Non-Thermal Pasteurization Market Size
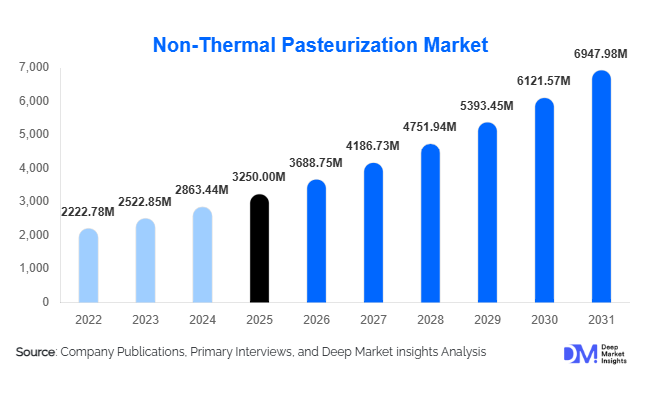
According to Deep Market Insights, the global non-thermal pasteurization market size was valued at USD 3,250 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 3,688.75 million in 2026 to reach approximately USD 6,947.98 million by 2031, expanding at a robust CAGR of around 13.5% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The growth of the non-thermal pasteurization market is primarily driven by rising demand for clean-label foods, increasing consumption of minimally processed products, and the global food industry’s focus on enhancing shelf life without compromising nutritional quality or sensory attributes.
Key Market Insights
- High Pressure Processing (HPP) dominates the market, accounting for over half of global revenues due to its versatility across beverages, meat, and ready-to-eat foods.
- Beverages represent the largest application segment, driven by strong growth in cold-pressed juices, functional drinks, and premium RTD beverages.
- North America leads global adoption, supported by advanced food safety regulations, early technology adoption, and strong demand for premium processed foods.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing regional market, fueled by food safety modernization, export-oriented food processing, and rising urban consumption.
- Contract pasteurization services are gaining traction, enabling small and mid-sized brands to access advanced processing without heavy capital investments.
- Technology integration with automation and digital monitoring is improving throughput, reducing operational costs, and accelerating adoption across industrial facilities.
What are the latest trends in the non-thermal pasteurization market?
Rising Adoption of High-Pressure Processing Across Food Categories
High-pressure processing has emerged as the most widely adopted non-thermal technology due to its ability to inactivate pathogens while preserving taste, texture, and nutrients. Initially concentrated in cold-pressed juices and guacamole, HPP adoption has expanded rapidly into ready-to-eat meals, deli meats, seafood, and dairy alternatives. Food manufacturers are increasingly positioning HPP-treated products as premium offerings, leveraging extended shelf life and clean-label credentials. This trend is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where consumer willingness to pay for minimally processed foods is high.
Automation and Smart Manufacturing Integration
Non-thermal pasteurization systems are increasingly being integrated with automated controls, data analytics, and real-time microbial monitoring. Smart sensors and digital dashboards enable processors to optimize pressure, exposure time, and energy usage, improving consistency and reducing waste. These advancements are helping manufacturers scale operations efficiently while meeting stringent regulatory requirements. As Industry 4.0 adoption expands across food processing, technologically advanced non-thermal systems are becoming a strategic investment rather than a niche solution.
What are the key drivers in the non-thermal pasteurization market?
Growing Demand for Clean-Label and Nutrient-Preserved Foods
Consumers globally are increasingly avoiding artificial preservatives and excessively heat-treated foods, driving demand for clean-label products with fresh-like characteristics. Non-thermal pasteurization directly addresses this demand by ensuring microbial safety without degrading vitamins, antioxidants, or flavor compounds. This driver is particularly strong in premium food categories such as organic beverages, plant-based products, and functional nutrition.
Expansion of Ready-to-Eat and Convenience Foods
Urbanization and changing lifestyles are fueling the consumption of ready-to-eat and ready-to-cook foods. Non-thermal pasteurization enables manufacturers to extend shelf life while maintaining quality, making it a critical technology for convenience food producers. The growth of chilled distribution channels further supports this driver, as non-thermal methods align well with cold-chain logistics.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Initial Capital Investment
Advanced non-thermal pasteurization systems, particularly HPP and pulsed electric field equipment, require substantial upfront investment. This limits adoption among small processors in developing regions and creates longer payback periods for new entrants. While contract processing models mitigate this challenge, capital intensity remains a key restraint.
Technology-Specific Application Constraints
Not all non-thermal technologies are suitable for every food matrix. Factors such as product density, packaging compatibility, and microbial load can limit applicability, requiring careful technology selection and increasing implementation complexity for manufacturers.
What are the key opportunities in the non-thermal pasteurization industry?
Growth of Contract Pasteurization Service Models
Contract pasteurization facilities are emerging as a high-growth opportunity, particularly in North America and Europe. These facilities allow food startups and mid-sized brands to access non-thermal technologies without owning equipment, enabling faster commercialization and lower financial risk. Expansion of such services into the Asia-Pacific presents significant untapped potential.
Rising Export-Oriented Food Processing
Global food exports increasingly require extended shelf life and compliance with strict importing country standards. Non-thermal pasteurization offers exporters a competitive advantage by reducing spoilage and enhancing product stability during long transit periods, creating strong demand from export-focused manufacturers.
Technology Insights
High Pressure Processing (HPP) accounts for approximately 52% of the global non-thermal pasteurization market share in 2025, making it the dominant technology worldwide. Its leadership is primarily driven by its wide applicability across multiple food matrices, including beverages, ready-to-eat meals, meat, seafood, and dairy alternatives. HPP is highly effective in eliminating pathogens while preserving taste, texture, and nutritional value, and it benefits from strong regulatory acceptance across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific. Additionally, HPP is compatible with flexible and rigid packaging formats, which has further accelerated adoption among large-scale food processors and premium food brands.
Ultraviolet (UV) treatment and cold plasma technologies occupy smaller but steadily expanding shares of the market. These technologies are primarily adopted for surface decontamination, packaging sterilization, and specialty applications, particularly where low energy consumption and targeted microbial control are required. Meanwhile, irradiation and ultrasound processing remain niche technologies but are gaining increased attention in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and medical nutrition applications, where sterility and precision processing are critical. Collectively, technology diversification is strengthening the overall resilience and scalability of the non-thermal pasteurization market.
Application Insights
Beverages represent the largest application segment, contributing nearly 34% of global market revenue in 2025. This dominance is driven by strong demand for cold-pressed juices, functional beverages, plant-based drinks, and premium alcoholic beverages that require extended shelf life without heat-induced degradation. Beverage manufacturers are increasingly using non-thermal pasteurization as a differentiation tool to support clean-label positioning and premium pricing strategies. Ready-to-eat (RTE) and ready-to-cook foods form the second-largest application segment, supported by rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and growing consumer reliance on convenience foods. Non-thermal pasteurization enables RTE manufacturers to maintain fresh-like quality while meeting stringent food safety standards, particularly in chilled and refrigerated product categories.
Meat, poultry, and seafood applications are expanding steadily as processors seek alternatives to chemical preservatives and traditional thermal treatments. Non-thermal methods help reduce pathogen risks while preserving protein structure and sensory quality, which is critical for premium and export-oriented protein products. Dairy and plant-based dairy alternatives are emerging as high-growth application areas, driven by increasing consumption of lactose-free, vegan, and functional dairy products, alongside ongoing innovation in non-thermal compatibility with complex dairy matrices.
End-Use Industry Insights
Food processing companies account for approximately 58% of total market demand, reflecting large-scale industrial adoption of non-thermal pasteurization technologies. These companies are leveraging non-thermal solutions to enhance food safety, extend shelf life, and meet evolving consumer and regulatory requirements without compromising product quality. Beverage manufacturers represent the second-largest end-use segment, driven by continuous innovation in functional drinks, clean-label juices, and premium beverages. Non-thermal pasteurization has become a core processing technology for beverage brands seeking differentiation in competitive markets.
Contract pasteurization service providers are the fastest-growing end-use segment, benefiting from the rise of asset-light food startups and mid-sized brands that prefer outsourcing advanced processing rather than investing in capital-intensive equipment. This model is accelerating market penetration, particularly in North America and Europe, and is gradually expanding into Asia-Pacific. Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical companies represent a smaller but rapidly expanding segment, especially for sterile liquid nutrition, medical beverages, and functional formulations. The need for precise microbial control and nutrient preservation is driving increased adoption of non-thermal technologies in these industries.
| By Technology Type | By Application | By End-Use Industry | By Equipment Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for nearly 38% of the global non-thermal pasteurization market in 2025, making it the largest regional market. The United States dominates regional demand due to early adoption of High Pressure Processing, strong consumer preference for clean-label and minimally processed foods, and a well-developed cold-chain infrastructure. Strict food safety regulations and a high incidence of premium and organic food consumption further support adoption. Canada contributes steadily to regional growth, particularly in beverage processing and meat applications, supported by expanding exports and regulatory alignment with U.S. food safety standards.
Europe
Europe holds approximately 27% of the global market share, led by Germany, France, the U.K., and Italy. Regional growth is driven by stringent food safety and labeling regulations, strong sustainability mandates, and high consumer awareness regarding food quality. European food manufacturers are increasingly adopting non-thermal pasteurization to reduce chemical preservatives and meet clean-label expectations. The region’s strong export orientation for processed foods further accelerates demand for shelf-life extension technologies.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with a CAGR exceeding 16%. Growth is driven by food safety modernization, rising urban populations, increasing packaged food consumption, and expanding food exports. China is leading adoption due to regulatory reforms and investments in advanced food processing infrastructure. Japan and South Korea contribute through demand for high-quality, premium processed foods, while India is emerging as a high-growth market driven by urbanization, growth in ready-to-eat foods, and rising adoption of global food safety standards.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for around 6% of global demand, with Brazil and Mexico as the primary contributors. Growth in the region is driven by strong juice and beverage exports, improving cold-chain infrastructure, and gradual adoption of advanced food processing technologies. Increasing participation in international food trade is encouraging processors to invest in non-thermal pasteurization to meet export quality requirements.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds approximately 4% market share. Growth is supported by high reliance on food imports, increasing demand for extended shelf-life products, and gradual investments in modern food processing facilities. Gulf countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia are driving regional adoption through investments in food security and domestic processing capabilities, while parts of Africa are witnessing early-stage adoption aligned with export-oriented food production.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|