Wireless Routers Market Size
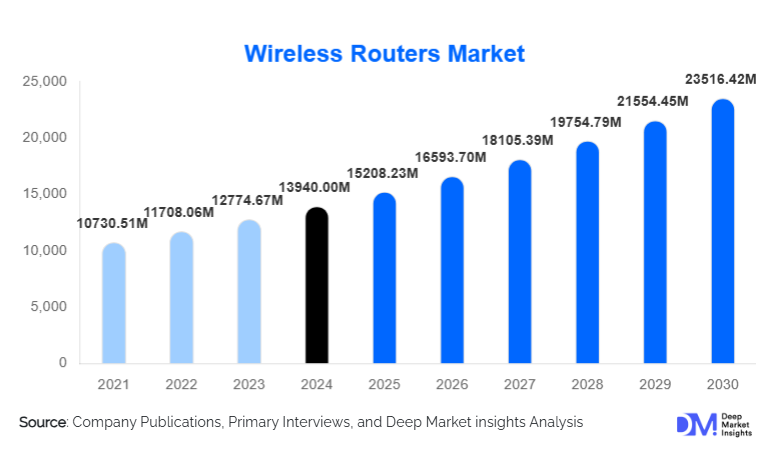
According to Deep Market Insights, the global wireless routers market size was valued at USD 13,940.00 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 15,208.23 million in 2025 to reach USD 23,516.42 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 9.11% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The wireless routers market growth is primarily driven by rapid broadband penetration, rising adoption of smart homes and connected devices, increasing enterprise network upgrades, and the global transition toward advanced Wi-Fi standards such as Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and Wi-Fi 7.
Key Market Insights
- Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E routers dominate global demand, accounting for a significant share of enterprise upgrades and telecom operator-bundled deployments.
- Residential applications remain the largest deployment segment, supported by remote work, streaming, gaming, and smart home ecosystems.
- Asia-Pacific leads the global market, driven by large-scale manufacturing, expanding broadband infrastructure, and strong demand from China and India.
- North America represents the most technologically advanced market, with early adoption of Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 routers.
- 5G-enabled and fixed wireless access (FWA) routers are emerging as high-growth categories, particularly in underserved and rural regions.
- Enterprise and industrial-grade routers are witnessing accelerated adoption due to cybersecurity, IoT, and cloud networking requirements.
What are the latest trends in the wireless routers market?
Rapid Adoption of Advanced Wi-Fi Standards
The wireless routers market is undergoing a technology-led transformation with the rapid adoption of Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and early-stage Wi-Fi 7 routers. These standards offer higher throughput, lower latency, improved spectrum efficiency, and better handling of dense device environments. Enterprises and high-income households are leading this transition, replacing legacy routers to support bandwidth-intensive applications such as cloud computing, 4K/8K streaming, AR/VR, and online gaming. Telecom operators are also accelerating this trend by bundling advanced routers with broadband and fiber subscriptions, driving large-scale replacement cycles.
Integration of 5G and Fixed Wireless Access
Another key trend is the integration of cellular connectivity into wireless routers. 5G- and LTE-enabled routers are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional wired broadband, particularly in regions with limited fiber infrastructure. These routers are increasingly used for temporary installations, remote offices, rural connectivity, and disaster recovery networks. The convergence of Wi-Fi and cellular technologies is expanding the addressable market and enabling new use cases across residential, commercial, and public infrastructure deployments.
What are the key drivers in the wireless routers market?
Explosion of Connected Devices and Data Traffic
The exponential increase in connected devices per household and enterprise is a primary driver of wireless router demand. Smartphones, laptops, smart TVs, IoT devices, and wearables are collectively increasing network load, requiring higher-capacity and more reliable wireless routers. This trend is particularly strong in urban households and digitally mature economies.
Growth of Remote Work, Cloud, and Digital Services
Hybrid work models, cloud-based enterprise applications, and digital collaboration tools have permanently raised expectations for network performance and reliability. Businesses are upgrading routers to support secure remote access, VPNs, and high-performance wireless connectivity, driving sustained demand from the commercial and enterprise segments.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Price Sensitivity in Emerging Economies
Despite strong demand, the high upfront costs of advanced wireless routers remain a barrier in price-sensitive markets. Consumers and small businesses in developing regions often delay upgrades or opt for lower-specification devices, limiting the penetration of premium routers.
Rapid Technological Obsolescence
Frequent advancements in wireless standards shorten product lifecycles and increase R&D and inventory risks for manufacturers. Companies must carefully manage product transitions to avoid margin erosion and unsold inventory.
What are the key opportunities in the wireless routers industry?
Government-Led Digital Infrastructure Programs
National broadband initiatives, smart city programs, and public Wi-Fi deployments are creating large procurement opportunities for wireless router manufacturers. Governments across Asia, the Middle East, and Africa are investing heavily in connectivity infrastructure, supporting long-term market growth.
Enterprise and Industrial IoT Expansion
The rise of Industry 4.0, smart factories, and connected logistics is driving demand for industrial-grade wireless routers with enhanced security, reliability, and centralized management capabilities. This segment offers higher margins and long-term service opportunities.
Product Type Insights
Wi-Fi 6 routers represent the leading product type, accounting for approximately 38% of the 2024 market, due to widespread adoption across residential and enterprise environments. Dual-band and tri-band routers continue to serve mid-range demand, while Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 routers are emerging as premium offerings with strong growth potential. Single-band routers are gradually declining but remain relevant in entry-level and cost-sensitive markets.
Application Insights
Residential networking applications dominate global demand, supported by smart home adoption and increased home internet usage. Commercial and enterprise applications are growing at a faster pace, driven by digital transformation initiatives, cloud adoption, and cybersecurity requirements. Industrial and public infrastructure applications, including smart cities and transportation networks, are emerging as high-growth niches.
Distribution Channel Insights
Telecom operator-bundled sales account for a significant share of global revenue, as ISPs increasingly include wireless routers with broadband subscriptions. E-commerce platforms are the fastest-growing channel, driven by price transparency, product variety, and direct-to-consumer strategies. Offline retail and direct enterprise sales continue to play an important role, particularly for high-performance and customized deployments.
| By Router Type | By Deployment Environment | By Connectivity Backhaul | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific leads the wireless routers market with approximately 34% share in 2024. China is the largest manufacturing and consumption hub, while India represents one of the fastest-growing markets due to expanding broadband access and digital inclusion initiatives. Japan and South Korea drive demand for premium and next-generation routers.
North America
North America accounts for around 28% of the global market, led by the United States. High broadband penetration, early adoption of advanced Wi-Fi standards, and strong enterprise IT spending support market leadership in terms of technology and value.
Europe
Europe holds roughly 21% market share, with Germany, the U.K., and France as major contributors. Enterprise upgrades, smart home adoption, and regulatory focus on cybersecurity are key demand drivers.
Latin America
Latin America represents a smaller but steadily growing market, led by Brazil and Mexico. Expansion of fiber broadband and rising e-commerce penetration are supporting router sales.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region is the fastest-growing, driven by government-led digital infrastructure investments, smart city projects, and increasing broadband adoption in Gulf countries and Africa.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|