Onion Seed Market Size
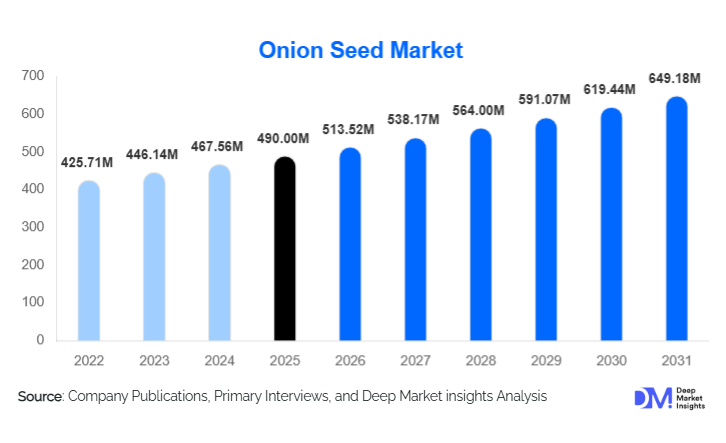
According to Deep Market Insights, the global onion seed market size was valued at USD 490 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 513.52 million in 2026 to reach USD 649.18 million by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The onion seed market growth is primarily driven by the rising global consumption of onions as a staple vegetable, increasing adoption of hybrid and genetically improved seed varieties, and the expansion of export-oriented commercial onion farming across Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America.
Key Market Insights
- Hybrid onion seeds dominate market value, accounting for over 60% share due to higher yields, disease resistance, and uniform bulb quality.
- Asia-Pacific leads global demand, supported by large cultivation areas in India and China and strong export activity.
- Commercial farming remains the largest end-use segment, driven by large-scale producers supplying fresh and processed onion markets.
- Export-driven onion production is accelerating demand for premium seed varieties with longer shelf life.
- Government-supported seed replacement programs are boosting certified seed adoption in developing economies.
- Climate-resilient and disease-tolerant seed development is emerging as a critical competitive differentiator.
What are the latest trends in the onion seed market?
Rapid Shift Toward Hybrid and Improved Varieties
The onion seed market is witnessing a pronounced shift from open-pollinated varieties toward hybrid and genetically improved (non-GMO) seeds. Farmers increasingly prefer hybrids due to their superior yield stability, uniform bulb size, improved color consistency, and higher resistance to pests and diseases. This trend is particularly strong in export-oriented farming regions, where quality specifications and post-harvest shelf life are critical. Seed companies are expanding hybrid portfolios tailored to regional climatic conditions, accelerating value-based growth across the market.
Rising Focus on Climate-Resilient Seed Technologies
Climate variability and water stress are driving demand for onion seed varieties with drought tolerance, heat resistance, and adaptability to changing weather patterns. Advanced seed treatment technologies, pelleted seeds, and improved germination traits are being adopted to enhance crop establishment and reduce production risks. This trend is gaining momentum in Africa, the Middle East, and parts of South Asia, where climatic uncertainty directly impacts farm productivity.
What are the key drivers in the onion seed market?
Growing Global Onion Consumption
Onions remain one of the most widely consumed vegetables globally, used extensively in fresh cooking, food processing, and foodservice applications. Population growth, urbanization, and increasing demand for processed foods are driving consistent onion production, which directly supports steady demand for high-quality onion seeds. This staple status ensures long-term market stability.
Expansion of Export-Oriented Onion Farming
Countries such as India, China, Egypt, the Netherlands, and Mexico are expanding onion exports to the Middle East, Europe, and Southeast Asia. Export markets require uniform size, color, and extended shelf life, making premium hybrid seeds essential. This structural shift toward export-grade production is a major driver of market value growth.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Cost of Hybrid Seeds
The relatively high price of hybrid onion seeds compared to traditional varieties remains a key barrier, particularly for smallholder farmers in developing regions. Limited access to credit and subsidies can slow adoption rates, affecting short-term market penetration.
Climate Sensitivity of Seed Production
Onion seed production is highly sensitive to climatic conditions, and adverse weather events can disrupt seed supply chains. This can lead to price volatility and availability challenges, posing risks for both producers and growers.
What are the key opportunities in the onion seed industry?
Government-Led Agricultural Modernization Programs
Government initiatives promoting certified seed usage, crop productivity, and farmer income stability present strong growth opportunities. Seed subsidy programs, public-private partnerships, and national agricultural missions in Asia and Africa are accelerating the adoption of improved onion seeds.
Export-Specific Seed Customization
There is growing demand for onion seed varieties customized for specific export markets, including traits such as storage durability and uniform bulb shape. Seed companies that develop region- and export-specific genetics can capture premium pricing and long-term contracts with commercial growers.
Type Insights
Red onion seeds continue to dominate the global onion seed market, accounting for approximately 42% of total value in 2024. This dominance is primarily driven by high domestic and export consumption in the Asia-Pacific and African regions, where red onions are staple ingredients in both fresh and processed forms. The strong preference for red onion varieties is also supported by higher market prices due to their superior shelf life and uniform bulb size, which are critical factors for export-grade production. Yellow onion seeds follow closely, particularly in North America and Europe, where they are extensively used in industrial processing, frozen food production, and foodservice sectors, representing roughly 28–30% of global market value. White and sweet onion seeds occupy smaller but steadily growing segments, benefiting from rising demand in niche culinary applications, gourmet food markets, and export-oriented programs, especially in the Middle East and Southeast Asian markets. Overall, consumer preference for consistent quality, storage longevity, and export compliance is the leading driver shaping the type-wise distribution in the onion seed market.
Breeding Technology Insights
Hybrid seeds hold a commanding position in the market, accounting for nearly 63% of the global onion seed market value in 2024. This segment is led by strong demand for higher-yielding, disease-resistant, and uniform-quality onions, which are increasingly essential for commercial farms and export-oriented production. Hybrid seeds are particularly preferred in regions such as India, China, the Netherlands, and Egypt, where large-scale cultivation and contract farming models are prevalent. Open-pollinated varieties continue to serve cost-sensitive markets in Africa and South Asia, where farmers prioritize affordability over advanced traits. Meanwhile, genetically improved non-GMO seeds are gaining traction in regions with regulatory restrictions on biotech adoption, offering climate resilience and pest resistance without entering GMO regulatory frameworks. The leading driver of growth in this segment is the proven yield and quality advantage of hybrid seeds, which is reinforcing their market penetration and shaping global adoption trends.
End-Use Insights
Commercial farming represents the largest end-use segment in the onion seed market, accounting for approximately 68% of global demand in 2024. This segment’s dominance is driven by large-scale production requirements for fresh consumption, processing, and export markets. Contract farming and export-oriented growers are the fastest-growing sub-segments, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, supported by long-term procurement agreements, government subsidies, and increasing international trade of onions. Institutional and government-led farming programs maintain stable demand, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia, where public sector initiatives promote certified seed use and productivity enhancement. Home gardening remains a smaller but steadily expanding segment, gaining traction in urban regions of North America and Europe due to increased interest in organic cultivation and kitchen gardening. The primary driver across the end-use landscape is the growing commercial demand for high-quality, uniform onion yields for both domestic consumption and international export, which incentivizes the adoption of certified and hybrid seeds.
Distribution Channel Insights
Agro-dealers and agricultural retail stores remain the dominant distribution channels, accounting for approximately 55% of global seed sales. These channels offer direct access to small and medium-scale farmers, particularly in the Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America. Direct sales to large commercial farms are increasing in regions such as Europe, North America, and India, where farm consolidation and contract farming agreements drive bulk seed procurement. Online and digital agriculture platforms are emerging rapidly, especially in developed markets and among younger, tech-savvy farmers, providing convenient access to improved seed varieties, agronomy advice, and tracking services. The leading driver of distribution channel growth is the increasing integration of digital technologies, enabling the seamless supply of high-quality seeds directly to farmers while enhancing traceability and supporting farm advisory services.
| By Onion Type | By Breeding Technology | By Cultivation Environment | By End Use | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific leads the global onion seed market, representing approximately 48% share in 2024, driven by India and China, which collectively account for nearly 37% of global demand. The region’s growth is fueled by vast cultivation areas, high domestic consumption, and strong export-oriented production. Government-led seed replacement programs, subsidies for hybrid seed adoption, and investment in R&D and seed processing infrastructure further support market expansion. Rising demand for red onion seeds in export markets and superior hybrid varieties for large-scale commercial farming are key drivers. Additionally, the growing trend of contract farming agreements in India and China ensures stable seed procurement, boosting the adoption of certified and hybrid seeds.
Europe
Europe holds around 18% market share, led by the Netherlands, Spain, and France. High adoption of hybrid seeds, advanced agronomic practices, and a strong focus on export-oriented onion production are driving market growth. The primary regional drivers include well-developed seed distribution infrastructure, strict quality standards, and the prevalence of large-scale processing industries. European growers increasingly prefer yellow onion hybrids due to their suitability for industrial applications and extended storage life, supporting both domestic and export markets. Government support for precision agriculture and sustainable cultivation practices also contributes to steady market growth.
North America
North America accounts for approximately 14% share, with the U.S. representing the majority of regional demand. Growth is driven by high consumption of processed onions and the adoption of high-yield commercial farming systems. Leading drivers include strong technological adoption, use of hybrid and true seeds for consistent yields, and well-established distribution networks through agro-dealers and retail stores. Increasing demand from the food processing industry and institutional buyers ensures a steady market for yellow and red onion seeds, particularly in California and other key growing states.
Middle East & Africa
This region represents about 12% of global demand, with Egypt and Nigeria as the largest markets. Africa is the fastest-growing region, experiencing a CAGR above 8%, driven by the rising adoption of certified seeds, government-backed seed subsidy programs, and increasing commercial farming initiatives. The demand for red onion seeds for domestic consumption and exports to the Middle East is a key growth driver. Investments in farmer education, seed multiplication programs, and improved irrigation infrastructure are also supporting regional market expansion. Moreover, hybrid seed adoption is accelerating as farmers seek higher yields and better disease resistance to meet both local and export demand.
Latin America
Latin America holds nearly 8% share, led by Mexico and Brazil. Growth is supported by expanding export-oriented onion production, the adoption of hybrid seeds for high-yield commercial farming, and increasing government support programs. Drivers of regional growth include rising international demand for onions, improved farm mechanization, and the development of integrated supply chains that connect producers with domestic and foreign buyers. The region is witnessing steady expansion in red and yellow onion seeds to meet both culinary and processing industry requirements.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Onion Seed Market
- Bayer CropScience
- Syngenta
- Corteva Agriscience
- BASF
- Sakata Seed
- Enza Zaden
- Rijk Zwaan
- Bejo Zaden
- East-West Seed
- Takii & Co.
- Advanta Seeds
- Namdhari Seeds
- UPL Seeds
- KWS Group
- Limagrain