vegetables and fruits are integral to menu offerings. The remaining share is driven by food and beverage processing and institutional consumption (schools, hospitals, corporate cafeterias), which are expanding due to rising demand for nutrition-focused programs, plant-based products, and convenience-oriented food solutions.
Distribution Channel Insights
Supermarkets and hypermarkets capture approximately 40–45% of global sales of fresh fruits and vegetables. Their dominance is underpinned by economies of scale, superior quality control, consistent supply, and private-label offerings. Traditional retail channels, including local grocers and wet markets, remain important in emerging economies due to accessibility and price sensitivity. However, online grocery platforms and direct-to-consumer (D2C) models are the fastest-growing channels, driven by urbanization, digital penetration, and consumer demand for convenience, wider assortment, and home delivery solutions. Subscription-based models and app-enabled fresh produce services are further accelerating growth in developed and emerging markets.
| By Product Type | By End Use | By Distribution Channel | By Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads the global market, accounting for over 40% of the total market share, with China and India as primary contributors. The region’s growth is driven by large population bases, strong domestic agricultural production, and cultural preference for fresh produce in daily diets. Urbanization, retail modernization, and increasing adoption of cold-chain logistics have enhanced distribution efficiency, reducing post-harvest losses and improving quality. Rising disposable incomes, growing health awareness, and the expansion of online grocery channels are further boosting demand. Additionally, government support for agri-tech, infrastructure modernization, and export promotion programs is reinforcing growth in both fruits and vegetables.
North America
North America holds approximately 25–30% of the global market share, led by the United States. Drivers include high per-capita consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits, strong demand for organic and convenience-oriented produce, and year-round access to imported and domestic supply through advanced logistics networks. Increasing consumer preference for healthy eating, plant-based diets, and ready-to-eat products fuels retail and foodservice demand. Technological adoption, including precision agriculture and cold-chain improvements, is enhancing crop quality and extending shelf life, ensuring the region maintains steady market growth.
Europe
Europe represents around 20–25% of the global market, with Germany, France, and the U.K. as major contributors. Growth is supported by high per-capita consumption, strong demand for organic and sustainably sourced produce, and strict food safety regulations. Urbanization, expanding modern retail, and consumer preference for convenience-driven products such as pre-cut vegetables and salad mixes are key drivers. Additionally, increasing government incentives for sustainable agriculture, environmental labeling, and healthy diet campaigns are reinforcing demand for both conventional and organic fresh produce.
Latin America
Latin America contributes approximately 8–10% of the market, with Mexico and Brazil as primary hubs. The market is driven by domestic consumption patterns, favorable climatic conditions, and large-scale production of both fruits and vegetables for export markets. Infrastructure improvements, expansion of modern retail, and government initiatives promoting agri-exports are supporting growth. The region also benefits from rising urbanization, which increases demand for convenience-focused and packaged fresh produce.
Middle East & Africa
MEA accounts for roughly 5–7% of global market share, with demand concentrated in countries such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. Key drivers include rapid urbanization, growing retail modernization, and high import reliance due to limited domestic production in arid regions. Investments in controlled-environment agriculture, greenhouse cultivation, and cold-chain infrastructure are enhancing local supply and import capacity. Rising awareness of health and nutrition is also boosting household consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, while institutional and foodservice demand continues to expand.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Market
- Dole plc
- Fresh Del Monte Produce, Inc.
- Driscoll’s, Inc.
- Chiquita Brands International
- Calavo Growers, Inc.
- Unifrutti Group
- Bonduelle S.A.
- Naturipe Farms
- Tanimura & Antle Fresh Foods, Inc.
- Andy Boy, LLC
- Goknur Gida
- BelOrta
- Fruitable Fresh Sdn Bhd
- FreshPoint Inc.
- Mirak Group