Bulk Tapioca Flour Market Size
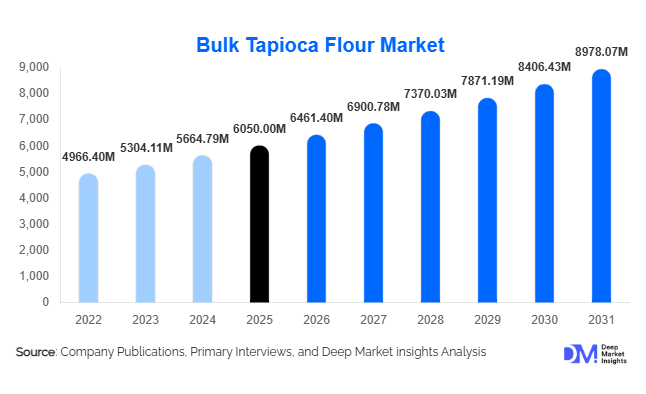
According to Deep Market Insights, the global bulk tapioca flour market size was valued at USD 6,050 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 6,461.40 million in 2026 to reach USD 8,978.07 million by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The market growth is primarily driven by rising demand for gluten-free food formulations, expanding processed food consumption, and increasing industrial utilization of starch-based ingredients in biodegradable packaging, adhesives, and paper applications. Growing consumer preference for clean-label and plant-based ingredients is further strengthening global demand for tapioca flour across developed and emerging economies.
Key Market Insights
- Food & beverage applications account for nearly 60% of global demand, supported by gluten-free bakery, snacks, and convenience foods.
- Asia-Pacific dominates production and consumption, holding approximately 45% of the global market share in 2025, led by Thailand, Vietnam, China, and India.
- Modified tapioca flour is the fastest-growing processing segment, driven by industrial applications in adhesives, paper coating, and biodegradable materials.
- Conventional tapioca flour represents about 78% of the total market, while organic variants are expanding steadily in premium food segments.
- Top five companies control nearly 38% of the global market, indicating moderate consolidation with strong regional competition.
- Export-driven trade flows from Southeast Asia to North America and Europe significantly influence pricing and supply dynamics.
What are the latest trends in the bulk tapioca flour market?
Shift Toward Clean-Label and Gluten-Free Ingredients
Bulk tapioca flour is increasingly being adopted as a clean-label alternative to chemically modified starches and gluten-based thickeners. With rising incidences of gluten intolerance and growing consumer awareness around ingredient transparency, food manufacturers are reformulating products to include tapioca flour as a natural thickening and binding agent. Clean-label bakery, dairy alternatives, sauces, and snack formulations are incorporating tapioca flour to improve texture and shelf stability without artificial additives. The trend is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where regulatory scrutiny and consumer expectations around labeling are stringent. Organic-certified tapioca flour is also witnessing accelerated uptake among premium food brands.
Expansion into Biodegradable and Bio-Based Materials
Sustainability mandates are encouraging industrial manufacturers to shift toward starch-based alternatives for packaging and adhesives. Tapioca flour-derived starch is increasingly used in compostable packaging films, paper coating, textile sizing, and eco-friendly adhesives. Governments across Asia and Europe are implementing single-use plastic reduction policies, creating structural demand for biodegradable materials. This is driving investments in modified tapioca flour technology to enhance water resistance, tensile strength, and industrial performance characteristics.
What are the key drivers in the bulk tapioca flour market?
Growth in Processed and Convenience Foods
The rapid expansion of the global processed food industry, valued at over USD 4 trillion, is a major growth driver. Urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and changing dietary habits are boosting demand for packaged snacks, ready-to-eat meals, and bakery products, all of which utilize tapioca flour as a stabilizer and thickener. Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing particularly strong consumption growth, directly influencing bulk ingredient procurement.
Industrial Diversification and Functional Performance Benefits
Modified tapioca flour offers superior viscosity stability, freeze-thaw resistance, and binding strength, making it suitable for paper, textile, and adhesive industries. As environmental regulations tighten globally, industries are increasingly replacing petroleum-based binders with starch-based alternatives. This functional versatility is expanding tapioca flour’s addressable market beyond traditional food uses.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Raw Material Price Volatility
Cassava root prices fluctuate due to climatic variability, pest outbreaks, and agricultural policy changes in producing countries. Since raw material costs account for nearly 60% of production expenses, price volatility can compress margins and disrupt long-term supply contracts.
Competition from Alternative Starches
Corn starch and potato starch present cost-effective substitutes in several applications. In regions with abundant maize production, corn starch may offer pricing advantages, compelling tapioca flour manufacturers to differentiate through quality consistency and functional performance.
What are the key opportunities in the bulk tapioca flour industry?
Export-Oriented Capacity Expansion in Southeast Asia
Major cassava-producing countries such as Thailand and Vietnam are investing in downstream processing infrastructure to enhance value addition. Expansion of automated milling facilities and export logistics hubs is strengthening competitiveness in North American and European markets. Export demand for certified gluten-free and sustainably sourced flour presents long-term revenue potential.
Premium Organic and Specialty Grade Development
The organic segment, though accounting for roughly 22% of the market, is expanding at a faster rate than conventional products. Companies investing in traceability systems, organic certification, and specialty pharmaceutical-grade flour can capture higher margins and long-term supply agreements with multinational food and healthcare manufacturers.
Product Type Insights
Conventional bulk tapioca flour continues to dominate the global market, accounting for approximately 78% of total volume share in 2025. Its leadership is primarily attributed to cost efficiency, wide availability, and suitability for large-scale industrial processing. The segment benefits from established cassava supply chains across Southeast Asia and competitive export pricing, making it the preferred choice for food manufacturers, paper producers, and adhesive formulators. The leading driver for this segment is its superior price-to-performance ratio, enabling high-volume applications in both developed and emerging markets. Organic bulk tapioca flour represents a smaller but rapidly expanding segment, supported by premium pricing structures and rising demand for clean-label, non-GMO, and sustainably sourced ingredients. Growth in this segment is strongly aligned with increasing consumer awareness regarding food transparency and organic certifications. Modified tapioca flour, which accounts for nearly 45% of total processing value, is expanding steadily as food and industrial manufacturers demand enhanced functional properties such as improved viscosity, stability, and freeze-thaw resistance. The growing need for tailored starch solutions in processed foods and specialty industrial formulations continues to accelerate modified flour adoption.
Application Insights
Food-grade tapioca flour represents nearly 64% of the global market in 2025, making it the leading application segment. Its dominance is driven by expanding usage in bakery products, snacks, soups, sauces, dairy alternatives, and gluten-free formulations. The primary driver for this segment is the global rise in gluten-free and allergen-free food consumption, combined with tapioca flour’s neutral taste, smooth texture, and clean-label compatibility. Industrial-grade tapioca flour accounts for approximately 28% of total demand, serving paper manufacturing, adhesives, textiles, and biodegradable material production. Increasing environmental regulations and the shift toward plant-based raw materials are supporting steady growth in this segment. Pharmaceutical-grade tapioca flour remains niche yet profitable, particularly in excipient and tablet-binding applications, where demand is rising in parallel with global generic drug production and expanding healthcare access in emerging economies.
Distribution Channel Insights
Direct B2B contracts dominate the bulk tapioca flour market, particularly among multinational food processors, industrial manufacturers, and pharmaceutical companies that require consistent volume supply and quality assurance. Long-term supply agreements help stabilize pricing and ensure raw material continuity. Ingredient suppliers and export traders play a critical role in facilitating cross-border trade, especially within Southeast Asia, where major producing countries maintain strong export-oriented infrastructures. The leading driver for distribution efficiency is the increasing globalization of cassava supply chains, supported by improved logistics networks and port infrastructure. Additionally, digital procurement platforms are gradually emerging as transformative channels, enhancing price transparency, contract management efficiency, and supplier diversification for mid-sized buyers.
End-Use Industry Insights
The food and beverage sector accounts for approximately 60% of total tapioca flour demand in 2025, maintaining its position as the largest end-use industry. The primary driver for this dominance is the expanding processed food industry, coupled with rising consumer demand for gluten-free, plant-based, and clean-label ingredients. Industrial applications collectively contribute around 40% of demand, with biodegradable packaging materials and eco-friendly adhesives representing the fastest-growing segments at a CAGR exceeding 7%. Growth in these segments is strongly supported by sustainability initiatives, regulatory pressure to reduce synthetic polymers, and increasing corporate commitments to carbon footprint reduction. Pharmaceutical demand continues to rise steadily, fueled by expanding generic drug manufacturing capacity and the need for cost-effective excipients in tablet formulation.
| By Source Type | By Grade | By Processing Method | By Application | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific holds nearly 45% of the global tapioca flour market share in 2025, making it the largest regional market. Countries such as Thailand, Vietnam, China, and India play central roles in both production and consumption. alone accounts for approximately 18% of global production, supported by strong cassava cultivation, advanced processing infrastructure, and export-oriented trade policies. contributes significantly through competitive processing costs and growing export volumes. remains a major importer, particularly for industrial-grade applications in paper and biodegradable materials. is witnessing rapid growth driven by expanding food processing capacity and rising domestic demand for gluten-free ingredients. The primary regional growth drivers include abundant cassava production, low-cost labor, export competitiveness, government support for agro-processing industries, and expanding domestic consumption across emerging economies.
North America
North America represents approximately 22% of the global market, led by the . The region’s growth is primarily driven by strong gluten-free product penetration, rising plant-based food consumption, and increasing industrial adoption of biodegradable materials. Food manufacturers are incorporating tapioca flour into clean-label formulations to meet evolving consumer preferences. Additionally, sustainability initiatives and regulatory encouragement of bio-based industrial inputs are stimulating demand in adhesives and packaging. The region remains one of the largest importers of tapioca flour due to limited domestic cassava production, strengthening trade ties with Southeast Asian exporters.
Europe
Europe accounts for roughly 20% of global demand, with key importing countries including , , and the . Regional growth is strongly supported by strict food safety standards, regulatory emphasis on clean labeling, and consumer preference for sustainably sourced ingredients. The leading growth driver is the increasing adoption of organic and non-GMO starch alternatives across bakery and specialty food segments. Industrial demand is further supported by the European Union’s environmental policies promoting biodegradable and renewable raw materials in packaging and manufacturing.
Latin America
Latin America holds nearly 8% of the global market share, with serving as both a significant producer and consumer. Regional growth is driven by expanding domestic food processing industries, improving agricultural productivity, and growing export potential. Rising investments in cassava farming technologies and regional trade agreements are enhancing production efficiency and supporting steady market expansion.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 5% of the global market, with growing demand concentrated in the and . Market growth is primarily driven by increasing processed food consumption, expanding retail infrastructure, and gradual industrial diversification. Import-dependent supply chains and rising investments in food manufacturing facilities are contributing to steady demand growth, while urbanization and shifting dietary patterns further support long-term expansion.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Bulk Tapioca Flour Market
- Cargill Incorporated
- Ingredion Incorporated
- Tate & Lyle PLC
- Roquette Frères
- AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG
- Thai Wah Public Company Limited
- Asia Modified Starch Co., Ltd.
- Visco Starch
- PT Budi Starch & Sweetener Tbk
- SPAC Starch Products (India) Ltd.
- Sanguan Wongse Industries Co., Ltd.
- Venus Starch Suppliers
- TCS Tapioca Starch Industry Co., Ltd.
- Psaltry International Company Limited
- Sonish Starch Technology Co., Ltd.