Food Robotics Market Size
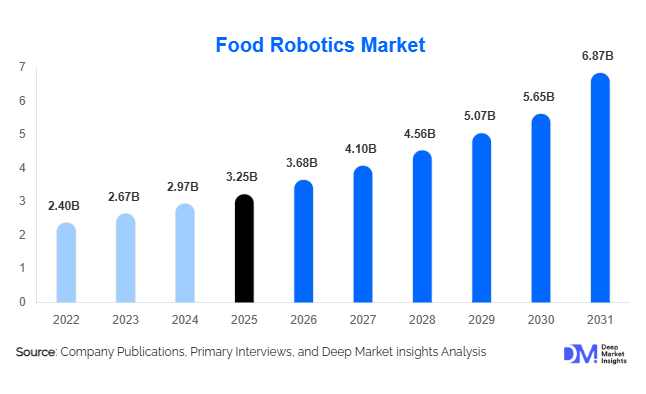
According to Deep Market Insights, the global food robotics market size was valued at USD 3.25 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 3.68 billion in 2026 to reach USD 6.87 billion by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 11.3% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The food robotics market growth is primarily driven by rising labor shortages in food processing, increasing demand for packaged and ready-to-eat foods, stringent food safety regulations, and rapid advancements in AI-enabled vision systems and collaborative robotics.
Key Market Insights
- Food robotics adoption is accelerating across processing and packaging lines, driven by hygiene, consistency, and labor efficiency requirements.
- Packaging & palletizing applications dominate, supported by strong growth in packaged and frozen food consumption globally.
- North America leads the global market due to early automation adoption, high labor costs, and advanced food manufacturing infrastructure.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by food industrialization, export-oriented processing, and government automation initiatives.
- Collaborative robots are gaining rapid traction, enabling automation adoption among small and mid-sized food processors.
- AI, machine vision, and soft robotics are transforming robotic handling of irregular, fragile, and fresh food products.
What are the latest trends in the food robotics market?
Expansion of AI-Enabled Vision and Soft Gripping Technologies
One of the most prominent trends in the food robotics market is the integration of artificial intelligence and advanced machine vision systems. Traditional robotic systems struggled with the natural variability of food products, but AI-powered vision now enables real-time recognition of shape, size, color, and defects. Combined with soft grippers made from adaptive materials, robots can handle delicate items such as fruits, bakery products, seafood, and confectionery without damage. This trend is significantly expanding robotics adoption in fresh and high-value food segments, improving yield rates and reducing food waste across processing lines.
Growing Adoption of Collaborative Robots in Food Manufacturing
Collaborative robots are increasingly being deployed alongside human workers in food processing environments. Their compact footprint, ease of programming, and enhanced safety features make them ideal for tasks such as tray loading, secondary packaging, and inspection. Cobots are especially attractive to small and mid-sized food manufacturers seeking automation without major facility redesigns. This trend is democratizing access to food robotics and accelerating market penetration beyond large multinational processors.
What are the key drivers in the food robotics market?
Labor Shortages and Rising Operational Costs
Chronic labor shortages across food processing industries remain the strongest driver for food robotics adoption. Food manufacturing roles are labor-intensive and experience high turnover, particularly in meat, poultry, and seafood processing. Rising wages and limited workforce availability have pushed manufacturers to automate repetitive and hazardous tasks. Robotic systems improve productivity, reduce absenteeism-related disruptions, and deliver predictable output levels, making them a strategic investment for long-term operational stability.
Stringent Food Safety and Hygiene Regulations
Food safety regulations are becoming increasingly strict, emphasizing contamination prevention, traceability, and standardized handling. Food-grade robots minimize human contact at critical control points, significantly reducing contamination risks. Washdown-capable stainless-steel robots are now widely adopted in protein, dairy, and ready-to-eat food facilities, reinforcing robotics as a compliance-driven necessity rather than an optional efficiency upgrade.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Initial Capital Investment
Despite favorable long-term returns, the high upfront cost of robotic systems remains a barrier, particularly for small processors in emerging markets. Investment in robots, vision systems, integration, and training can delay adoption without access to financing or government incentives.
Integration Challenges in Legacy Facilities
Many food processing plants were not originally designed for automation. Retrofitting robots into existing layouts can require downtime, infrastructure upgrades, and workforce reskilling, which may slow implementation timelines and increase project risk.
What are the key opportunities in the food robotics industry?
Automation Penetration in Small and Mid-Sized Food Processors
The growing availability of modular, scalable, and cost-effective robotic solutions presents a major opportunity among SMEs. As system costs decline and ease of deployment improves, food robotics vendors can tap into a vast underserved segment across bakery, dairy, and fresh produce processing.
Export-Oriented Food Processing Expansion
Governments across Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Latin America are investing heavily in domestic food processing infrastructure to improve food security and export competitiveness. Greenfield processing plants increasingly integrate robotics from inception, creating sustained demand for automated food handling and packaging systems.
Robot Type Insights
Delta and parallel robots dominate the global food robotics market, accounting for approximately 28% of the total market value in 2025. Their leadership is primarily driven by their unmatched speed, positional accuracy, and compact design, which make them ideally suited for high-throughput pick-and-place operations in bakery, confectionery, snack foods, and packaged food lines. These robots enable food manufacturers to maintain consistent cycle times, reduce product damage, and meet growing volume requirements driven by packaged food demand. The rising need for gentle handling of lightweight and irregular food items further reinforces the dominance of delta and parallel robots.
Articulated robots represent the second-largest robot type segment, supported by their multi-axis flexibility and ability to perform complex tasks such as cutting, slicing, deboning, palletizing, and case packing. Their adaptability across both processing and end-of-line applications makes them particularly valuable in meat, poultry, seafood, and ready-to-eat food facilities where diverse operations are required within a single production line.
Application Insights
Packaging and palletizing applications account for nearly 32% of total food robotics revenue in 2025, making this the leading application segment globally. Growth in this segment is driven by the rapid expansion of packaged, frozen, and ready-to-eat food consumption, along with the need for high-speed, consistent end-of-line operations. Robotic palletizing systems help manufacturers manage increasing SKU complexity, reduce manual handling injuries, and support high-volume distribution requirements, particularly in export-oriented food production.
Pick-and-place and sorting applications continue to expand rapidly, driven by demand for high-speed handling, precision placement, and quality inspection in both fresh and processed food segments. The integration of machine vision and AI-based inspection systems is enabling robots to identify defects, sort by size or quality, and operate effectively in high-mix production environments, further strengthening this application segment’s growth outlook.
Payload Capacity Insights
Medium payload robots (5–20 kg) lead the food robotics market with approximately 41% market share in 2025. This dominance is driven by their versatility across a wide range of food handling applications, including carton loading, tray handling, case packing, and mixed-product packaging. Medium payload robots offer an optimal balance between strength, speed, and flexibility, making them suitable for most processing and packaging tasks in food manufacturing.
Low payload robots continue to dominate high-speed food handling and pick-and-place operations, particularly in bakery, confectionery, and snack food applications where lightweight products and rapid cycle times are critical. High payload robots are primarily deployed in palletizing, depalletizing, and bulk material handling environments, where they support heavy loads, high stacking heights, and warehouse-level automation.
Food Category Insights
Meat, poultry, and seafood processing represent the largest food category segment, accounting for nearly 29% of the global food robotics market in 2025. The leading drivers for this segment include stringent hygiene standards, worker safety concerns, high labor intensity, and persistent labor shortages. Robotics adoption in protein processing is accelerating as manufacturers seek to reduce contamination risks, improve cutting consistency, and minimize workplace injuries associated with manual handling.
Bakery and confectionery follow closely, supported by high-volume production requirements and the need for precise, high-speed handling of delicate products. The growth of packaged bakery goods, frozen dough, and premium confectionery products has increased demand for robotic systems capable of maintaining product integrity while operating at high throughput. Other food categories, such as dairy, fruits and vegetables, and ready-to-eat meals, are also witnessing rising automation adoption, driven by quality consistency and shelf-life optimization requirements.
| By Robot Type | By Application | By Payload Capacity | By Food Category |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for approximately 34% of the global food robotics market in 2025, led predominantly by the United States. Regional growth is driven by high labor costs, chronic workforce shortages, and advanced food manufacturing infrastructure. Stringent food safety regulations and strong enforcement standards further encourage automation adoption to reduce human contact and improve traceability. Additionally, the presence of large multinational food processors and early adoption of AI-enabled robotics systems continue to sustain strong investment momentum across the region.
Europe
Europe holds around 27% market share, with Germany, France, and the Netherlands leading adoption. Growth in this region is driven by strict food safety and hygiene regulations, high automation density, and strong emphasis on sustainable and energy-efficient manufacturing. European food processors are increasingly investing in robotics to comply with regulatory standards while improving operational efficiency and reducing dependence on migrant labor, particularly in the meat and dairy processing industries.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents approximately 25% of the global market and is the fastest-growing region, expanding at over 14% CAGR. China, Japan, and South Korea dominate regional demand, supported by rapid food industrialization, expanding middle-class consumption, and export-oriented food processing. Government-backed automation initiatives, rising labor costs in urban centers, and large-scale investments in modern food processing facilities are key drivers accelerating food robotics adoption across the region.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for nearly 8% of global food robotics demand, led by Brazil and Mexico. Growth is driven by expanding processed food exports, increasing foreign direct investment in food manufacturing, and the gradual modernization of processing facilities. Regional food producers are increasingly adopting robotics to meet international quality standards and improve competitiveness in global export markets.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds approximately 6% market share, with Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa driving adoption. Growth is supported by food security initiatives, government-led investments in domestic food processing, and large-scale industrial diversification programs. Rising demand for packaged and halal-certified food products, combined with greenfield processing plant development, is creating new opportunities for food robotics deployment across the region.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Food Robotics Market
- ABB
- FANUC
- KUKA
- Yaskawa Electric
- Kawasaki Robotics
- Universal Robots
- Stäubli
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Denso Robotics
- Omron
- Nachi-Fujikoshi
- Comau
- Epson Robots
- Rockwell Automation
- Festo