In-Car Wireless Charging Market Size
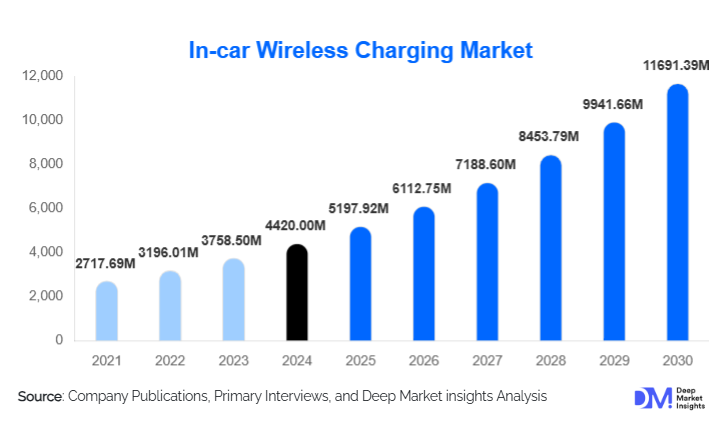
According to Deep Market Insights, the global in-car wireless charging market size was valued at USD 4,420.00 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 5,197.92 million in 2025 to reach USD 11,691.39 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 17.60% during the forecast period (2025–2030). Market growth is fueled by a surge in demand for cable-free convenience inside passenger vehicles, rapid OEM adoption of factory-integrated wireless charging pads, the rise of EVs and connected cars, and strong consumer preference for seamless smartphone integration within the vehicle ecosystem.
Key Market Insights
- Inductive wireless charging dominates global installations, driven by technology maturity, lower cost, and wide OEM adoption.
- OEM-integrated wireless chargers account for over half of global revenues, supported by increasing inclusion in mid-range and premium vehicles.
- Passenger vehicles contribute more than 70% of total market demand, aligning with global automotive production trends.
- Asia-Pacific leads the market with 40–45% share, driven by high vehicle production in China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
- Aftermarket wireless chargers are booming in price-sensitive regions with large older vehicle fleets.
- Technology advancements in coil efficiency, magnetic resonance, and alignment tolerance are improving performance and consumer adoption.
What are the latest trends in the In-car Wireless Charging Market?
OEM Integration Accelerates as Wireless Charging Becomes a Standard Car Feature
Automakers increasingly view wireless charging as a must-have convenience feature, integrating Qi-compatible charging pads across mid-range and premium vehicle models. Many OEMs are now positioning wireless charging as part of their infotainment and connected-car packages, bundling it with advanced telematics and smartphone mirroring solutions. This trend is reshaping the cabin experience as automakers shift toward cable-free interiors, ergonomic center consoles, and enhanced human-machine interfaces (HMI). The expansion of EVs is also stimulating integration, as wireless charging aligns with the digital-first design philosophy common in electric vehicles.
Magnetic Resonance and High-Efficiency Systems Gain Traction
While inductive charging remains dominant, magnetic resonance technologies are emerging due to their ability to charge through varying phone alignments and thicker casings. OEM R&D spending is rising toward high-efficiency, high-wattage systems capable of powering multiple devices simultaneously. Advanced coil designs, thermal management improvements, and improved EMI shielding are resulting in safer and more reliable systems. The trend is also penetrating the aftermarket, where premium accessory brands are offering resonant-charging retrofits for luxury and older vehicles.
What are the key drivers in the In-car Wireless Charging Market?
Increasing Consumer Demand for Convenience and Cable-Free Functionality
Consumers now expect wireless charging as a standard feature in both personal and shared mobility vehicles. The rising dependency on smartphones for navigation, infotainment, payments, and productivity enhances the need for continuous charging without cable clutter. Wireless charging pads offer an elegant, reliable, and safe alternative to wired ports, which often suffer from wear and tear. With smartphone makers globally standardizing wireless charging capabilities, in-car adoption is accelerating rapidly.
Automotive OEM Feature Upgrades and Premiumization
As automakers compete on technology differentiation, wireless charging is becoming a core value-added feature. Vehicle models launching post-2024 increasingly bundle wireless charging with digital dashboards, voice assistants, and connected infotainment systems. In premium vehicles, multi-device charging pads, integrated cooling solutions, and smart charging indicators are becoming standard. OEMs see wireless charging integration as a low-cost, high-impact upgrade that enhances perceived vehicle value.
Rapid Proliferation of Smartphones and Connected Mobility
Smartphone penetration exceeding 80% in many regions drives demand for convenient charging on the move. As mobility services like ride-hailing and corporate fleets expand, wireless charging offers greater device availability for drivers and passengers. Connected mobility ecosystems, including telematics and mobile payment platforms, rely on smartphones being continuously powered, making in-car wireless charging a functional necessity.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Production and Retrofit Costs
Despite growing adoption, in-car wireless charging systems remain costlier than traditional wired ports. OEM integration increases production cost due to coil assemblies, shielding materials, safety components, and software validation. Aftermarket kits are also often priced at a premium, making adoption difficult in price-sensitive markets. These cost barriers limit widespread penetration in entry-level vehicles.
Compatibility Limitations and Lack of Universal Standards
While Qi has emerged as the dominant global charging standard, automotive implementations vary by OEM. Misalignment issues, variable output wattage, and differences in thermal performance across models create user dissatisfaction. The lack of a unified automotive wireless-charging standard slows ecosystem development and complicates integration for multi-device users and fleet operators.
What are the key opportunities in the In-car Wireless Charging Industry?
Connected-Car and EV Ecosystem Integration
Wireless charging aligns perfectly with the digital interiors of next-generation vehicles. EV adoption is amplifying this opportunity: drivers increasingly rely on smartphone applications to manage charging sessions, navigation, and vehicle diagnostics. OEMs can combine in-car wireless charging with AI-driven HMI systems, driver-monitoring systems, and advanced infotainment platforms. Future designs may integrate wireless charging directly into armrests, dashboards, and multi-device trays.
Aftermarket Expansion in Emerging Markets
Millions of vehicles in APAC, LATAM, and MEA lack factory-installed charging systems, creating an enormous retrofit opportunity. Affordable aftermarket pads and universal mounts cater to consumers seeking modern features without buying a new car. As smartphone penetration continues to rise in India, Southeast Asia, Brazil, and Africa, demand for aftermarket wireless charging accessories is expected to surge, supported by strong e-commerce channels and cross-border accessory trade.
Fleet and Ride-Hailing Adoption
Ride-hailing companies, taxis, commercial fleets, and corporate mobility providers increasingly prioritize vehicle convenience features that enhance driver productivity and passenger satisfaction. Wireless charging reduces wear on USB ports and eliminates charging disputes in shared-mobility environments. For fleet operators, wireless charging enhances operational efficiency and can serve as a differentiating premium service.
Product Type Insights
OEM-integrated wireless charging systems dominate global revenues, driven by widespread inclusion in new passenger vehicle models, accounting for roughly 50–55% of the market. These systems offer superior aesthetics, safety, and integration with infotainment systems. Aftermarket wireless chargers continue gaining traction in developing economies, offering lower-cost access to wireless features and appealing to consumers with older vehicles. Innovations such as magnetic-resonance retrofits and multi-coil pads are pushing the aftermarket segment into a higher-value space.
Application Insights
Personal vehicle usage represents the bulk of wireless charging installations, contributing over 60% of total demand. Fleet vehicles, including ride-hailing cars and delivery vans, account for a rapidly expanding segment. These applications prioritize convenience, device uptime, and reduced wear on charging ports, critical factors for drivers who rely heavily on smartphones for navigation, tracking, and communication. Commercial vehicle adoption is still nascent but expected to grow steadily as fleet electrification increases.
Distribution Channel Insights
The OEM channel dominates due to factory-installed systems in new vehicles. However, the aftermarket channel is growing faster as consumers in emerging markets retrofit older cars with wireless charging pads. Online retail platforms play a major role in distributing aftermarket products, while brick-and-mortar auto accessory stores remain vital in Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America. Premium aftermarket brands are adopting direct-to-consumer (D2C) strategies with modular designs and model-specific fitments.
End-User Insights
Individual car owners form the largest consumer base, driven by lifestyle upgrades and increased smartphone usage. Shared mobility operators, such as Uber, Lyft, Grab, and Ola, are emerging high-value buyers, prioritizing wireless charging as a competitive passenger convenience feature. Corporate fleets are showing rising demand for integrated wireless charging solutions to support mobile productivity for traveling employees. Delivery and logistics fleets may adopt wireless charging for driver device uptime, although adoption is currently limited.
| By Technology Type | By Product Type | By Vehicle Type | By Application | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America holds around 20–25% of the market. Strong consumer preference for premium automotive features, high smartphone usage, and the proliferation of connected-car systems drive regional demand. The U.S. leads adoption, with wireless charging increasingly offered in mid-range SUVs, sedans, and EVs. Aftermarket adoption is also strong due to a large existing vehicle fleet.
Europe
Europe accounts for 15–20% of global demand. Germany, the UK, and France lead adoption due to strong premium car sales and early integration by leading European automakers. Strict safety and electromagnetic compliance regulations accelerate standardization and quality improvements. Europe’s growing EV ecosystem further boosts the adoption of convenience features like wireless charging.
Asia-Pacific
With a dominant 40–45% share, APAC is the largest and fastest-growing region. China leads global production of both vehicles and aftermarket accessories, while India is experiencing rapid growth in budget and mid-range vehicle upgrades. Japan and South Korea, home to major automakers, continue to set benchmarks for OEM integration. APAC’s rising urbanization and smartphone penetration amplify demand for in-car wireless solutions.
Latin America
LATAM accounts for roughly 3–5% of the global market. Brazil and Mexico show rising adoption through aftermarket channels. Growth is supported by increasing vehicle ownership and expanding e-commerce networks, distributing wireless charging accessories.
Middle East & Africa
MEA represents a small but rapidly expanding share of 5–7%. High-end vehicle ownership in GCC countries fuels OEM integration, while Africa's expanding used-car market boosts demand for aftermarket charging pads. Increasing smartphone usage across the region ensures long-term growth potential.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the In-Car Wireless Charging Market
- Hella GmbH
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Panasonic Automotive
- Samsung Electronics (Wireless Charging Components Division)
- Yazaki Corporation
- TE Connectivity
- Infineon Technologies
- Aircharge Automotive
- Laird Connectivity
- Belkin
- Zens Automotive
- ConvenientPower
- Leggett & Platt Automotive
- Mophie
- Shenzhen Baseus Technology
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Bosch Automotive launched a next-generation Qi-compatible charging module with 30% improved efficiency and integrated thermal control for EV interiors.
- In January 2025, Panasonic Automotive partnered with a leading Japanese automaker to integrate multi-device wireless charging trays in upcoming 2026 models.
- In June 2024, Aircharge Automotive introduced a magnetic-resonance aftermarket charging pad designed for trucks and commercial fleets.