Fermentation-Enabled Alternative Proteins Market Size
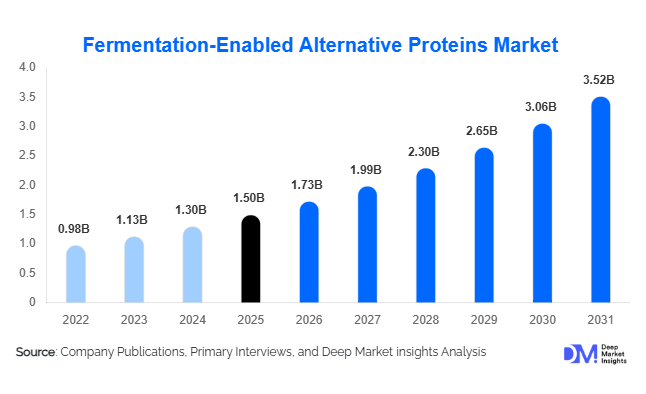
According to Deep Market Insights, the global fermentation-enabled alternative proteins market size was valued at USD 1.5 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 1.73 billion in 2026 to reach USD 3.52 billion by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 15.3% during the forecast period (2026–2031). Market growth is primarily driven by rising demand for sustainable protein sources, advancements in precision and biomass fermentation technologies, and increasing commercialization of animal-free dairy, meat, and egg proteins across global food systems.
Key Market Insights
- Precision fermentation accounts for the largest technology share (approximately 42% in 2025), driven by its ability to produce high-value functional proteins such as casein and albumin analogs.
- Food & Beverage represents nearly 50% of total demand, supported by rapid innovation in dairy alternatives, meat analogues, and protein-fortified products.
- North America leads the global market with ~35% share, benefiting from strong venture capital inflows and regulatory clarity.
- Europe accounts for approximately 30% share, driven by sustainability mandates and strong consumer adoption of alternative proteins.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, projected to grow above 18% CAGR through 2031 due to rising protein demand in China and India.
- The top five companies collectively hold nearly 45–50% market share, reflecting moderate consolidation in precision fermentation niches.
What are the latest trends in the fermentation-enabled alternative proteins market?
Precision Fermentation Scaling Toward Commercial Parity
Precision fermentation is transitioning from pilot-scale innovation to commercial production. Companies are investing heavily in strain engineering, AI-assisted process optimization, and large-scale bioreactors to reduce the cost per kilogram of protein output. This trend is accelerating the commercialization of dairy-identical proteins and egg substitutes without animal inputs. Partnerships between biotech startups and multinational food manufacturers are expanding market reach, allowing fermentation-derived ingredients to enter mainstream retail channels. Continuous fermentation systems and improved downstream purification processes are further enhancing production efficiency, reducing operational expenditure, and improving profit margins.
Hybrid and Functional Protein Formulations
Food manufacturers are increasingly blending fermentation-derived proteins with plant-based ingredients to enhance texture, taste, and nutritional quality. Hybrid formulations enable better amino acid balance and improved sensory characteristics, addressing earlier criticisms of plant-only proteins. In parallel, fermentation-derived bioactive proteins are being introduced into nutraceuticals, sports nutrition, and fortified beverages, expanding the market beyond conventional meat and dairy substitutes. Functional applications in cosmetics and biomaterials are also emerging, positioning fermentation as a versatile protein production platform.
What are the key drivers in the fermentation-enabled alternative proteins market?
Growing Demand for Sustainable Protein Systems
Rising concerns about livestock emissions, land use, and water consumption are accelerating demand for low-carbon protein alternatives. Fermentation-enabled proteins offer significantly lower environmental footprints compared to conventional animal agriculture. Corporate sustainability commitments and ESG targets among food producers are further driving the adoption of fermentation-based ingredients to reduce Scope 3 emissions across supply chains.
Advancements in Bioprocessing and Strain Engineering
Technological improvements in microbial strain optimization, synthetic biology, and automated bioreactor systems have increased protein yields and reduced contamination risks. AI-enabled predictive fermentation modeling allows producers to shorten development cycles and improve scalability. These advancements are narrowing the cost gap between fermentation-derived proteins and traditional animal proteins, enhancing commercial viability.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Capital Expenditure and Production Costs
Fermentation facilities require significant upfront investment in specialized bioreactors, sterilization systems, and downstream purification infrastructure. Precision fermentation in particular remains capital-intensive, limiting rapid global scale-up. Raw material inputs such as sugar substrates and growth media also influence cost structures, impacting pricing competitiveness.
Regulatory Complexity and Approval Timelines
Novel proteins derived through fermentation often require comprehensive safety assessments and regulatory approvals before commercialization. Variations in food safety frameworks across regions can delay product launches and increase compliance costs. Regulatory harmonization remains critical for accelerating global adoption.
What are the key opportunities in the fermentation-enabled alternative proteins industry?
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific and Latin America present strong long-term growth opportunities due to expanding middle-class populations and rising protein consumption. Localized fermentation facilities and region-specific product formulations can unlock new revenue streams. Export-driven demand from multinational food companies seeking sustainable ingredients further enhances opportunity potential.
Cross-Industry Applications Beyond Food
Fermentation-derived proteins are gaining traction in animal feed, aquaculture, cosmetics, and specialty biomaterials. Replacing fishmeal in aquaculture feed or integrating bioengineered collagen into skincare formulations opens diversified revenue channels. Such applications reduce dependence on traditional food markets and strengthen long-term industry resilience.
Process Type Insights
Precision fermentation dominates with approximately 42% share in 2025, owing to its ability to produce highly functional, animal-identical proteins such as dairy caseins, whey proteins, collagen, and egg albumin with molecular precision. This segment leads the market primarily due to its superior performance in replicating taste, texture, solubility, and emulsification properties that traditional plant proteins struggle to achieve. The demand for clean-label, lactose-free, cholesterol-free dairy alternatives and allergen-free egg substitutes has significantly accelerated precision fermentation adoption. Additionally, strong venture capital investments, advancements in synthetic biology, and AI-assisted strain optimization have enhanced yield efficiency and scalability, further supporting segment leadership. Premium pricing potential and intellectual property advantages also make precision fermentation attractive to investors and multinational food manufacturers.
Biomass fermentation holds around 38% share, driven by its scalability and cost efficiency in producing whole-cell microbial proteins for meat analogues, animal feed, and aquaculture applications. This segment benefits from lower production complexity compared to precision fermentation and is increasingly adopted in hybrid protein formulations. Traditional fermentation accounts for the remaining 20%, primarily focused on flavor enhancement, mycoprotein production, and conventional fermented food applications. However, its growth remains comparatively moderate due to limited functional customization capabilities.
Product Type Insights
Meat alternative proteins account for roughly 35% of total market revenue, making them the leading product segment. Growth is fueled by increasing consumer adoption of flexitarian diets, rising environmental concerns related to livestock farming, and strong retail penetration of plant-forward products. Fermentation technologies significantly improve texture, juiciness, and amino acid balance in meat analogues, making them more competitive with conventional meat products. Strategic partnerships between fermentation companies and global food brands have further strengthened this segment’s commercial footprint.
Dairy alternative proteins represent nearly 30% market share, supported by rising lactose intolerance awareness, veganism trends, and demand for high-protein dairy substitutes. Egg alternatives contribute approximately 15%, largely driven by bakery and foodservice industries seeking stable, allergen-free binding agents. Protein isolates and specialty ingredients comprise the remaining 20%, with growing applications in sports nutrition, medical nutrition, and functional beverages. Meat alternatives remain the leading segment due to strong consumer visibility, innovation velocity, and higher product turnover in global retail markets.
End-Use Insights
Food & Beverage leads with nearly 50% market share, supported by the rapid commercialization of fermented dairy, bakery ingredients, confectionery applications, ready-to-drink beverages, and meat substitute products. Major food manufacturers are increasingly incorporating fermentation-derived proteins to enhance nutritional content, improve sensory profiles, and meet ESG commitments. Strong supermarket penetration and online retail expansion further accelerate growth in this segment.
Nutraceuticals and supplements account for approximately 20% of market demand, driven by rising interest in high-performance proteins, muscle recovery supplements, and gut-health formulations. This segment is projected to grow at over 17% CAGR, supported by premiumization trends and increasing consumer awareness of functional nutrition. Animal feed contributes around 18%, with aquaculture emerging as a particularly high-growth niche due to sustainability concerns surrounding fishmeal. Functional ingredients in cosmetics, biomedical scaffolds, and biomaterials comprise the remaining share, reflecting expanding cross-industry adoption.
| By Process Type | By Product Type | By End Use | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America holds approximately 35% of the global market in 2025, with the United States accounting for nearly 30% of global demand. The region’s dominance is driven by a mature biotechnology ecosystem, high venture capital inflows, strong intellectual property frameworks, and early regulatory clarity for novel food approvals. Consumer acceptance of plant-based and alternative proteins is significantly higher compared to other regions, supported by widespread retail distribution and the strong presence of leading fermentation startups. Additionally, corporate ESG commitments and partnerships between biotech firms and multinational food companies are accelerating commercialization. Government funding for sustainable food systems and tax incentives for biotech manufacturing facilities further support regional growth.
Europe
Europe represents nearly 30% market share, led by Germany, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and France. Regional growth is primarily driven by stringent sustainability regulations, carbon-reduction mandates, and strong consumer preference for environmentally friendly food products. The European Union’s supportive R&D funding frameworks and innovation grants encourage fermentation infrastructure development. Additionally, high levels of veganism and flexitarian adoption contribute to strong demand for meat and dairy alternatives. Europe also serves as a key exporter of fermentation-derived protein ingredients to North America and Asia, strengthening its supply-chain influence.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, projected to expand at over 18% CAGR through 2031. Rapid urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and increasing protein consumption are primary demand drivers. China and India represent major high-growth markets due to large population bases and expanding middle-class dietary shifts toward higher-protein diets. Government biotechnology initiatives and food security programs are encouraging domestic fermentation capacity development. Japan and Singapore are investing heavily in advanced bioprocessing infrastructure and precision fermentation R&D to reduce reliance on imported protein sources. Growing awareness of sustainability and increasing adoption of alternative proteins among younger consumers further support long-term expansion.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for approximately 5–7% of the global market, with Brazil and Mexico leading regional adoption. Growth is driven by increasing interest in sustainable agriculture, expanding plant-based food industries, and export-oriented feed applications. Brazil’s strong agribusiness infrastructure and fermentation expertise support biomass fermentation expansion. Rising environmental awareness and international trade partnerships are gradually strengthening demand for fermentation-enabled proteins across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region contributes around 5% share, with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries driving most of the growth. Government-led food security initiatives, limited arable land, and high dependency on protein imports are encouraging investment in alternative protein technologies. The UAE and Saudi Arabia are investing in domestic biotechnology hubs and fermentation facilities to enhance self-sufficiency. In Africa, South Africa is emerging as an innovation center due to its established food processing sector and growing interest in sustainable protein production. Long-term growth in the region is supported by population expansion, rising urbanization, and strategic investments in food technology infrastructure.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Fermentation-Enabled Alternative Proteins Market
- Perfect Day
- Geltor
- MycoTechnology
- The EVERY Company
- Motif FoodWorks
- Nature’s Fynd
- Impossible Foods
- Quorn
- Remilk
- New Culture
- Clara Foods
- C16 Biosciences
- Fermify
- Change Foods
- Planterra Foods