3D Printed Steaks Market Size
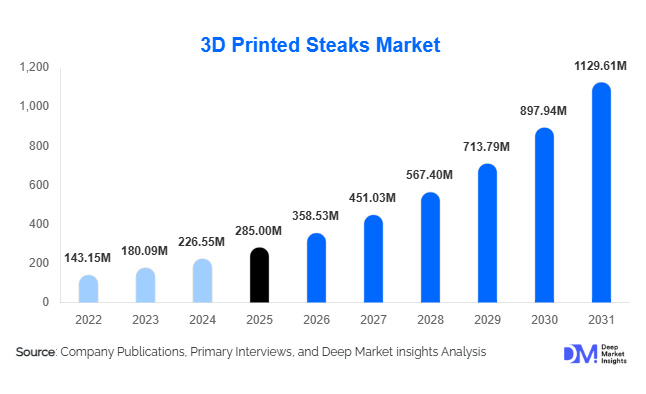
According to Deep Market Indsights, the global 3D printed steaks market size was valued at USD 285 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 358.53 million in 2026 to reach approximately USD 1,129.61 million by 2031, expanding at a CAGR of 25.8% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The 3D printed steaks market growth is primarily driven by rapid advancements in food-grade bioprinting technologies, rising investments in alternative proteins, and increasing global demand for sustainable, ethical, and resource-efficient meat substitutes that closely replicate conventional whole-cut steaks.
Key Market Insights
- 3D printed steaks are emerging as a premium alternative protein category, offering realistic muscle-fiber texture, marbling, and customizable nutrition profiles.
- Foodservice and HoReCa channels dominate early adoption, as fine-dining restaurants and luxury hospitality brands leverage printed steaks for sustainability branding and menu differentiation.
- North America leads the global market, supported by strong food-tech funding, regulatory momentum, and early commercialization partnerships.
- Europe is the fastest-growing regulated market, driven by sustainability-focused consumers and government-backed protein transition initiatives.
- Asia-Pacific is emerging as a high-growth region, led by Singapore, Japan, and South Korea, where regulatory openness and protein security concerns are accelerating adoption.
- Technological integration, including AI-driven texture modeling, hybrid cell-plant formulations, and multi-material extrusion systems, is significantly improving scalability and cost efficiency.
What are the latest trends in the 3D printed steaks market?
Hybrid Cell-Plant Steak Formulations Gaining Momentum
One of the most prominent trends in the 3D printed steaks market is the shift toward hybrid formulations that combine cultivated animal cells with plant-based protein matrices. This approach enables manufacturers to achieve realistic taste, fat distribution, and mouthfeel while keeping production costs lower than fully cell-based steaks. Hybrid steaks are also facing fewer regulatory hurdles in several markets, accelerating commercialization timelines. As a result, many leading players are prioritizing hybrid product pipelines to balance scalability, sensory quality, and regulatory compliance.
Expansion of Premium Foodservice Pilots
High-end restaurants, boutique hotels, and experiential dining venues are increasingly adopting 3D printed steaks as limited-edition or signature menu items. These pilots allow companies to test consumer acceptance, refine formulations, and position printed steaks as a luxury, sustainable alternative to conventional beef. The premium positioning also supports higher margins during the early stages of market development, helping offset high production costs.
What are the key drivers in the 3D printed steaks market?
Sustainability and Carbon Reduction Pressures
Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and land-use intensity associated with livestock farming are strongly driving demand for 3D printed steaks. Compared to conventional beef, printed steaks require significantly less land, water, and feed inputs, aligning with corporate ESG goals and national climate targets. This sustainability advantage is particularly influential among institutional buyers and premium foodservice operators.
Advancements in Food-Grade Bioprinting Technology
Technological improvements in extrusion-based bioprinting, shear-thinning bio-inks, and multi-nozzle systems have enabled manufacturers to replicate complex tissue structures with high consistency. These advancements have narrowed the sensory gap between printed and traditional steaks, improving consumer acceptance and repeat purchase potential.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Production and Equipment Costs
Despite rapid innovation, 3D printed steaks remain significantly more expensive than conventional meat and plant-based alternatives. High costs associated with bioprinters, cultivated cell media, and skilled labor continue to limit mass-market penetration, confining adoption largely to premium and institutional segments.
Regulatory Fragmentation Across Regions
Inconsistent regulatory frameworks for cultivated and printed meat products across countries create uncertainty for manufacturers. Lengthy approval processes and labeling restrictions can delay market entry and limit cross-border trade, slowing overall market growth.
What are the key opportunities in the 3D printed steaks industry?
Government Support for Protein Security
Governments in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and the Middle East are increasingly funding alternative protein research to enhance food security and reduce reliance on meat imports. Public procurement opportunities in defense, healthcare, and space research offer stable, long-term demand for 3D printed steaks.
B2B Licensing and IP Monetization
Beyond direct product sales, companies are unlocking value through licensing of printing formulations, texture algorithms, and proprietary hardware designs. This asset-light revenue model allows rapid global expansion without heavy manufacturing investments.
Product Type Insights
Among product types, whole-cut 3D printed steaks dominate the global market, accounting for approximately 41% of revenue in 2025. These steaks closely replicate traditional beef in terms of appearance, marbling, texture, and mouthfeel, making them highly attractive to premium foodservice buyers and fine-dining establishments. The growing consumer preference for realistic meat analogues is the primary driver behind this segment’s leadership, supported by advancements in multi-material extrusion bioprinting that allow precise muscle fiber alignment and fat distribution. Structured steak analogues, featuring layered fibers that simulate conventional steak texture, follow in market share and are increasingly adopted in mid-tier HoReCa and retail applications. Customized nutritional steaks are gaining traction within medical nutrition, wellness, and high-protein diets, offering personalized macro- and micronutrient profiles tailored for hospitals, health-focused consumers, and institutional clients. Innovations in bio-inks and AI-driven printing design are expected to further accelerate adoption across these emerging applications.
Application Insights
The foodservice and HoReCa sector remains the largest application segment, contributing nearly 46% of the 2025 market. Restaurants, luxury hotels, and boutique dining establishments are adopting 3D printed steaks to differentiate menus, meet sustainability commitments, and appeal to premium-conscious consumers. Institutional applications, including hospitals, defense establishments, and government catering programs, are emerging as high-volume, stable demand segments due to growing emphasis on nutrition, food safety, and alternative protein sourcing. Retail and direct-to-consumer channels currently represent a smaller portion of the market but are projected to gain traction post-2026 as production costs decline, regulatory approvals expand, and consumer awareness of alternative proteins increases. The key driver across applications is the ability of 3D printed steaks to replicate the sensory and nutritional profile of traditional meat while supporting sustainability and ethical sourcing initiatives.
Distribution Channel Insights
B2B contract manufacturing continues to dominate distribution, accounting for around 44% of total market value. Centralized production models remain more economical and allow manufacturers to scale rapidly while ensuring quality and consistency in printed steaks. Licensing-based distribution is expanding, particularly among technology-focused players who provide IP, formulations, or proprietary bio-inks to food brands and foodservice operators. In-house production by large food brands is gradually increasing, especially among players seeking direct control over product innovation and brand positioning. The leading driver for distribution channel adoption is operational efficiency: centralized B2B models reduce upfront capital costs, optimize production, and facilitate entry into high-value markets such as premium restaurants and institutional buyers.
| By Product Type | By Application | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America represents approximately 38% of the global 3D printed steaks market in 2025, led by the United States. Regional growth is primarily driven by strong venture capital funding, supportive regulatory developments, and collaborations between food-tech startups and global food conglomerates. The United States benefits from an early-mover advantage in cultivated and 3D printed meat technologies, a high concentration of research institutions, and an innovative foodservice landscape seeking sustainable alternatives. The leading segment driver -premium whole-cut steaks -is particularly relevant here, as fine-dining restaurants and luxury HoReCa operators fuel high-value adoption. Additionally, growing consumer awareness of sustainability and protein diversification is accelerating demand across institutional and retail channels.
Europe
Europe holds around 32% market share, with the Netherlands, Germany, and the U.K. driving growth. Expansion is fueled by sustainability-driven consumer preferences, supportive government policies, and initiatives encouraging alternative protein adoption, such as protein transition programs and green food subsidies. The adoption of premium whole-cut 3D printed steaks is led by high-end restaurants, gastronomy-focused cities, and luxury catering services seeking environmentally friendly protein options. Technological infrastructure in countries like the Netherlands and Germany supports rapid product scale-up, while regulatory clarity within the EU provides confidence for new entrants. Europe’s leading growth driver is the combination of consumer sustainability awareness and regulatory support, which incentivizes both foodservice and institutional buyers to adopt alternative protein solutions.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, expanding at a CAGR of nearly 29%. Singapore leads commercialization due to early regulatory approvals for cultivated and printed meat, extensive government R&D funding, and a focus on protein security initiatives. Japan and South Korea are investing heavily in food-tech infrastructure, alternative proteins, and bioprinting technologies. The region’s growth is driven by increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and consumer demand for premium protein options, particularly in fine-dining and wellness-focused applications. Whole-cut 3D printed steaks are gaining prominence as luxury restaurants experiment with novel, sustainable menu items. Additionally, export opportunities from Asia-Pacific to North America and Europe are contributing to market expansion.
Latin America
Latin America remains an early-stage market, with Brazil and Chile leading pilot adoption. Growth is primarily driven by research collaborations with North American and European technology partners, as well as export-oriented production for international markets. Increasing awareness of sustainable protein alternatives and emerging investment in local food-tech startups are supporting adoption. While retail penetration is limited, institutional and HoReCa channels are expected to be early drivers of demand. The leading product segment -whole-cut 3D printed steaks -is positioned for growth among premium restaurants and culinary innovation hubs in São Paulo, Santiago, and other urban centers.
Middle East & Africa
Israel and the UAE are key innovation hubs in this region, supported by strong government funding, protein security initiatives, and technology-driven agricultural strategies. High-income consumer populations and rapidly growing foodservice sectors are accelerating market uptake, particularly in luxury hotels, international restaurants, and institutional buyers. Government-backed R&D programs and incubation centers for alternative proteins encourage early-stage commercialization. Whole-cut printed steaks are the preferred segment due to their premium positioning and alignment with sustainability and innovation-focused dining experiences. Additionally, intra-regional collaborations and strategic exports to the Asia-Pacific and Europe are providing additional growth momentum.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|