Electronic Dictionary Market Size
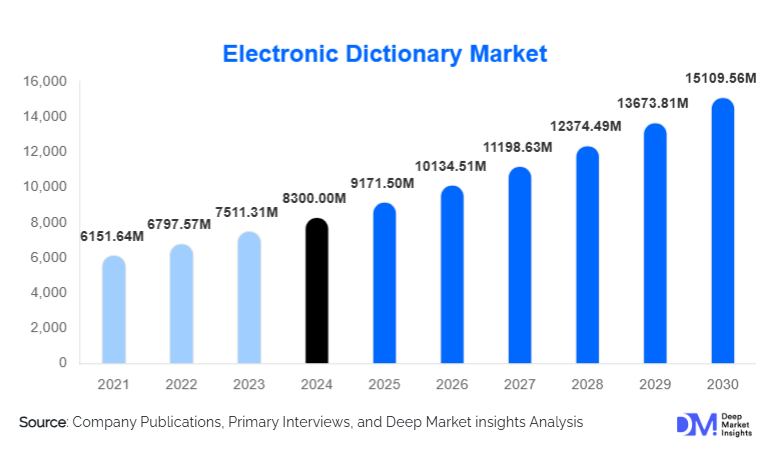
According to Deep Market Insights, the global electronic dictionary market size was valued at USD 8,300.00 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 9,171.50 million in 2025 to reach USD 15,109.56 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 10.5% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The electronic dictionary market growth is primarily driven by increasing digital education adoption, the rising need for multilingual communication, the proliferation of smartphone-based dictionary apps, and the growing demand for AI-powered translation and learning tools.
Key Market Insights
- Mobile and app-based dictionaries dominate global usage, supported by rising smartphone penetration and demand for real-time, on-the-go language assistance.
- Bilingual dictionaries account for nearly half of global revenue, driven by strong student and professional demand for English–foreign language translation pairs.
- Asia-Pacific leads the global electronic dictionary market, with China, Japan, South Korea, and India representing the largest user bases.
- North America remains a high-value market due to professional demand, immigrant language-learning needs, and strong digital adoption.
- AI-enabled pronunciation, voice recognition, and offline access are transforming product innovation and user engagement.
- Educational institutions and e-learning platforms increasingly integrate digital dictionaries into language-learning curricula and professional upskilling programs.
What are the latest trends in the electronic dictionary market?
AI-Powered Language Learning and Contextual Translation
Artificial intelligence is reshaping the electronic dictionary landscape. Modern dictionaries now integrate machine learning algorithms that enable contextual translation, adaptive vocabulary training, and real-time pronunciation correction. Voice recognition technology allows users to speak into devices or apps, instantly retrieving definitions, translations, and usage examples. AI-powered systems provide personalized learning paths, helping students and language learners improve retention and comprehension. These advancements are transforming dictionaries from simple lookup tools into comprehensive language-learning companions. The integration of AI also supports professional use cases in business communication, corporate training, and global remote work environments.
Shift from Hardware Devices to Mobile and Cloud-Based Platforms
Traditional handheld dictionary devices are gradually being replaced by app-based platforms and cloud-enabled dictionaries. Mobile applications now contribute nearly 40% of market revenue, driven by widespread smartphone adoption and the convenience of constant accessibility. Cloud-based dictionaries sync user data, track learning progress, and deliver cross-device functionality, making them appealing to students, travelers, and professionals. Frequent content updates, expanded vocabulary databases, and support for multiple languages further enhance usability. This trend is accelerating as hardware manufacturers pivot toward hybrid software models and subscription-based digital learning ecosystems.
What are the key drivers in the electronic dictionary market?
Growing Digital Education and E-Learning Penetration
Educational institutions worldwide are rapidly integrating digital tools into language curricula. Students increasingly rely on dictionary apps and software platforms for vocabulary building, translation support, and exam preparation. The surge in online courses and remote learning during recent years has amplified this shift, making electronic dictionaries essential components of modern classrooms. Schools and universities also license digital dictionaries for large groups, providing manufacturers with high-volume opportunities.
Globalization and Multilingual Communication Needs
As global trade expands, immigration grows, and remote work becomes widespread, demand for bilingual and multilingual dictionaries continues to rise. Professionals require accurate translation tools for business communication, while international travelers and expatriates depend on portable dictionary solutions for real-time language support. This trend is especially strong in Asia-Pacific, where English-learning initiatives in China, India, and Southeast Asia significantly boost market demand.
Technological Advancements in Speech, Voice, and Offline Access
Modern electronic dictionaries incorporate text-to-speech, speech recognition, offline translation databases, and grammar-learning modules. These features enhance usability for students and travelers, particularly in regions with limited internet connectivity. Offline dictionaries with multi-language support and pronunciation guides are becoming essential tools for cross-border mobility. As technology improves, device capabilities expand, making electronic dictionaries indispensable across educational and professional environments.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Proliferation of Free Online Dictionaries and Translation Tools
A major challenge for the electronic dictionary market is the widespread availability of free or low-cost alternatives, such as web-based translation platforms and freemium mobile dictionary apps. These tools reduce the need for paid hardware or premium app subscriptions, particularly among casual users and students. As online resources improve in accuracy and feature depth, the competitive pressure on paid solutions intensifies, limiting growth potential for standalone dictionary devices.
Market Fragmentation and Low Entry Barriers
The market for dictionary apps is highly fragmented due to the ease of developing basic dictionary software. Numerous small companies and independent developers saturate app marketplaces with low-cost or free offerings. This fragmentation reduces pricing power for established brands and leads to margin pressure across the industry. For hardware devices, high manufacturing and distribution costs further challenge smaller players attempting to compete.
What are the key opportunities in the electronic dictionary industry?
AI-Integrated Language Learning Ecosystems
There is a major opportunity to integrate electronic dictionaries with broader AI-driven learning platforms. These ecosystems can combine grammar tools, interactive lessons, speech recognition, and personalized vocabulary training, offering end-to-end language mastery. Companies that invest in AI-based predictive learning and real-time language analytics can capture high-value students, institutions, and professional segments. Subscription models also provide strong recurring revenue potential.
Localized and Emerging-Market Language Expansion
Demand for bilingual and multilingual dictionaries in developing regions presents an attractive growth opportunity. Support for regional languages, such as Hindi, Tamil, Thai, Swahili, and Arabic, is still limited among global providers. Brands that expand localized content libraries can access large, underserved user bases. Governments promoting multilingual education in Asia and Africa further strengthen this opportunity.
Product Type Insights
Mobile and app-based dictionaries dominate the market, driven by their affordability, ease of access, and feature-rich interfaces. This segment accounts for nearly 40% of global revenue and continues to grow rapidly due to smartphone penetration and cloud connectivity. Dedicated handheld electronic dictionaries maintain relevance in regions like Japan and South Korea, where students prefer physical devices for exam preparation. Software-based dictionaries for PCs and laptops serve professional and academic users who require detailed linguistic datasets, technical vocabularies, or extended offline functionality. The continued rise of subscription-based learning apps is reshaping product portfolios, with companies focusing on hybrid models integrating dictionary functions with grammar, translation, and pronunciation tools.
Application Insights
Student usage remains the largest application area, accounting for an estimated 30–35% of global demand. Academic institutions, language-learning centers, and e-learning platforms increasingly rely on digital dictionaries for coursework support. Professional users, including translators, researchers, and global business workers, represent a stable and high-value segment requiring multilingual accuracy and advanced features such as AI-driven translation. Travelers and expatriates form another rapidly expanding group, benefiting from offline access and quick-translation tools. New applications are emerging in corporate training, language certification programs, and migrant integration services, broadening market relevance.
Distribution Channel Insights
Online distribution channels dominate the global landscape, accounting for 55–60% of total market revenue. App stores, e-commerce marketplaces, and direct-to-consumer digital platforms enable fast, scalable distribution. Offline retail remains significant for hardware devices, particularly in East Asia, where dedicated dictionary brands maintain a strong in-store presence. Subscription-based digital platforms are gaining traction as consumers shift toward monthly or annual licensing. Direct institutional sales, especially to schools and universities, represent a growing channel that offers predictable volume and long-term agreements.
End-User Insights
Students form the largest end-user group, influenced by rising digital education adoption and integration of language-learning tools in school curricula. Language learners, particularly adults engaging in self-study, represent a fast-growing demographic. Professionals increasingly rely on multilingual dictionaries for cross-border communication in globalized workplaces. Travelers and expatriates also drive notable demand, especially for offline-capable dictionary tools. Emerging end-users include multinational corporations implementing employee language training programs and governments offering digital resources for migrant populations.
| By Product Type | By Language Support | By Features | By End-User | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for approximately 20–25% of global revenue. Strong digital adoption, high smartphone penetration, and the presence of multicultural populations drive demand for bilingual and multilingual dictionaries. The U.S. leads the region due to extensive educational technology use and corporate demand for language-learning tools. Canada’s high immigrant population also sustains growth, particularly for English–foreign language pairs.
Europe
Europe represents 15–20% of the global electronic dictionary market, driven by high language-learning engagement and strong cross-border mobility. Countries such as Germany, France, and the U.K. exhibit significant demand across schools, universities, and professional sectors. Multilingual environments create strong use cases for dictionaries supporting English, French, German, and other European languages. The region’s emphasis on digital education continues to support market expansion.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific leads the global market with a 35–40% share. China, Japan, South Korea, and India are the largest contributors. High student populations, multilingual education policies, and widespread exam preparation cultures drive adoption. Japan and South Korea maintain strong preferences for dedicated handheld devices, while India and China show rapid adoption of mobile-based dictionary apps. APAC is also the fastest-growing region due to rising income levels and expanding digital literacy.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 5–8% share with growing demand in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. English-language learning is a significant trend, driven by globalization and higher education requirements. App-based dictionaries are particularly popular due to affordability and mobile-first digital behavior across the region.
Middle East & Africa
MEA accounts for 5–8% of global revenue. Demand is driven by educational modernization, workforce migration, and government-led digital learning initiatives. Gulf countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia exhibit strong uptake of premium language-learning tools. In Africa, multilingual education policies and growing smartphone access fuel the adoption of mobile dictionaries.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Company Market Share
The electronic dictionary market is moderately fragmented, with the top five companies collectively accounting for approximately 40–50% of global revenue. Hardware-focused companies dominate East Asia, while software and app developers maintain global reach via digital distribution. Market share distribution is shaped by product innovation, language database depth, and AI feature integration.
Key Players in the Electronic Dictionary Market
- Casio Computer Co. Ltd.
- ECTACO Inc.
- Sharp Corporation
- iFLYTEK Co. Ltd.
- Hanvon Technology Co. Ltd.
- Canon Inc.
- Vasco Electronics
- Merriam-Webster
- Besta (Ellton Enterprise)
- Alfa Link
- Collins Dictionary (HarperCollins)
- Oxford University Press (Digital Dictionaries)
- Langenscheidt Digital
- Cambridge University Press & Assessment (Digital Division)
- Lingvo (ABBYY)