Anti-Aging Drugs Market Size
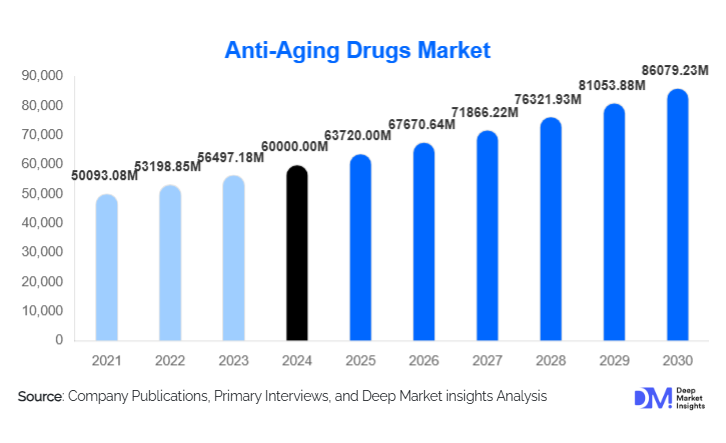
According to Deep Market Insights, the global anti-aging drugs market size was valued at USD 60,000.00 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 63,720.00 million in 2025 to reach USD 86,079.23 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 6.2% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market growth is primarily driven by rapid advancements in geroscience, increasing prevalence of age-related chronic diseases, rising healthcare expenditure on preventive medicine, and growing consumer acceptance of pharmacological interventions aimed at extending healthspan rather than lifespan alone.
Key Market Insights
- Anti-aging drugs are transitioning from cosmetic-focused solutions to disease-modifying therapeutics, targeting cellular senescence, mitochondrial dysfunction, and epigenetic aging.
- Hormone-based therapies remain the most commercially established segment, benefiting from clinical familiarity and faster regulatory approvals.
- North America dominates the global market, supported by high R&D spending, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and strong consumer demand for longevity treatments.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by aging populations in Japan and China and rising preventive healthcare adoption in India.
- Longevity clinics and regenerative medicine centers are emerging as key distribution channels, reshaping traditional pharmaceutical commercialization models.
- AI-driven drug discovery and genomics integration are accelerating pipeline development and reducing clinical trial timelines.
What are the latest trends in the anti-aging drugs market?
Shift Toward Geroscience-Based Therapeutics
The market is witnessing a fundamental shift toward drugs that directly target the biological mechanisms of aging. Senolytic and senomorphic drugs that eliminate or suppress senescent cells are gaining strong traction due to their potential to delay multiple age-related diseases simultaneously. Autophagy-inducing drugs and mitochondrial enhancers are also advancing through clinical pipelines, supported by a growing scientific consensus that aging is a modifiable biological process. This trend is attracting substantial venture capital and pharmaceutical partnerships, accelerating the translation of laboratory research into commercial therapeutics.
Personalized and Preventive Longevity Medicine
Another major trend is the rise of personalized anti-aging drug regimens based on genetic profiling, biomarkers, and metabolic assessments. Longevity clinics are increasingly offering customized hormone therapies, antioxidant drugs, and epigenetic modulators tailored to individual aging trajectories. This preventive approach is expanding demand beyond elderly populations to middle-aged consumers seeking early intervention. Digital health platforms and AI-driven analytics are further supporting personalized dosing, adherence monitoring, and long-term outcome optimization.
What are the key drivers in the anti-aging drugs market?
Rapid Growth of the Global Aging Population
The rising proportion of individuals aged 60 years and above is a primary driver of market growth. Increasing life expectancy has amplified the prevalence of age-related conditions such as neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and musculoskeletal degeneration. Anti-aging drugs that delay functional decline and improve quality of life are increasingly viewed as essential components of modern healthcare systems, particularly in developed economies.
Advancements in Biotechnology and Drug Discovery
Breakthroughs in cellular biology, epigenetics, and regenerative medicine have significantly expanded the therapeutic potential of anti-aging drugs. AI-enabled drug discovery platforms are identifying novel senolytic compounds and epigenetic modulators at an accelerated pace, reducing R&D costs and improving success rates. These advancements are enabling pharmaceutical companies to develop next-generation therapies with broader clinical applications.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Regulatory and Ethical Uncertainty
One of the major restraints is the lack of standardized regulatory frameworks for anti-aging drugs. Many therapies fall into a gray area between cosmetic enhancement and disease treatment, leading to prolonged approval timelines and inconsistent reimbursement policies. Ethical concerns regarding lifespan extension and equitable access further complicate regulatory decision-making, particularly in publicly funded healthcare systems.
High Development Costs and Clinical Complexity
Anti-aging drug development requires long-term clinical studies and validated aging biomarkers, significantly increasing development costs and financial risk. These challenges can limit market participation to well-capitalized pharmaceutical companies and restrict innovation from smaller biotech firms.
What are the key opportunities in the anti-aging drugs industry?
Expansion of Longevity Clinics and Preventive Care Models
The global expansion of longevity and regenerative medicine clinics presents a major growth opportunity. These centers act as direct commercialization platforms for anti-aging drugs, bypassing traditional hospital-centric models. As preventive healthcare gains policy support, demand for long-term anti-aging pharmacotherapy is expected to rise substantially.
Emerging Market Penetration and Regulatory Alignment
Emerging economies in the Asia-Pacific and Latin America are aligning their regulatory frameworks with global pharmaceutical standards. This creates opportunities for multinational companies to expand market presence, supported by growing middle-class populations, increasing healthcare access, and rising awareness of preventive aging therapies.
Drug Type Insights
Hormone-based therapies dominate the anti-aging drugs market, accounting for approximately 28% of the 2024 market share, due to established clinical usage and strong physician acceptance. Senolytic and senomorphic drugs represent the fastest-growing drug type, driven by promising clinical trial outcomes and their ability to target multiple age-related pathways simultaneously. Antioxidant and mitochondrial function drugs maintain steady demand, particularly within preventive and home-based care settings.
Mechanism of Action Insights
Cellular senescence suppression leads the market with nearly 24% share in 2024, reflecting growing focus on disease-modifying anti-aging interventions. Hormonal regulation mechanisms follow closely, supported by widespread adoption in metabolic and musculoskeletal aging treatments. Epigenetic reprogramming and telomere preservation mechanisms are emerging as high-potential areas, although commercialization remains in early stages.
Route of Administration Insights
Oral anti-aging drugs account for approximately 46% of global demand, owing to ease of administration and high patient compliance. Injectable therapies are widely used in hormone-based and regenerative treatments, particularly in clinical and specialty care settings. Transdermal and implantable delivery systems are gaining traction for long-term, controlled-release applications.
End-Use Insights
Hospitals and specialty clinics represent the largest end-use segment, holding around 41% of the market in 2024, driven by physician-supervised therapies and clinical validation requirements. Longevity and regenerative medicine centers are the fastest-growing end-use segment, expanding at over 18% CAGR, while home-based preventive care is emerging as a strong secondary demand driver.
| By Drug Type | By Mechanism of Action | By Route of Administration | By End Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America dominates the anti-aging drugs market with approximately 38% market share in 2024. The United States accounts for the majority of regional demand, supported by high healthcare spending, strong R&D ecosystems, and widespread adoption of preventive longevity therapies.
Europe
Europe holds nearly 27% of the global market, led by Germany, France, and the United Kingdom. Strong public healthcare systems, aging demographics, and regulatory support for advanced therapeutics drive sustained demand.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for around 24% of global demand and is the fastest-growing region. Japan and China dominate regional consumption, while India is emerging as a high-growth market with an estimated CAGR of 18% due to expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing and rising preventive healthcare awareness.
Latin America
Latin America represents a developing market, led by Brazil and Mexico. Growth is driven by increasing private healthcare investments and rising adoption of hormone-based anti-aging therapies.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region shows moderate but rising demand, particularly in the UAE and Saudi Arabia, where premium longevity clinics and medical tourism are expanding.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Anti-Aging Drugs Market
- AbbVie
- Pfizer
- Novartis
- Roche
- Johnson & Johnson
- Merck & Co.
- Bayer
- Amgen
- Eli Lilly
- GSK
- Sanofi
- AstraZeneca
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- Biogen
- Lonza Group