Groceries Transportation Market Size
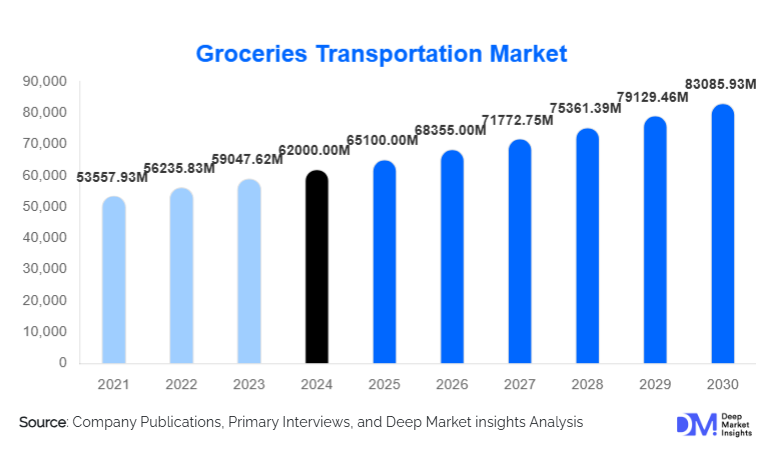
According to Deep Market Insights, the global groceries transportation market size was valued at USD 62,000.00 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 65,100.00 million in 2025 to reach USD 83,085.93 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 5.0% during the forecast period (2025–2030). Growth in the groceries transportation market is primarily driven by rising online grocery penetration, increasing demand for fresh and perishable food items, rapid cold-chain expansion, and the evolution of multi-modal logistics networks supporting retail and e-commerce fulfillment.
Key Market Insights
- Road-based logistics dominate the groceries transportation ecosystem, representing the majority of last-mile and mid-mile shipments across developed and emerging markets.
- Fresh produce (fruits & vegetables) is the largest transported grocery category, accounting for the highest logistics volume due to perishability and daily replenishment cycles.
- Online grocery delivery is the fastest-growing channel globally, driven by urban demand, digital adoption, and the rapid expansion of hyperlocal fulfillment networks.
- Cold-chain infrastructure investment is accelerating, enabling safer long-distance transport of dairy, meat, seafood, and frozen goods.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and expanding organized retail.
- Technology adoption, IoT tracking, AI routing, and temperature-controlled fleet upgrades are transforming transport reliability and cost-efficiency.
What are the latest trends in the groceries transportation market?
Cold-Chain Modernization Accelerating Across Regions
Cold-chain expansion has become a top priority for retailers, logistics operators, and governments due to rising consumption of perishables such as dairy, meat, seafood, and fresh produce. Companies are deploying advanced refrigerated fleets, multi-temperature vehicles, and automated cold storage to reduce spoilage rates and improve food safety compliance. IoT-enabled temperature monitoring systems are increasingly used to track conditions in real time, minimizing risk and enabling traceability across the supply chain. Governments in emerging markets are supporting cold-chain development through subsidies, infrastructure programs, and public-private partnerships, significantly improving regional capacity. This trend is reshaping long-haul, regional, and last-mile grocery logistics.
Digitization & Real-Time Visibility Transforming Operations
Digital transformation is reshaping groceries transportation through smart logistics tools such as AI-powered route optimization, blockchain-enabled traceability, digital freight platforms, and automated demand forecasting. Retailers and logistics providers now rely on real-time tracking dashboards to monitor delivery times, temperature compliance, vehicle utilization, and driver performance. Fleet telematics combined with predictive analytics helps reduce fuel consumption, improve reliability, and optimize vehicle scheduling. E-commerce grocery fulfillment centers are leveraging robotics, micro-fulfillment systems, and automated inventory management, significantly reducing lead times and increasing order accuracy.
What are the key drivers in the groceries transportation market?
Explosive Growth in Online Grocery Shopping
The surge in global online grocery demand, driven by convenience, rapid delivery expectations, and expanding digital ecosystems, has dramatically increased the need for reliable mid-mile and last-mile grocery transportation. Hyperlocal delivery models, dark stores, and micro-fulfillment centers require frequent replenishment, accelerating logistics activity. Retailers are adopting express delivery models with 30–90-minute service windows, raising the importance of efficient fleet management, temperature control, and real-time inventory synchronization.
Rising Consumption of Fresh & Perishable Foods
Consumers worldwide increasingly prefer fresh produce, refrigerated dairy, and minimally processed foods. This trend requires temperature-controlled transportation, faster turnaround times, and stringent food safety compliance. Fresh fruits and vegetables alone represent 30–35% of all grocery transport value, underscoring their importance in shaping logistics demand. Retailers and producers are investing heavily in perishables logistics to meet quality expectations and reduce waste.
Expansion of Organized Retail & Cross-Border Food Trade
Supermarket chains, specialty grocers, and FMCG retailers continue to expand regionally and internationally, driving substantial demand for multimodal grocery transportation. Growth in cross-border trade for fresh produce, seafood, and packaged foods, particularly between Asia, Europe, and the Middle East, requires advanced refrigerated sea and air freight solutions. Improved trade corridors, FTAs, and modern distribution hubs contribute to rising logistics volumes.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Costs of Cold-Chain Infrastructure & Fleet Modernization
Cold-chain development, including refrigerated vehicles, temperature-controlled warehouses, and compliance systems, requires significant upfront investment. High operational costs, fuel usage, and maintenance expenses increase barriers for new entrants and small logistics companies. In emerging markets, fragmented supply chains further raise operating costs and reduce scalability.
Regulatory Compliance, Spoilage Risk & Operational Complexity
Strict food safety laws, temperature mandates, and international sanitary requirements require careful monitoring and documentation throughout the transport cycle. Non-compliance can lead to costly product losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage. Perishability adds operational complexity, making scheduling, routing, and load balancing more challenging than in standard freight transport.
What are the key opportunities in the groceries transportation industry?
E-commerce Grocery Logistics & Hyperlocal Delivery Expansion
Hyperlocal grocery delivery has emerged as one of the biggest opportunities in the logistics sector. On-demand grocery delivery models require fast-moving, tech-enabled fleets and micro-fulfillment infrastructure. Logistics players can partner with e-commerce platforms or launch dedicated perishable delivery services to capture this fast-growing segment. Urban regions with high digital adoption and dense populations offer particularly strong growth potential.
Cold-Chain Network Growth in Emerging Markets
Developing regions across Asia, Africa, and Latin America lack adequate refrigerated fleet density and temperature-controlled warehousing. This infrastructure gap creates substantial room for investment in modern cold-chain solutions. Companies that expand vertically into cold storage, reefer transport, and food handling services can secure long-term contracts with retailers and exporters. Government-backed initiatives to reduce food waste are further accelerating cold-chain adoption.
Technology-Driven Efficiency, Automation & Predictive Logistics
IoT sensors, predictive analytics, digital freight platforms, and AI-based planning tools provide opportunities for logistics companies to reduce costs and improve reliability. Automation in warehouses, robotics for item picking, and blockchain-based transparency solutions can significantly enhance service quality. Technology investment, once a differentiator, is rapidly becoming a requirement for competing in the high-growth, perishables-driven grocery transport segment.
Product Type Insights
Fresh fruits and vegetables dominate the product-type segment, representing around 30–35% of the market’s transportation value in 2024. Their high perishability, daily replenishment cycles, and volume demand make them the most frequently transported grocery items. Dairy products and meat/seafood follow, driven by rising consumption of protein-rich diets and growing cold-chain capacity. Non-perishable grocery items, such as packaged foods and beverages, continue to grow steadily, but at lower transportation intensity compared to perishables.
Transportation Mode Insights
Roadways lead the transportation mode segment, accounting for 60–65% of the global market in 2024. Road transport is essential for last-mile delivery, regional distribution, and short-haul movement from warehouses to retail stores. Refrigerated trucks, mini-reefers, and two-wheeler cold boxes for hyperlocal delivery are seeing rapid adoption. Sea freight remains crucial for the cross-border movement of seafood, frozen foods, and bulk items, while air freight is used selectively for high-value perishables requiring rapid transit.
Distribution Channel Insights
Online grocery retail is the fastest-growing distribution channel, accounting for nearly 25–30% of grocery transportation value in 2024. E-commerce companies increasingly rely on dark stores, cloud warehouses, and micro-fulfillment centers, dramatically increasing delivery frequency and fleet utilization. Traditional supermarkets and hypermarkets still dominate the overall share but are adopting omnichannel strategies to compete.
Application Insights
Retail applications dominate the market, contributing approximately 50–55% of overall revenues in 2024. Grocery chains, convenience stores, and online delivery platforms require continuous replenishment, creating recurring demand. Foodservice operators, restaurants, hotels, QSRs, and institutional kitchens represent a rapidly growing application segment, driven by expanding dine-out culture and centralized kitchen operations.
| By Product Type | By Transportation Mode | By Distribution Channel | By Application |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for the largest share of the groceries transportation market, representing about 30–35% in 2024. The U.S. leads demand due to its advanced retail ecosystem, high per-capita grocery consumption, and rapid adoption of online grocery delivery. Cold-chain infrastructure is well established, enabling efficient long-distance movement of dairy, meat, and fresh produce. Canada contributes steadily with rising demand for fresh imports and cross-border logistics integration.
Europe
Europe contributes 20–25% of the global share, supported by strict food safety regulations, a dense supermarket network, and high standards for cold-chain compliance. Countries like Germany, France, the U.K., Italy, and the Netherlands are core markets. Sustainability initiatives, electric fleets, carbon-neutral logistics, and circular packaging are shaping procurement decisions across retailers and logistics operators.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, capturing roughly 25–30% of the market in 2024. China and India lead demand, driven by urbanization, rising incomes, and rapid adoption of online grocery platforms. Southeast Asian markets, including Indonesia, Vietnam, and Thailand, are experiencing strong growth as modern retail expands. Australia and Japan maintain stable, high-efficiency grocery logistics networks with increasing automation and fleet modernization.
Latin America
Latin America is an emerging region for groceries transportation, with demand growing steadily across Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. Urban expansion, rising supermarket penetration, and increasing import dependency for certain perishables are driving logistics volume. Infrastructure gaps in cold-chain development present challenges but also major investment opportunities.
Middle East & Africa
MEA is experiencing rising demand for grocery transport due to heavy import reliance, expanding supermarket chains, and rapid urban population growth. Gulf nations like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar have advanced cold-chain systems and high per-capita consumption of imported foods. African nations, particularly Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa, show strong growth potential as governments invest in food security, cold-chain corridors, and modern retail.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Top Players in the Groceries Transportation Market
- DHL Supply Chain
- Kuehne + Nagel
- C.H. Robinson
- XPO Logistics
- Nippon Express
- DB Schenker
- Maersk Logistics
- Americold Logistics
- Lineage Logistics
- FedEx Supply Chain
- UPS Supply Chain Solutions
- GEFCO
- CEVA Logistics
- DSV
- Yusen Logistics
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Maersk Logistics expanded its temperature-controlled warehousing network in Southeast Asia to support growing cross-border produce shipments.
- In January 2025, DHL Supply Chain launched an AI-powered route optimization platform to reduce fuel consumption in grocery delivery fleets.
- In November 2024, Americold announced new cold-storage facilities in Mexico and the UAE to support rising demand for perishable food imports.