Newspapers Market Size
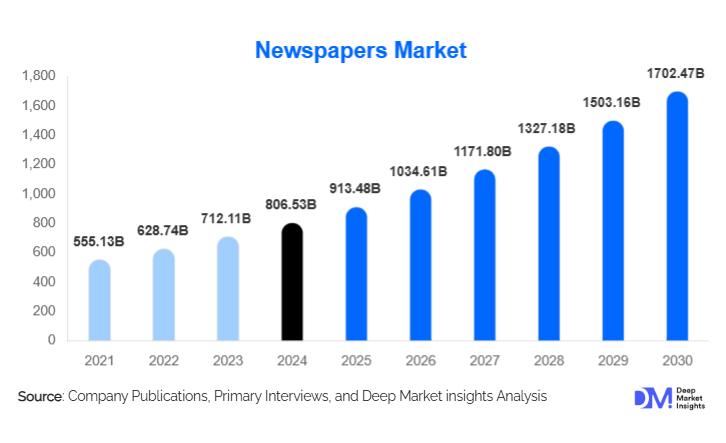
According to Deep Market Insights, the global newspapers market size was valued at USD 806.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 913.48 billion in 2025 to reach USD 1,702.47 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 13.26% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The newspaper market's growth trajectory reflects a structurally mature industry undergoing long-term transformation, driven by declining print advertising revenues in developed economies, a gradual shift in readership to digital platforms, and rising cost pressures. However, the market continues to demonstrate resilience due to sustained demand from government advertising, institutional subscriptions, and strong readership bases in emerging economies, particularly across Asia-Pacific, Africa, and parts of Latin America.
Key Market Insights
- Print newspapers continue to dominate revenue generation, accounting for nearly two-thirds of the global market in 2024, supported by habitual readership and institutional dependence.
- Vernacular and regional-language newspapers lead circulation volume, driven by high trust, affordability, and penetration in semi-urban and rural regions.
- The Asia-Pacific region represents the largest market, driven by its large population, rising literacy rates, and strong local advertising demand.
- Government and public sector advertising remains a critical revenue anchor, ensuring baseline demand despite private-sector ad migration to digital media.
- Hybrid print–digital subscription models are stabilizing revenues, enabling publishers to defend market share while improving customer lifetime value.
- Industry consolidation is accelerating, particularly in North America and Europe, as publishers seek scale efficiencies and cost optimization.
What are the latest trends in the newspapers market?
Rise of Vernacular and Hyperlocal Newspapers
One of the most prominent trends shaping the newspaper market is the growing dominance of vernacular and hyperlocal publications. Regional-language newspapers are expanding readership in Asia-Pacific and Africa, where local content, political relevance, and community-focused reporting resonate strongly with audiences. These publications benefit from lower operating costs, loyal subscriber bases, and consistent advertising from local SMEs and government bodies. Hyperlocal editions focusing on municipal governance, education, and employment are also gaining traction, reinforcing newspapers’ relevance in grassroots information dissemination.
Hybrid Print–Digital Monetization Models
Publishers are increasingly adopting hybrid monetization strategies that bundle print subscriptions with digital replicas and mobile access. This approach helps offset declining single-copy sales while maintaining engagement with younger audiences. Digital replicas, typically PDF-based e-papers, are especially popular among diaspora readers and institutional subscribers. Automation in editorial workflows, AI-assisted layout design, and data-driven ad targeting are further enhancing operational efficiency and revenue optimization.
What are the key drivers in the newspapers market?
Continued Reliance on Newspapers for Government Communication
Governments across multiple regions continue to mandate newspapers for public notices, tenders, election communication, and regulatory disclosures. This structural dependence ensures recurring advertising revenue and long-term demand stability, particularly for national and regional dailies. Public infrastructure expansion and increased regulatory transparency requirements are further reinforcing this driver.
Strong Rural and Semi-Urban Readership Base
In emerging economies, newspapers remain a primary source of news due to limited internet access, affordability, and high trust levels. Rural and semi-urban households often maintain daily newspaper subscriptions, supporting circulation volumes and advertiser reach. This demographic resilience plays a crucial role in moderating overall market decline.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Structural Decline in Print Advertising
Print advertising budgets continue to shift toward digital platforms, particularly in developed economies. This has reduced high-margin revenue streams for publishers and increased dependence on lower-margin subscriptions and government advertising, constraining profitability.
Rising Input and Operational Costs
Volatility in newsprint prices, energy costs, and logistics expenses poses a major challenge for publishers. Smaller and mid-sized newspapers face margin pressure, accelerating consolidation and exit from the market in highly competitive regions.
What are the key opportunities in the newspapers industry?
Expansion in Emerging and Underserved Markets
Emerging economies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America offer significant growth potential through rising literacy rates and expanding regional advertising demand. Vernacular publications and affordable subscription models provide attractive entry points for both existing players and new entrants.
Digital Replica and Institutional Subscription Growth
Digital replicas tailored for institutions, corporates, and international readers represent a scalable opportunity. These formats preserve traditional newspaper branding while reducing printing and distribution costs, improving margins.
Content Type Insights
General news newspapers dominate the global newspapers market, accounting for approximately 42% of total revenue in 2024. This leadership is primarily driven by their high-frequency consumption, broad demographic reach, and relevance across political, economic, and social domains. Daily general news publications benefit from habitual readership patterns, making them the preferred platform for both national and local advertisers. Government notifications, political coverage, and public-interest reporting further reinforce their dominance, particularly in emerging economies where newspapers remain the most trusted information source.
Business and financial newspapers represent a smaller but strategically important segment, characterized by higher average revenue per reader. This segment is supported by institutional subscriptions, corporate readership, and premium advertising from financial services, consulting, and technology firms. While circulation volumes are lower compared to general news newspapers, pricing power and subscription-led revenue models enhance profitability.
Distribution Format Insights
Print newspapers remain the dominant distribution format, contributing approximately 68% of the global market value in 2024. The continued leadership of print is driven by entrenched reading habits, credibility advantages, and legal mandates in many countries that require print publication of government notices and tenders. Print formats also maintain strong appeal among older demographics and rural populations, where digital access remains limited or inconsistent.
Digital replica newspapers, including PDF-based e-papers, are witnessing steady growth, particularly among urban professionals, institutional readers, and international audiences. These formats allow publishers to extend geographic reach while significantly reducing printing and logistics costs. Digital replicas also support archival access and corporate subscriptions, making them attractive to educational institutions and businesses.
End-Use Insights
Households represent the largest end-use segment in the newspapers market, supported by long-standing daily readership habits and subscription-based consumption. In many regions, newspapers remain a primary source of local news, public affairs, and educational content, particularly among middle-aged and senior demographics. Government bodies and public institutions form the fastest-growing end-use segment, driven by statutory advertising requirements, public information dissemination, election-related communication, and infrastructure project disclosures. Governments continue to rely on newspapers for transparency and regulatory compliance, providing publishers with stable, non-cyclical revenue streams.
Educational institutions and corporate entities contribute a steady demand through bulk subscriptions, research usage, and archival access. Universities, libraries, and corporate offices value newspapers for historical reference, policy analysis, and media monitoring. While growth in this segment is moderate, it offers predictable demand and long-term contracts, supporting revenue stability.
| By Content Type | By Distribution Format | By End Use | By Geography |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific leads the global newspapers market with approximately 38% share in 2024, making it the largest regional contributor by both value and circulation volume. India, China, and Japan dominate the regional landscape, supported by large populations, rising literacy rates, and deeply entrenched vernacular newspaper ecosystems. India alone accounts for nearly 17% of global market value, driven by strong regional-language penetration, affordable pricing, and robust government advertising. Key growth drivers in Asia-Pacific include expanding rural and semi-urban readership, high trust in print media, and the continued importance of newspapers for political engagement and public communication. Local advertisers and SMEs heavily rely on newspapers for outreach, further reinforcing demand across regional markets.
North America
North America accounts for approximately 21% of the global newspapers market, led primarily by the United States. The region is experiencing a faster structural decline due to widespread digital substitution and shifting advertising budgets toward online platforms. However, demand is partially offset by strong institutional subscriptions, premium journalism models, and paywalled content strategies adopted by leading publishers. Regional stability is supported by high-value readership segments, strong corporate and academic demand, and continued reliance on newspapers for legal disclosures and public notices. Consolidation and cost optimization initiatives are also helping publishers maintain profitability despite volume declines.
Europe
Europe holds approximately 24% of the global market share, with Germany, the U.K., and France as the principal contributors. The region benefits from strong public trust in established news brands, consistent government advertising, and regulatory frameworks that mandate print disclosures. Although private-sector advertising is gradually declining, Europe’s newspapers market remains relatively stable due to subscription-led revenue models, public broadcasting partnerships, and continued readership among older demographics. High-quality journalism and national political coverage remain key demand drivers across Western and Northern Europe.
Latin America
Latin America represents about 9% of the global market value, led by Brazil and Mexico. Newspaper demand in the region is supported by urbanization, political engagement, and a strong culture of national daily readership. Newspapers continue to play a critical role in political discourse, election coverage, and public accountability. Economic volatility and uneven digital penetration sustain reliance on print media, particularly for national and regional dailies. Government advertising and public-sector communication remain important demand drivers across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa account for approximately 8% of the global newspapers market and represent the fastest-growing region in relative terms. Nigeria, South Africa, Egypt, and GCC countries are key demand centers, supported by population growth, rising literacy, and expanding urban middle classes. Growth in this region is driven by increasing political participation, government-led information campaigns, and limited digital infrastructure in certain markets. Newspapers continue to serve as a trusted medium for public announcements, education, and national discourse, positioning the region as a long-term growth opportunity despite its smaller current market share.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Top Companies in the Newspapers Industry
- News Corp
- Gannett Co., Inc.
- The New York Times Company
- Daily Mail and General Trust
- Schibsted ASA
- Nikkei Inc.
- Axel Springer SE
- Grupo Globo
- Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd.
- Fairfax Media
- Sanoma Group
- PRISA Group
- Asahi Shimbun Company
- Mainichi Newspapers
- China Daily Group