Capsule Hotel Market Size
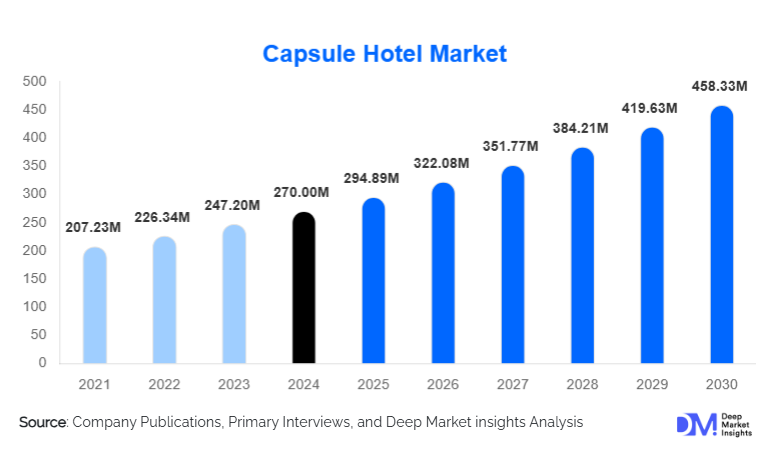
According to Deep Market Insights, the global capsule hotel market size was valued at USD 270.00 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 294.89 million in 2025 to reach USD 458.33 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 9.22% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The capsule hotel market growth is primarily driven by rising solo travel, increasing demand for affordable urban accommodation, expansion of pod-style properties across high-density cities, and the integration of smart technologies that enhance guest convenience and space efficiency.
Key Market Insights
- Single-capsule formats dominate the global market, accounting for nearly 55% of revenue due to high adoption among solo travelers and cost-sensitive consumers.
- Asia-Pacific leads the global market with over 58% share, supported by dense urban populations, high travel volumes, and cultural familiarity with compact living.
- Online booking channels are rapidly expanding, driven by digital adoption among Gen Z and millennials and the rise of mobile-first travel ecosystems.
- Urban real-estate constraints are accelerating capsule-hotel expansion, as developers favor high-density lodging formats to maximize yield per square foot.
- Remote work and digital nomadism are reshaping demand, creating new opportunities for hybrid “stay + workspace” capsule concepts.
- Technological integration, such as IoT-enabled pods, smart lockers, AI check-in, and app-based facility management, is becoming a core differentiator for operators.
What are the latest trends in the capsule hotel market?
Smart Capsule and Automation-Driven Guest Experience
Capsule hotel operators are increasingly adopting smart automation technologies to enhance guest comfort, streamline operations, and reduce labor costs. Smart capsules equipped with IoT lighting, climate control, soundproofing panels, and app-based privacy settings are becoming mainstream. Automated check-in/out kiosks, AI-driven concierge systems, and dynamic pricing algorithms allow operators to improve efficiency while appealing to digitally savvy travelers. Mobile integration has become central, enabling guests to manage lockers, booking extensions, pod settings, and amenities through unified applications. This trend strongly resonates with the preferences of millennials and Gen Z, who expect seamless, tech-forward accommodation experiences.
Adaptive Reuse and High-Density Urban Expansion
As global cities face rising real-estate prices and space shortages, capsule hotels are being used as efficient solutions for high-density lodging. Operators are increasingly converting unused office buildings, warehouses, commercial floors, and older hotels into pod-based accommodations. Such adaptive reuse models reduce upfront capital expenditure while enabling rapid scaling in prime urban locations. Governments in the Asia-Pacific and parts of Europe are supporting this trend through urban-regeneration programs and affordable-lodging incentives. The result is a new wave of micro-hospitality formats emerging across transportation hubs, financial districts, and college zones where demand for short-stay and low-cost lodging is surging.
What are the key drivers in the capsule hotel market?
Rising Solo Travel and Budget Urban Tourism
The growing volume of solo travelers, particularly younger demographics, is a major driver of capsule hotel adoption. As global tourism rebounds and low-cost airlines expand routes, travelers increasingly seek affordable short-stay options close to transit hubs and urban attractions. Capsule hotels provide precisely this value proposition: minimalistic yet functional accommodation at a fraction of traditional hotel costs. The rising popularity of short weekend trips, backpacking, and city-hopping is further fuelling demand across Asia, Europe, and North America.
Acceleration of Digital Travel Behavior
With online travel bookings surging globally, capsule hotels are benefiting from digital-native consumer behavior. Mobile-first travelers prefer properties offering digital check-in, app-based pod access, and seamless online reservations. Operators leveraging online travel agencies (OTAs), direct booking engines, and social-media-driven visibility gain a competitive advantage. This shift in customer behavior directly supports the scalable, standardized, limited-service model that capsule hotels offer, reducing operating costs and increasing occupancy rates.
Urbanization and Real Estate Economics
In major global cities, rising real-estate costs, declining availability of affordable rooms, and increased urban mobility are driving the adoption of capsule hotels. Developers are capitalizing on the high-density layout of capsules to maximize returns per square meter. Cities experiencing rapid urban influx, including Tokyo, Shanghai, Mumbai, London, and New York, are seeing expanded opportunities for pod-style accommodations in transit zones, business districts, and student hubs. This structural shift in urban development continues to support market growth.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Perception of Limited Comfort and Privacy
Although capsule hotels offer efficient lodging, many travelers still perceive pods as too compact, lacking privacy, or unsuitable for extended stays. This limits adoption among family travelers, corporate executives, and guests accustomed to full-service hotels. Overcoming these perception barriers will require design innovations, upgraded amenities, and improved soundproofing.
Regulatory and Zoning Challenges
Capsule hotels must navigate complex fire-safety standards, ventilation requirements, and zoning regulations, particularly when converting older buildings. In some cities, hospitality regulations do not yet formally recognize capsule accommodations, causing delays in licensing and inspections. Such regulatory uncertainty can increase development costs and slow expansion across certain markets.
What are the key opportunities in the capsule hotel industry?
Smart Tech-Integrated Capsule Ecosystems
IoT-based pod customization, smart lockers, automated housekeeping, and AI-enabled operational management represent significant growth opportunities. Capsule hotels can position themselves as “micro smart hotels,” appealing strongly to tech-forward travelers and creating premium revenue tiers for enhanced pods. Integration of coworking pods and VR-enhanced rest spaces presents further diversification opportunities for operators.
Expansion in Emerging and High-Density Markets
Countries undergoing rapid urbanization, such as India, Indonesia, Vietnam, Brazil, and parts of Africa, represent major white-space opportunities. Rising domestic tourism and the need for affordable short-stay lodging in transit hubs make capsule hotels well-suited for railway stations, airports, industrial corridors, and university zones. Market entrants can secure early dominance through adaptive reuse strategies and scalable pod installations.
Product Type Insights
Single capsules dominate the market, accounting for nearly 55–60% of global revenue in 2024. Their low setup cost, suitability for solo travelers, and efficient space utilization make them the preferred choice for operators. Double capsules and premium pods are growing niches, driven by travelers seeking slightly more comfort and privacy. Themed capsules, such as business pods, wellness pods, and gaming pods, are emerging as differentiators in competitive urban markets.
Application Insights
Leisure tourism remains the largest application segment, capturing about 50–60% of total capsule-hotel stays. Business travel is the second-largest application, especially for short work trips and layovers near transportation hubs. Long-stay applications such as student housing, migrant-worker lodging, and budget corporate stays are gaining momentum. Pod-based coworking and day-use capsule models are also emerging, driven by remote work trends.
Distribution Channel Insights
Online booking dominates the capsule hotel distribution landscape, accounting for over 45% of total reservations in 2024. Travelers increasingly rely on OTAs, mobile apps, and direct digital platforms for booking short-stay accommodations. Offline channels continue to serve transit travelers and walk-ins, especially in railway and airport capsule installations. Direct hotel websites with loyalty offers and real-time pod availability are gaining traction as operators prioritize digital engagement.
Traveler Type Insights
Solo travelers drive approximately 70% of capsule-hotel demand, reflecting the model’s strong alignment with individual travel behavior. Backpackers, young professionals, and digital nomads represent key customer segments. Couples and group travelers use capsule hotels primarily when cost optimization outweighs the need for large rooms. Corporate travelers increasingly adopt capsule hotels for short stays near business districts or airport terminals.
Age Group Insights
The 25–39 age group represents the largest share of capsule-hotel guests, contributing around 40% of demand. These digitally savvy travelers prioritize affordability, urban accessibility, and tech-enabled convenience. The 18–24 segment fuels growth in backpacker and student markets, while older age groups show slower but growing adoption as premium pod designs improve comfort and privacy features.
| By Capsule Type | By Booking Mode | By Traveler Type | By Age Group | By Purpose of Stay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for around 10% of the global market. Demand is strongest in cities with high accommodation costs, such as New York, San Francisco, and Toronto. Increasing acceptance of compact living and rising solo-business travel are supporting capsule-hotel expansion, with operators targeting airport zones and digital nomad hubs.
Europe
Europe holds 12–15% of the global share, with demand led by the U.K., Germany, the Netherlands, and France. Cost-conscious urban travelers and students drive the market, while growing tourism inflows position capsule hotels as attractive alternatives to traditional hostels. Sustainability-focused consumers are pushing operators toward energy-efficient pod designs.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominates the global capsule hotel market with approximately 58% share in 2024. Japan remains the pioneer, while China, South Korea, Singapore, Thailand, and India are rapidly expanding pod-style accommodations in metro hubs. The region’s dense populations, high domestic travel activity, and rising youth demographics continue to accelerate market growth.
Latin America
Latin America is gradually adopting capsule hotels, with Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia leading the expansion. Capsule formats appeal to backpackers, budget tourists, and students. Growing tourism and redevelopment in city centers create long-term opportunities for pod installations and adaptive reuse projects.
Middle East & Africa
MEA markets are emerging, with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa showing rising interest in capsule hotels near airports, financial districts, and pilgrimage zones. The region’s focus on tourism diversification and scalability of lodging infrastructure will support the adoption of compact accommodation styles.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Capsule Hotel Market
- Nine Hours
- The Pod Hotels
- First Cabin
- CityHub
- Capsule Inn Osaka
- Cabana
- Book and Bed Tokyo
- The O Pod Hotel
- Bloc Hotels
- St Christopher’s Pods
- Petra Capsule Hostel
- Urban Pod
- Sleep Box
- Yotel (Pod Rooms)
- Space Inn
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Nine Hours announced an expansion into three new Japanese cities using modular pod installations aimed at reducing construction time and cost.
- In January 2025, CityHub launched upgraded IoT-enabled capsules in Amsterdam and London, enhancing privacy controls and app-based guest features.
- In February 2025, First Cabin revealed its plan to convert unused commercial floors in Tokyo into hybrid capsule-co-working spaces for remote professionals.