3D Food Printing Market Size
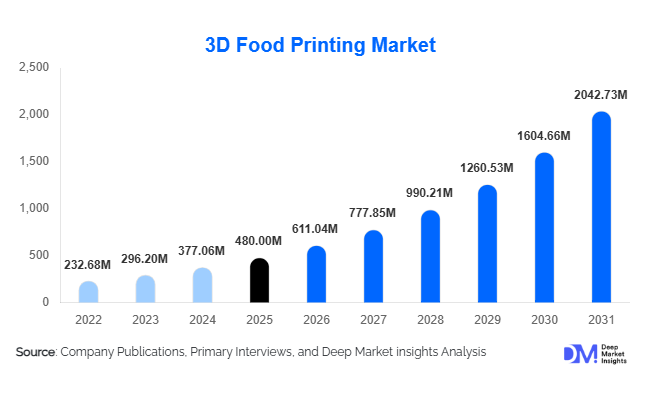
According to Deep Market Insights, the global 3D food printing market size was valued at USD 480 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 611.04 million in 2026 to reach approximately USD 2,042.73 million by 2031, expanding at a robust CAGR of 27.3% during the forecast period (2026–2031). The growth of the 3D food printing market is driven by rising demand for personalized nutrition, increasing adoption of food automation technologies, and growing interest in sustainable and alternative food production systems across commercial, healthcare, and industrial applications.
Key Market Insights
- Extrusion-based 3D food printing dominates the market, owing to its versatility across carbohydrates, proteins, and multi-material food formulations.
- Commercial food service is the leading application, driven by demand for customization, labor efficiency, and visual differentiation in restaurants and bakeries.
- North America leads global adoption, supported by strong food-tech investments, early commercialization, and favorable regulatory frameworks.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by China, Japan, and Singapore, driven by government-backed food innovation programs.
- Healthcare and medical nutrition applications are expanding rapidly, particularly for elderly care and dysphagia-friendly diets.
- Sustainability and food waste reduction are emerging as critical value propositions for industrial adoption.
What are the latest trends in the 3D food printing market?
Personalized and Functional Nutrition Adoption
Personalized nutrition is emerging as one of the most influential trends shaping the 3D food printing market. The technology enables precise control over nutrient composition, texture, and portion size, allowing food products to be tailored for specific dietary requirements. Healthcare institutions are increasingly using 3D food printers to create customized meals for patients with swallowing disorders, malnutrition, or chronic illnesses. At the consumer level, fitness-oriented and wellness-focused users are showing growing interest in customized protein-rich and functional foods, accelerating adoption beyond pilot-stage deployments.
Integration of Alternative and Sustainable Ingredients
The use of alternative proteins, including plant-based, insect-based, and cell-cultured ingredients, is gaining momentum within 3D food printing. The technology enables improved texture, structure, and visual appeal of alternative protein foods, helping overcome consumer acceptance challenges. Food manufacturers are leveraging 3D printing to reduce waste by repurposing surplus ingredients into printable food pastes, aligning with global sustainability goals and circular economy initiatives.
What are the key drivers in the 3D food printing market?
Rising Demand for Food Customization
Consumers are increasingly seeking foods tailored to individual preferences, allergies, and nutritional goals. 3D food printing offers unmatched customization capabilities compared to traditional food processing, making it highly attractive for premium foodservice and healthcare nutrition. This driver is particularly strong in developed markets, where consumers demonstrate a higher willingness to pay for personalized food solutions.
Advancements in Food-Grade Additive Manufacturing
Continuous improvements in printer hardware, multi-nozzle extrusion systems, and food-safe ingredient formulations are significantly enhancing print speed, reliability, and scalability. These advancements are enabling broader commercial adoption across restaurants, bakeries, and small-scale food manufacturing facilities, while reducing operational complexity.
Focus on Sustainability and Waste Reduction
3D food printing supports sustainable food production by enabling precise ingredient usage and minimizing waste. Food manufacturers and governments are increasingly viewing the technology as a tool to address food security concerns and environmental impact, further driving market growth.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Initial Capital Costs
The upfront investment required for industrial-grade 3D food printers remains high, limiting adoption among small and mid-sized food businesses. Additionally, current systems have lower throughput compared to conventional mass-production equipment, restricting their use in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Regulatory and Food Safety Challenges
Inconsistent food safety regulations and limited standardization across regions pose challenges for commercialization. Approval processes for printed food ingredients and equipment can delay market entry, particularly in emerging economies.
What are the key opportunities in the 3D food printing industry?
Healthcare and Medical Nutrition Expansion
The growing global elderly population and rising prevalence of diet-related medical conditions present significant opportunities for 3D food printing in healthcare. Hospitals and care facilities are increasingly adopting the technology for texture-modified and nutrient-dense foods, creating stable, institutional demand.
Commercial Foodservice Automation
Labor shortages and rising operational costs in the foodservice industry are accelerating demand for automation. Compact and easy-to-use 3D food printers are being deployed in restaurants and bakeries to improve efficiency while enabling menu innovation and customization.
Technology Insights
Among the various 3D food printing technologies, extrusion-based systems dominate, accounting for approximately 62% of the global market share in 2025. This dominance is driven by its ability to process a wide variety of food materials, including dough, chocolate, protein pastes, and multi-ingredient formulations, combined with relatively simple operational requirements. The versatility and scalability of extrusion technology make it the preferred choice for both commercial kitchens and industrial food manufacturers. Inkjet and binder jetting technologies are gaining traction in niche applications, particularly in confectionery, chocolate decoration, and high-precision food aesthetics. Additionally, hybrid systems that allow multi-material printing are emerging, enabling complex food structures and customized nutrition solutions. Continuous R&D in nozzle design, food-safe materials, and print speed enhancements is further strengthening the technological landscape and expanding adoption across industries.
Application Insights
The commercial food service segment leads the market, accounting for nearly 38% of total revenue in 2025. This growth is driven by demand for menu differentiation, labor efficiency, and customizable offerings in restaurants, bakeries, and hotels. Consumers increasingly seek visually appealing, personalized, and high-quality foods, which 3D food printing enables at scale. Following commercial food service, the industrial food manufacturing segment is expanding as manufacturers integrate 3D printing for alternative proteins, functional foods, and premium product lines. The healthcare and medical nutrition segment, representing approximately 18% of the market, is the fastest-growing due to regulatory support, the aging global population, and institutional adoption for dysphagia diets, nutrient-enriched meals, and customized clinical nutrition.
Distribution Channel Insights
Direct sales from OEMs to enterprise customers continue to dominate the distribution landscape, particularly for industrial and healthcare applications that require high-capacity printers and tailored service agreements. Meanwhile, online platforms, e-commerce, and food-tech partnerships are enabling smaller businesses, research institutions, and individual consumers to access desktop 3D food printers. These channels also facilitate recurring revenue models through ingredient cartridges, software updates, and service contracts, which are critical for scaling adoption. The growth of hybrid distribution models, combining direct sales with digital platforms, is helping manufacturers reach new markets while maintaining control over quality and customization.
| By Technology Type | By Ingredient / Food Material Type | By Application / End-Use | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounted for approximately 34% of the global 3D food printing market in 2025, with the United States representing nearly 26% of global demand. Market leadership in the region is fueled by strong R&D activity, early adoption by commercial foodservice chains, and supportive regulatory frameworks for food safety and technology integration. Drivers for growth include increasing labor costs in foodservice, growing demand for on-demand customized foods, and rapid adoption of sustainable food practices. The healthcare sector, particularly hospitals and eldercare facilities, is also emerging as a key growth driver due to increasing investment in personalized nutrition and clinical dietary solutions.
Europe
Europe holds around 29% market share and is driven by countries such as Germany, the Netherlands, France, and the UK. The region’s growth is supported by strong government initiatives promoting alternative proteins, food sustainability programs, and funding for food-tech innovation. Consumer demand for personalized, high-quality, and sustainable foods is another key driver. The presence of established food manufacturing infrastructure enables rapid adoption of extrusion-based and hybrid technologies. Additionally, healthcare institutions in Europe are increasingly implementing 3D food printing for medical nutrition and dietary management, further bolstering regional growth.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for approximately 24% of the market and is the fastest-growing region, with China projected to record a CAGR exceeding 30% through 2031. Rapid urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and a growing middle-class population are key growth drivers. Government-backed initiatives such as food-tech innovation hubs and smart kitchen programs are accelerating adoption, while increasing interest in alternative proteins and functional foods is driving industrial applications. Japan, South Korea, and Singapore are also contributing to market expansion due to early technology adoption in commercial kitchens, research institutions, and healthcare facilities.
Latin America
Latin America is an emerging market, with adoption increasing in premium foodservice, hospitality, and research sectors, particularly in Brazil and Mexico. Drivers include rising urbanization, growing awareness of technological food innovation, and a desire for high-end, customized culinary experiences. Niche sectors, such as luxury restaurants and experimental gastronomy, are spearheading market adoption, while gradual investment in food-tech infrastructure is supporting industrial expansion.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East, led by the UAE and Saudi Arabia, is adopting 3D food printing in luxury hospitality, defense rations, and high-end culinary applications. Drivers include high disposable income, growing tourism, government investments in smart kitchens and food innovation programs, and demand for customized nutrition in healthcare and wellness facilities. Africa shows early-stage adoption primarily in research institutions, universities, and pilot industrial applications, driven by government-backed innovation initiatives and partnerships with international technology providers. Growth in the region is further supported by increased awareness of food sustainability and efforts to integrate alternative protein sources into local diets.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|