Sugarcane Market Size
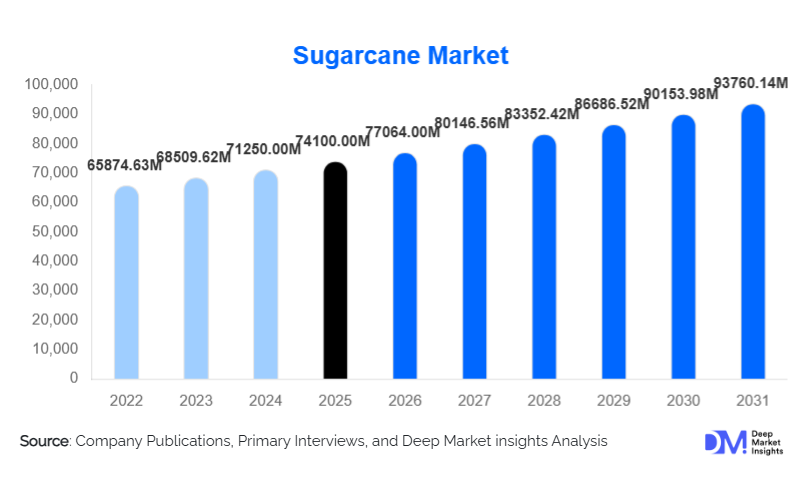
According to Deep Market Insights, the global sugarcane market size was valued at USD 74,100.00 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 77,064.00 million in 2026 to reach USD 93,760.14 million by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 4.0% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The sugarcane market growth is primarily driven by sustained global demand for sugar, accelerating ethanol blending mandates, rising investments in renewable energy, and the expanding role of sugarcane as a feedstock for bio-based chemicals and materials.
Key Market Insights
- Sugar production remains the largest value segment, accounting for over 60% of total sugarcane utilization globally.
- Ethanol and biofuel applications are the fastest-growing segment, supported by government blending mandates in India, Brazil, and Thailand.
- Asia-Pacific dominates the global sugarcane market, led by India, China, and Thailand in both cultivation area and consumption.
- Brazil remains the single largest country market, driven by its integrated sugar–ethanol production ecosystem.
- Mechanized harvesting and processing adoption is accelerating, improving yields, reducing labor dependency, and enhancing mill profitability.
- Sustainability certifications and ESG compliance are becoming critical for export-oriented sugarcane producers.
What are the latest trends in the sugarcane market?
Rapid Expansion of Ethanol-Based Sugarcane Utilization
One of the most significant trends in the sugarcane market is the increasing diversion of cane toward ethanol production. Countries pursuing energy security and decarbonization goals are expanding ethanol blending targets, transforming sugarcane into a strategic energy crop. Sugar mills are increasingly integrating distillery operations to stabilize revenues and reduce reliance on volatile sugar prices. This trend is particularly pronounced in Brazil and India, where ethanol now accounts for a growing share of sugarcane value realization. The expansion of flex-fuel vehicles and renewable fuel standards is expected to sustain this momentum over the long term.
Integration of Bio-based and Circular Economy Applications
Sugarcane by-products such as bagasse and molasses are increasingly utilized in bio-power generation, bioplastics, and green chemicals. Mills are evolving into integrated bio-refineries, generating electricity from bagasse, producing industrial alcohols, and supplying feedstock for bio-polymers. This circular economy approach improves asset utilization and profitability while aligning with global sustainability goals. Growing demand from the packaging, automotive, and consumer goods industries for renewable materials is reinforcing this trend and expanding sugarcane’s industrial relevance beyond food and fuel.
What are the key drivers in the sugarcane market?
Rising Global Sugar Consumption
Population growth, urbanization, and increased consumption of processed foods and beverages continue to drive steady demand for sugarcane-derived sugar. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America are witnessing rising per-capita sugar consumption, supporting long-term cultivation growth. Despite increasing health awareness, sugar remains a staple ingredient across multiple food categories, ensuring consistent baseline demand for sugarcane production.
Government Support for Renewable Energy and Ethanol
Policy-driven support for ethanol blending and renewable energy generation is a major growth driver for the sugarcane market. Governments are offering price guarantees, subsidies, and infrastructure investments to encourage ethanol production from sugarcane. Bagasse-based cogeneration is also being promoted through renewable power tariffs, enabling sugar mills to export surplus electricity to national grids. These initiatives significantly enhance revenue diversification and reduce financial risk for producers.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Climatic Dependency and Water Intensity
Sugarcane cultivation is highly dependent on rainfall and water availability, making production vulnerable to droughts, floods, and climate variability. Increasing water stress in key producing regions poses a long-term challenge to sustainable cultivation. Yield volatility caused by adverse weather conditions directly impacts supply stability and pricing, creating uncertainty for both farmers and processors.
Government Pricing and Trade Interventions
Regulated cane pricing, export quotas, and import duties often distort market dynamics. While such measures aim to protect farmers and domestic markets, they can compress mill margins and limit global trade competitiveness. Frequent policy changes add uncertainty to investment planning and can delay capacity expansion decisions within the sugarcane industry.
What are the key opportunities in the sugarcane market?
Expansion of Sustainable and Certified Sugarcane
Rising demand for sustainably sourced sugar and ethanol presents strong opportunities for certified sugarcane producers. Global food, beverage, and consumer goods companies are increasingly prioritizing certified supply chains to meet ESG commitments. Adoption of sustainability standards enables producers to access premium export markets, improve traceability, and command better pricing, particularly in Europe and North America.
Emerging Bio-chemicals and Bioplastics Market
The growing global shift toward bio-based materials offers significant opportunities for sugarcane-derived chemicals and polymers. Advances in fermentation and processing technologies are enabling commercial-scale production of bioplastics, organic acids, and green solvents from sugarcane feedstocks. These applications offer higher margins compared to traditional sugar production and reduce exposure to commodity price cycles.
Product Type Insights
Sugar production remains the dominant product type, accounting for approximately 62% of the global sugarcane market value in 2024. Ethanol and biofuels represent around 22% of the market and are the fastest-growing segment due to blending mandates and renewable energy policies. Power generation from bagasse contributes close to 10%, while molasses and emerging bio-based products collectively account for the remaining share. Growth is increasingly skewed toward energy and industrial applications, reflecting diversification across the value chain.
Application Insights
Food and beverage applications remain the largest end use for sugarcane, consuming nearly 60% of total output. The energy and utilities sector is the fastest-growing application segment, driven by ethanol fuel demand and biomass-based power generation. Chemical and materials applications, including bioplastics and industrial alcohols, are emerging as high-growth niches. Pharmaceutical and personal care industries also utilize sugarcane derivatives, supporting steady specialty demand.
Distribution Channel Insights
Direct procurement by sugar mills dominates the distribution landscape, accounting for roughly 70% of sugarcane transactions globally. Cooperative procurement models are widely used in the Asia-Pacific region, particularly in India, enabling farmer aggregation and price stability. Government-regulated procurement remains significant in key producing countries, influencing pricing and supply allocation. Digital platforms and contract farming models are gradually improving supply chain transparency and efficiency.
| By End Product | By Farming Type | By Mechanization Level | By Distribution Channel | By End-Use Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for approximately 45% of the global sugarcane market in 2024, led by India, China, and Thailand. India alone represents nearly 18% of the global market value, supported by large cultivation areas and rapid ethanol capacity expansion. Rising food demand and supportive government policies continue to drive regional growth.
Latin America
Latin America holds around 32% of the global market, with Brazil dominating regional demand and production. Brazil’s integrated sugar–ethanol model and strong export orientation make it the most influential country in global sugarcane pricing and trade.
North America
North America accounts for roughly 8% of global market value, driven primarily by ethanol production and refined sugar demand in the United States. Technological adoption and mechanized farming are high across the region.
Europe
Europe represents about 7% of the global sugarcane market, relying largely on imports for raw sugar and specialty products. Demand is shaped by sustainability standards and specialty sugar applications.
Middle East & Africa
Africa is among the fastest-growing regions, supported by rising food demand, export potential, and investments in modern sugar mills. The Middle East remains a major importing region, driven by high per-capita sugar consumption.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Sugarcane Market
- Cosan S.A.
- Raízen
- Wilmar International
- Mitr Phol Group
- Südzucker AG
- Tereos Group
- Thai Roong Ruang Group
- Balrampur Chini Mills
- EID Parry
- Louis Dreyfus Company
- Nordzucker
- Illovo Sugar Africa
- Tongaat Hulett
- Cristal Union
- Shree Renuka Sugars