Moving Services Market Size
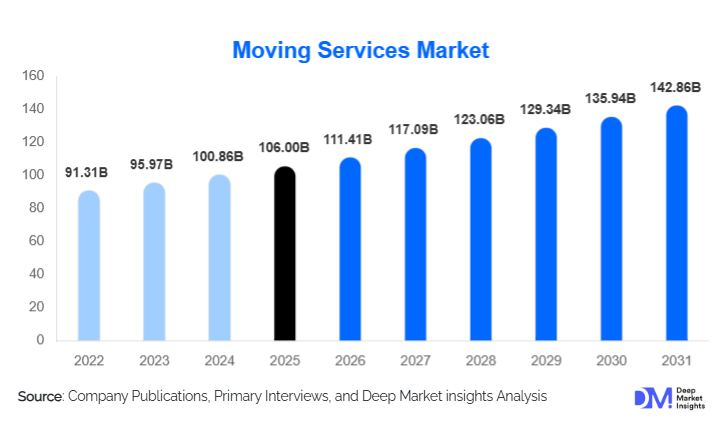
According to Deep Market Insights, the global moving services market size was valued at USD 106.00 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 111.41 billion in 2025 to reach USD 142.86 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 5.1% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The moving services market growth is primarily driven by rising urbanization, increasing residential and corporate mobility, expansion of global workforce relocation, and the growing adoption of value-added services such as packing, storage, and insurance-backed moves.
Key Market Insights
- Residential household moving services dominate global demand, driven by urban rental mobility, housing transitions, and short lease cycles.
- Corporate and industrial relocations are the fastest-growing revenue segments, supported by office consolidation, manufacturing shifts, and supply chain restructuring.
- North America leads the global market, with the U.S. accounting for the highest share due to interstate migration and enterprise relocations.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by urban expansion, infrastructure development, and rising middle-class mobility.
- International moving services generate the highest average revenue per move, owing to customs handling, insurance, and storage requirements.
- Digital booking platforms and fleet optimization technologies are reshaping operational efficiency and customer experience.
What are the latest trends in the moving services market?
Technology-Enabled Moving Solutions
Technology adoption is transforming the moving services industry through AI-driven route optimization, GPS-enabled fleet tracking, and digital booking platforms. Companies are investing in proprietary customer portals that allow real-time pricing, scheduling, and move tracking. IoT-enabled inventory management reduces damage claims and improves operational transparency, while CRM-driven engagement enhances customer retention. These innovations are particularly important for large enterprises managing multi-location relocations and for residential customers demanding predictable pricing and timelines.
Rising Demand for Bundled Value-Added Services
Customers increasingly prefer end-to-end relocation solutions that combine packing, unpacking, storage, insurance, and specialty item handling under a single contract. Bundled services reduce coordination complexity and improve cost predictability. Storage-as-a-service offerings are gaining traction in urban markets where temporary housing gaps are common. Premium services such as pet relocation, vehicle transport, and white-glove handling of high-value goods are also expanding, particularly in international and corporate moves.
What are the key drivers in the moving services market?
Urbanization and Residential Mobility
Rapid urbanization and changing housing preferences are driving frequent residential moves. Younger working populations increasingly shift between cities for employment opportunities, while urban rental markets encourage shorter tenancy durations. This trend sustains high-volume demand for local and interstate moving services, particularly in North America, Europe, and emerging Asian cities.
Expansion of Corporate and Industrial Relocation
Global enterprises are consolidating offices, relocating headquarters, and shifting manufacturing bases to optimize costs and supply chains. These activities generate sustained demand for commercial office moves and heavy equipment relocation. Industrial moves, though fewer in number, contribute disproportionately to revenue due to higher service complexity, regulatory compliance, and project-based contracts.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Rising Labor and Fuel Costs
The moving services market is highly sensitive to labor availability and fuel price volatility. Skilled labor shortages and rising wages increase operating costs, while fuel price fluctuations directly impact transportation expenses. Smaller players often struggle to absorb these costs, leading to pricing pressure and margin volatility.
Fragmented Regulatory Landscape
Licensing requirements, insurance mandates, and customs regulations vary widely across regions and countries. For international moves, compliance complexity increases operational risk and cost. Regulatory fragmentation acts as a barrier to seamless global expansion for moving service providers.
What are the key opportunities in the moving services industry?
Corporate Mobility Management Programs
Enterprises increasingly outsource employee relocation and mobility management to specialized moving service providers. Long-term corporate contracts offer stable revenue, higher margins, and cross-selling opportunities for storage, immigration assistance, and insurance services. This segment presents strong growth potential for organized players with global networks.
Emerging Market Penetration
Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and parts of Africa present untapped opportunities due to rapid urban development and infrastructure expansion. Formalizing moving services in traditionally unorganized markets through branded offerings and standardized pricing can unlock significant growth for new entrants and global players alike.
Service Type Insights
Household residential moving services account for approximately 42% of the global moving services market revenue in 2024, making it the leading service type globally. This dominance is primarily driven by high residential mobility rates, urban rental housing expansion, shorter lease tenures, and rising job-related relocations across metropolitan areas. Growing preference for professional movers over informal services, particularly in developed economies, further strengthens this segment’s leadership. Commercial and office relocation services contribute around 28% of total market revenue, supported by enterprise restructuring, office consolidation, hybrid work transitions, and expansion of co-working spaces. Large corporations increasingly outsource office moves to minimize downtime and ensure compliance with asset handling and data security standards, sustaining demand for specialized commercial movers.
Industrial and heavy equipment moving services represent approximately 18% of the market and generate disproportionately higher margins. Growth in this segment is driven by manufacturing plant relocations, infrastructure projects, data center construction, and supply chain reconfiguration. These moves require specialized equipment, regulatory compliance, and project management expertise, making them less price-sensitive and more value-driven. Specialty item moving services, including artwork, antiques, vehicles, medical equipment, and pianos, account for the remaining market share. This segment benefits from premium pricing, rising high-net-worth populations, growth in art logistics, and increasing demand for insured, white-glove relocation services.
Move Distance Insights
Interstate moving services dominate the market with nearly 36% share in 2024, emerging as the leading distance-based segment. This leadership is driven by employment-led migration, corporate transfers, housing affordability shifts, and demographic movements from high-cost urban centers to secondary cities. Interstate moves typically involve higher service value due to longer distances, storage requirements, and bundled offerings.
Local moving services account for around 33% of global revenue, supported by frequent intra-city residential moves, rental housing churn, student migration, and small business relocations. This segment benefits from consistent volume, particularly in densely populated urban regions. International moving services, while lower in transaction volume, generate over 21% of total market revenue due to higher complexity and pricing. Growth is fueled by global workforce mobility, expatriate employment, international education, and diplomatic postings. Customs handling, insurance, and long-term storage significantly increase per-move revenue. Intrastate moving services represent the remaining share, supported by regional job changes, internal migration, and state-level economic development programs.
Customer Type Insights
Individual consumers constitute the largest customer segment, accounting for approximately 48% of total market demand in 2024. High move frequency, urban lifestyle changes, and increased adoption of professional services over informal movers continue to drive this segment’s dominance. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) contribute around 22% of market revenue, driven by office expansions, retail relocations, and warehouse moves. SMEs increasingly prefer organized moving service providers to ensure business continuity and asset protection.
Large enterprises and multinational corporations account for nearly 20% of total revenue, despite lower move volumes. This segment generates high-value contracts through employee relocation programs, office campus moves, and international transfers, often bundled with long-term storage and mobility management services. Government and public sector customers represent a smaller but stable segment, supported by institutional relocations, defense logistics, public infrastructure projects, and administrative restructuring.
| By Service Type | By Move Distance | By Customer Type | By Property Type | By Value-Added Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for approximately 34% of global moving services revenue in 2024, maintaining its position as the largest regional market. The United States leads regional demand due to high interstate migration, strong housing market activity, and widespread adoption of professional moving services. Corporate relocations, military transfers, and premium residential moves significantly contribute to market value. Canada supports steady growth through urban housing mobility, immigration-driven relocations, and cross-border corporate movement between the U.S. and Canada.
Europe
Europe represents about 22% of the global market, with strong demand across Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and the Netherlands. Growth is driven by cross-border labor mobility within the European Union, corporate restructuring, and increasing demand for regulated, insured moving services. Sustainability-driven logistics practices, strict labor regulations, and high consumer preference for organized movers are shaping service standards and supporting long-term market stability.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific holds nearly 29% of the global market share and is the fastest-growing region, with a CAGR exceeding 7% during the forecast period. China and India dominate regional demand due to rapid urbanization, large-scale infrastructure development, industrial relocation, and expanding middle-class housing mobility. Japan and Australia contribute through premium residential, corporate, and international relocations. Increasing formalization of the logistics sector and rising adoption of professional movers are key growth drivers.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for approximately 7% of global demand, led by Brazil and Mexico. Urban housing development, industrial expansion, and growing foreign investment are supporting market growth. However, high market fragmentation and the prevalence of informal movers limit organized sector penetration, presenting long-term consolidation opportunities.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region contributes around 8% of the global market. Demand in the Middle East is driven by expatriate workforce mobility, large-scale construction projects, and economic diversification initiatives in countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia. In Africa, industrial development, mining projects, and infrastructure investments are increasing demand for industrial and commercial moving services, while residential mobility is gradually formalizing in urban centers.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Top Companies in the Moving Services Market
- United Van Lines
- Allied Van Lines
- Mayflower Transit
- Atlas Van Lines
- North American Van Lines
- Crown Worldwide Group
- SIRVA
- Graebel Companies
- Bekins Van Lines
- Arpin Van Lines
- Pickfords
- Two Men and a Truck
- AGS Movers
- Santa Fe Relocation
- Conroy Moving & Storage