Wildlife Photography Camera Market Size
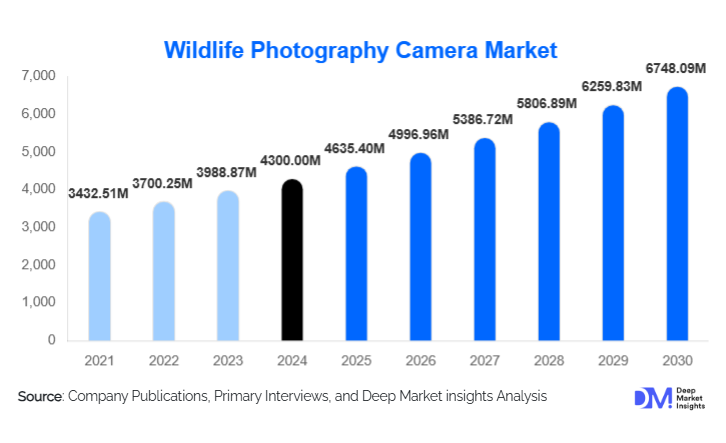
According to Deep Market Insights, the global wildlife photography camera market size was valued at USD 4,300 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 4,635.40 million in 2025 to reach USD 6,748.09 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market growth is driven by rising adoption of AI-enhanced camera systems, increasing demand for wildlife content on streaming platforms, and growing interest in conservation-centric photography among professionals and amateurs. Advancements in telephoto lenses, mirrorless systems, and sensor technology have further enhanced usability across extreme wildlife locations, promoting wider adoption among photographers, research bodies, and documentary producers.
Key Market Insights
- Mirrorless cameras dominate the wildlife photography market due to superior autofocus, lightweight design, and AI-based subject tracking.
- Super-telephoto lenses play a crucial role in professional wildlife imaging, accounting for 35% of lens-based revenues.
- North America leads the market due to high professional adoption, strong content production, and active wildlife conservation initiatives.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by flourishing eco-tourism, rising photography communities, and wildlife documentary production.
- Cloud-enabled and AI-integrated cameras are emerging rapidly, supporting real-time data transfer, remote monitoring, and automated species recognition.
- Professional wildlife photographers represent the largest end-use segment, accounting for 45% of the total market share in 2024.
What are the latest trends in the Wildlife Photography Camera Market?
AI-Integrated Autofocus and Animal Detection
AI-powered subject recognition is advancing beyond eye and face detection to identify entire animal species, body posture, and behavioral patterns. These systems can differentiate between birds in flight, stalking predators, and rapidly moving herbivores, enabling precise focus and exposure adjustments in real-time. Predictive autofocus technology anticipates animal movement, allowing cameras to lock onto subjects before they enter the frame, improving accuracy in fast-paced wildlife scenes. AI is also enhancing burst shooting, enabling high-frame-rate capture for fast-moving species such as hummingbirds and cheetahs without loss of sharpness. Integration of AI into post-processing supports automated tagging, editing, and optimized color grading for wildlife-specific scenes, improving workflow efficiency for filmmakers and photographers.
Rise of Rugged, Weather-Sealed Mirrorless and Full-Frame Cameras
Manufacturers are incorporating advanced weather-sealing at every joint, button, and dial to protect against dust, rain, and sub-zero temperatures, making cameras usable in deserts, rainforests, and tundra-like environments. Temperature-resistant battery systems now deliver longer runtime in extreme heat and cold, improving reliability during extended field shoots. Magnesium alloy and engineered polymer bodies are replacing traditional materials to reduce camera weight while increasing structural strength and shock resistance. Full-frame mirrorless cameras now integrate deeper ISO sensitivity ranges, dual card slots, and enhanced in-body stabilization to support handheld shooting on uneven terrains. These innovations make equipment more resilient without compromising optical performance, ideal for remote locations.
What are the key drivers in the Wildlife Photography Camera Market?
Expansion of Content Production for Streaming Platforms
The rising demand for wildlife documentaries and nature-based educational content has led to increased purchases of cinema-grade cameras and super-telephoto lenses by production studios and streaming networks. Wildlife content creators are increasingly using 8K and high HDR dynamic range video formats to meet the technical standards of platforms like Netflix, BBC Earth, and Disney+. The integration of drones equipped with high-resolution camera rigs allows filmmakers to capture aerial perspectives of animal migrations, marine wildlife, and remote ecosystems. Monetization streams from YouTube, digital licensing, and photography-based stock content are increasing the commercial viability of wildlife photography, supporting equipment upgrades and long-term investments.
Growth of Eco-Tourism and Wildlife Expeditions
Photography-focused wildlife tours are becoming commercially structured offerings, providing travelers with access to private reserves, guided workshops, and rental camera equipment during safaris. Camera manufacturers are collaborating with expedition organizers to offer specialized photo kits, lens packages, and on-site technical support. Certification-based wildlife photography training programs in Kenya, Tanzania, India, and Australia are gaining traction, creating demand for professional-grade gear among learners. Integration of photography with eco-tourism is expanding camera rental businesses, pop-up service centers, and experience-focused sales channels, creating new revenue opportunities beyond conventional retail.
What are the restraints for the market?
High Cost of Premium Wildlife Photography Equipment
Full-frame mirrorless cameras, advanced stabilization features, and super-telephoto lenses can exceed USD 15,000 for professional setups, making them financially inaccessible for hobbyists and early-stage content creators. The need for multiple accessories such as rugged tripods, memory systems, lens filters, drones, and power storage significantly increases total investment. Additionally, expensive camera components such as sensors, lens glass elements, and stabilization motors add to replacement and repair costs, discouraging frequent use in volatile outdoor environments.
Environmental Wear and Limited Durability in Harsh Conditions
Wildlife equipment is frequently exposed to sand, moisture, condensation, and prolonged humidity, which can damage sensor components, gimbal motors, and electronic viewfinders. Fogging in optical lenses, corrosion due to saltwater conditions, and internal dust accumulation can reduce image clarity and autofocus responsiveness. Frequent cleaning and calibration are necessary, increasing overall maintenance costs. Limited access to specialized repair services in remote ecosystems such as African safaris, South American forests, or Arctic zones creates equipment downtime and impacts user productivity.
What are the key opportunities in the Wildlife Photography Camera Market?
AI-Enhanced Camera Traps and Conservation Tech
AI-integrated wildlife camera traps can automatically detect, identify, and log species without human monitoring, making them valuable tools for conservationists, park agencies, and research institutions. Ultra-low-power camera traps with solar charging and satellite connectivity enable real-time monitoring in remote zones. These systems can recognize poaching behavior, log animal migration patterns, and provide habitat change data for climate impact studies. Demand is rising for camera traps that combine infrared, thermal imaging, and cloud-based storage to support research purposes and anti-poaching surveillance, expanding camera adoption beyond photography into environmental technology.
Expansion into Wildlife Tourism and Educational Workshops
Camera brands can collaborate with safari lodges, expedition tour operators, and national parks to offer rental kits, photography tutorials, and equipment demonstration programs. Educational workshops on wildlife composition, low-light shooting, and nature videography are gaining popularity among travelers, creating additional sales channels. Photography-driven tourism packages in regions like Maasai Mara, Ranthambore, Great Barrier Reef, and Costa Rica are increasingly including camera rental and guided field learning as bundled offerings. Manufacturers can develop specialized gear optimized for travel and short-term rentals, including lightweight lens kits and durable storage systems.
Product Type Insights
Mirrorless cameras hold a 42% share in 2024 due to fast autofocus, silent shooting, compact design, and real-time animal detection technology. They deliver high-speed burst shooting without mirror bounce and provide accurate focus in low-light environments. Mirrorless cameras now integrate dual image stabilization, enhanced sensor responsiveness, and wireless connectivity for field uploads, appealing to both professionals and advanced hobbyists. DSLR usage is declining due to bulkier bodies and mechanical limitations, though they remain preferred in long-term fieldwork due to optical reliability and long battery life.
Sensor Type Insights
Full-frame sensors account for 38% of the market, providing superior clarity, maximum dynamic range, and deeper light sensitivity for wildlife scenes during golden hours or under dense canopy cover. Their larger surface area allows enhanced pixel density, delivering higher resolution and better subject isolation, particularly when combined with wide-aperture telephoto lenses. APS-C sensors remain a strong alternative due to their effective crop factor, which increases reach and provides cost advantages for semi-professional users.
Lens Type Insights
Super-telephoto lenses represent 35% of total lens segment revenue, offering focal lengths between 400mm to 800mm, allowing photographers to capture wildlife without physical proximity. These lenses are equipped with fast autofocus motors, image stabilization modules, and lightweight carbon body construction, enabling extended handheld shooting. Wide-aperture variants, such as f/2.8 or f/4, are preferred for tracking birds in flight, sunrise and sunset photography, and nocturnal wildlife documentation, making them indispensable for professional users.
Price Range Insights
High-end cameras (USD 3,000–7,000) contribute 37% of market revenue due to strong adoption among professional photographers and documentary filmmakers. This category offers flagship models with fast shutter speeds, high FPS rates, advanced weather sealing, and AI-based animal tracking. Premium cameras exceeding USD 7,000 are mostly used in scientific research, film production, and specialized wildlife assignments, while mid-range and entry-level segments are suitable for skill development and amateur photography.
End-Use Insights
Professional wildlife photographers command a 45% market share owing to consistent demand for high-performance gear, field durability, and interchangeable lens systems. Documentary houses and conservation organizations represent growth segments due to rising demand for evidence-based wildlife documentation. Research institutions are deploying camera traps, drone-mounted systems, and long-range optical lenses for non-invasive wildlife tracking, creating new procurement models. Amateur hobbyists increasingly contribute to entry-level mirrorless and action camera shipments through travel, social media, and safari-based learning experiences.
| By Product Type | By Sensor Type | By Lens Type | By Price Range | By End-Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America leads with 35% market share, driven by strong wildlife filmmaking presence, high purchasing power, and advanced camera distribution networks. The United States contributes 28%, due to strong adoption by filmmaking studios, wildlife researchers, and digital creators. The availability of lens rental companies, photography schools, and specialized repair centers further supports market growth. Canada demonstrates growing interest in wildlife photography across national parks, tundra landscapes, and northern territories, supporting camera adoption.
Europe
Europe accounts for 27% of total market demand, led by Germany, the U.K., France, and Nordic countries. Demand is supported by widespread participation in bird-watching photography, wildlife tourism, and cinematography in fjords, Arctic regions, and migratory bird reserves. Germany is a major importer of Japanese and U.S.-manufactured professional cameras and premium lenses. The U.K. has strong wildlife documentary production capacity, particularly through BBC Natural History Unit.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region with a projected CAGR of 10.3%, supported by rising eco-tourism in India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, and Australia. Japan remains a key production hub for cameras and optical components, while India and Australia lead demand for wildlife tourism and photography education. China’s growing social media content creation industry is driving purchases of mid to high-end camera models for wildlife and travel photography.
Latin America
Latin America shows emerging demand, particularly in Brazil, Costa Rica, Argentina, and Peru, where lush biodiversity and eco-tourism are boosting interest in wildlife photography. Adventure tours in the Amazon, Pantanal wetlands, and Patagonia are attracting amateur photographers and documentary content creators. Adoption is growing among photography clubs and wildlife travel agencies.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa exhibit strong demand, driven by African safari destinations including Kenya, Tanzania, Botswana, and South Africa. Wildlife tourism and professional photography workshops are fueling high equipment rentals and sales. The UAE and Saudi Arabia contribute to premium market demand through luxury wildlife expeditions and high-end travel photography. Regional camera rental platforms are expanding due to increased tourism flows.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Top Players in the Wildlife Photography Camera Market
- Canon Inc.
- Sony Corporation
- Nikon Corporation
- Fujifilm Holdings
- Panasonic Corporation
- Leica Camera AG
- Olympus Corporation
- Ricoh Imaging
- Hasselblad
- GoPro, Inc.
- DJI
- Sigma Corporation
- Tamron Co., Ltd.
- Blackmagic Design
- RED Digital Cinema
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Sony introduced an AI-driven mirrorless camera with species recognition and enhanced real-time tracking for wildlife professionals.
- In October 2024, Canon released a super-telephoto lens with advanced anti-vibration technology for long-range wildlife captures.
- In August 2024, Nikon launched a conservation partnership to supply advanced camera traps and imaging kits to African wildlife monitoring agencies.