Cooking Wine Market Size
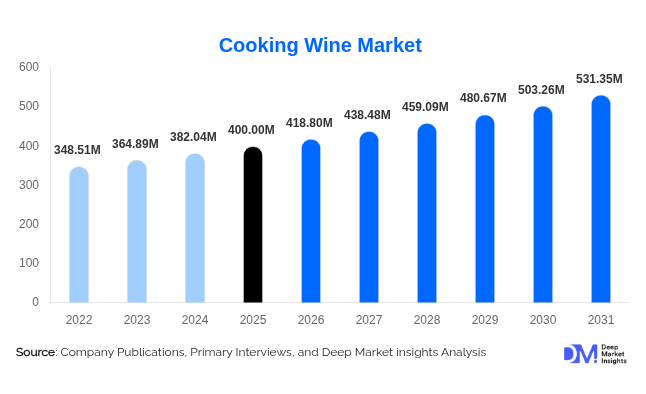
According to Deep Market Insights, the global cooking wine market size was valued at USD 400.00 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 418.80 million in 2026 to reach USD 531.35 million by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 4.7% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The cooking wine market's growth is primarily driven by the globalization of cuisines, rising demand for authentic flavor-enhancing ingredients, the expansion of the foodservice and HoReCa sectors, and increasing household adoption, supported by digital cooking platforms and premium home cooking trends.
Key Market Insights
- Asian cuisine-based cooking wines dominate global demand, led by rice-based variants such as Shaoxing wine and mirin used extensively in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean cooking.
- Commercial foodservice remains the largest end-use segment, accounting for a significant share of global volume due to standardized flavor requirements in restaurants and catering services.
- The Asia-Pacific region leads global consumption, driven by its large population bases, strong culinary traditions, and expanding food processing industries.
- Premium and clean-label cooking wines are gaining traction in North America and Europe, driven by health-conscious and gourmet-focused consumers.
- E-commerce and specialty food retail channels are expanding rapidly, improving product discovery and penetration among home cooks.
- Moderate market fragmentation exists, with the top five players accounting for approximately 38% of global market share.
What are the latest trends in the cooking wine market?
Premiumization and Clean-Label Formulations
The cooking wine market is witnessing a steady shift toward premium and clean-label products. Consumers are increasingly demanding low-sodium, preservative-free, and naturally fermented cooking wines that align with clean eating and wellness trends. Manufacturers are responding by introducing organic and artisanal variants, particularly in developed markets. Premium glass packaging, geographical origin labeling, and traditional brewing narratives are being used to differentiate products and justify higher price points.
Rising Integration with Ready-to-Eat and Meal Kits
Cooking wine is increasingly being integrated into ready-to-eat meals, frozen foods, and meal kits. Food processors are using cooking wine to enhance flavor consistency and authenticity at scale. Meal kit companies are also including small-format cooking wine sachets or bottles, driving incremental household adoption and increasing brand visibility among younger consumers.
What are the key drivers in the cooking wine market?
Globalization of Cuisines
The rapid spread of Asian, Mediterranean, and fusion cuisines across global markets is a major growth driver. Cooking wine is a core ingredient in many traditional recipes, and rising consumer interest in authentic home-cooked meals has boosted retail demand. Restaurants and foodservice operators increasingly rely on standardized cooking wine to maintain flavor consistency across outlets.
Expansion of the Foodservice and HoReCa Sector
The growth of quick-service restaurants, casual dining chains, cloud kitchens, and catering services has significantly increased bulk demand for cooking wine. Commercial kitchens value cooking wine for its functional role in marination, deglazing, and aroma enhancement, making it a staple ingredient across cuisines.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Regulatory and Alcohol Content Restrictions
Cooking wine faces regulatory scrutiny in certain regions due to its alcohol content. Import restrictions, labeling requirements, and religious or cultural limitations can restrict market penetration, particularly in the Middle East and parts of Africa.
Price Sensitivity in Emerging Economies
In price-sensitive markets, traditional substitutes such as vinegar, soy sauce, or local fermented liquids can limit cooking wine adoption. Higher logistics and packaging costs also impact affordability in developing regions.
What are the key opportunities in the cooking wine industry?
Growth in Emerging Foodservice Markets
Rapid urbanization and rising disposable incomes in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of the Middle East are creating new opportunities for cooking wine manufacturers. Expansion of regional restaurant chains and localized food processing facilities is expected to drive sustained B2B demand.
E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Expansion
The rise of online grocery platforms and specialty food e-commerce is unlocking new growth channels. Brands that invest in digital marketing, influencer-driven recipe content, and smaller household pack sizes are well-positioned to capture repeat purchases and premium margins.
Product Type Insights
Rice-based cooking wine dominates the global cooking wine market, accounting for approximately 42% of the total market share in 2025. This leadership is primarily driven by its indispensable role in Asian cuisines, where it is a foundational ingredient in marinades, stir-fries, sauces, and processed food formulations. The large-scale consumption of rice-based cooking wines in China, Japan, and Southeast Asia, combined with their extensive use in commercial foodservice and packaged foods, supports consistent high-volume demand. Additionally, the affordability and availability of rice-based variants compared to grape-based alternatives further strengthen their dominance.
Grape-based cooking wines, including red and white variants, maintain a strong presence in European and Western culinary applications. These products are widely used in French, Italian, and Mediterranean cooking, where wine reduction and deglazing techniques are integral to traditional recipes. Fortified cooking wines such as sherry and marsala cater to specialized culinary uses, particularly in European desserts and gourmet sauces, resulting in stable but niche demand. Meanwhile, specialty and regional cooking wines, including sake and herbal-infused variants, are gaining popularity among gourmet chefs and experimental home cooks, supported by premiumization trends and growing interest in authentic regional flavors.
Alcohol Content Insights
Medium alcohol cooking wines with an alcohol content of 10–18% ABV lead the market, holding nearly 48% share in 2025. This segment’s dominance is driven by its ability to deliver optimal flavor extraction, aroma enhancement, and meat tenderization without excessive volatility during cooking. Medium-alcohol variants also benefit from broader regulatory acceptance across global markets, making them suitable for both household and commercial applications.
Low-alcohol cooking wines are gaining traction in health-conscious and regulated markets, particularly in North America and parts of Europe, where consumers prefer lighter formulations with reduced alcohol perception. High-alcohol cooking wines remain concentrated in professional kitchens and specialty food manufacturing, where their strong flavor profiles are valued for concentrated sauces and slow-cooked dishes.
Distribution Channel Insights
Supermarkets and hypermarkets remain the dominant distribution channel, accounting for approximately 38% of global cooking wine sales. Their leadership is driven by extensive shelf visibility, wide product assortments, and consumer trust in organized retail. These outlets serve as primary access points for household consumers, particularly in urban and semi-urban regions.
Foodservice supply channels represent a close second, supported by bulk procurement from restaurants, catering services, and institutional kitchens. Meanwhile, e-commerce is the fastest-growing distribution channel, driven by increasing online grocery adoption, improved cold-chain logistics, and the influence of digital cooking content. Online platforms are particularly effective in promoting premium, specialty, and imported cooking wine variants that may have limited availability in traditional retail stores.
End-Use Insights
Commercial foodservice is the largest end-use segment, contributing approximately 44% of total market revenue in 2025. This dominance is driven by the widespread use of cooking wine in restaurant kitchens to ensure flavor consistency, operational efficiency, and menu standardization. The rapid expansion of quick-service restaurants, casual dining chains, and cloud kitchens has further strengthened demand from this segment.
Household consumption is growing steadily, particularly in urban markets where home cooking experimentation and exposure to global cuisines are increasing. Food processing and ready-to-eat manufacturing represent a high-growth end-use segment, as cooking wine is increasingly used in frozen meals, sauces, and packaged foods to enhance taste profiles and improve shelf stability.
| By Product Type | By Alcohol Content | By Distribution Channel | By End Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the global cooking wine market, with an estimated 48% share in 2025. China and Japan lead regional consumption due to deeply rooted culinary traditions that rely heavily on cooking wine, combined with large-scale food processing industries. The region’s dominance is further supported by high population density, strong restaurant penetration, and the availability of locally produced cooking wine at competitive prices. India represents the fastest-growing market within Asia-Pacific, driven by rapid foodservice expansion, rising disposable incomes, and increasing consumer exposure to East Asian and Western cuisines.
North America
North America accounts for approximately 22% of global market share, supported by premium home cooking trends, multicultural food preferences, and a diverse restaurant landscape. The United States leads regional demand, driven by high consumption of international cuisines, strong retail infrastructure, and growing interest in clean-label and organic cooking wine products. The expansion of specialty food retailers and online grocery platforms further supports regional growth.
Europe
Europe holds nearly 19% market share, with strong demand from France, Italy, Spain, and Germany. The region’s growth is driven by long-established culinary traditions that incorporate grape-based and fortified cooking wines into daily cooking. High consumer awareness, premium product positioning, and the presence of established wine-producing ecosystems support steady demand. Additionally, Europe benefits from strong foodservice recovery and increasing exports of specialty cooking wine products.
Latin America
Latin America is an emerging wine market, led by Brazil and Mexico. Growth is supported by rising urbanization, an expanding middle class, and increased exposure to international cuisines through tourism and global restaurant chains. The growing presence of Asian and Mediterranean restaurants in major cities is contributing to gradual but consistent demand growth across the region.
Middle East & Africa
Demand in the Middle East & Africa remains selective due to alcohol regulations and cultural constraints. However, growth is visible in tourist hubs and premium foodservice segments, particularly in the UAE and South Africa. International hotels, fine-dining restaurants, and expatriate populations are key demand drivers. In Africa, South Africa’s established foodservice sector and wine production capabilities support localized consumption and export-oriented growth.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Cooking Wine Market
- Kikkoman Corporation
- Foshan Haitian Flavouring & Food
- Lee Kum Kee
- Mizkan Holdings
- Takara Shuzo
- COFCO Group
- Pearl River Bridge
- Yamasa Corporation
- Haday Group
- Eden Foods