Amber Glass Vials Market Size
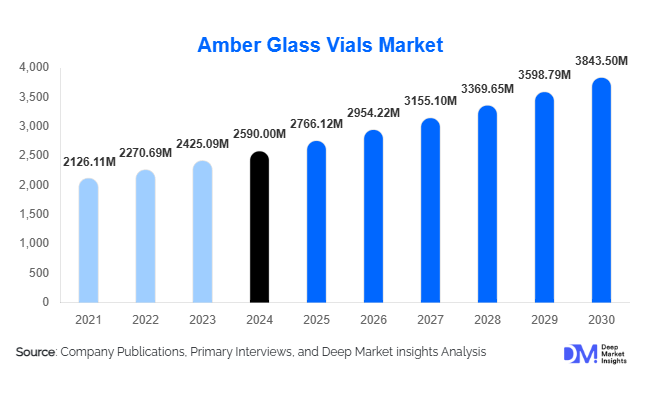
According to Deep Market Insights, the global amber glass vials market size was valued at USD 2,590 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 2,766.12 million in 2025 to reach USD 3,843.50 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for biologics and vaccines requiring light-protective primary packaging, rising adoption of pre-sterilized and ready-to-use vial formats, and regional manufacturing expansion in Asia-Pacific and Latin America to meet supply chain localization needs.
Key Market Insights
- Type I borosilicate sterile vials are increasingly dominating the market, as they meet the rigorous chemical resistance and leachables/leachables requirements demanded by injectable biologics and high-value therapies.
- Pre-sterilized, ready-to-fill vial formats are gaining traction, with pharmaceutical and biotech firms outsourcing fill/finish to contract manufacturers, requiring validated vial supply chains and reducing time to market.
- Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, driven by India and China ramping up vaccine and biologic production, local vial manufacturing, and export-oriented pharma manufacturing hubs.
- North America remains a major value market, supported by large biologics pipelines, advanced CMOs, and stringent regulatory demand for high-spec vial formats.
- Technological upgrades in vial manufacturing, such as surface treatments to reduce extractables, automated inspection, and traceability integration, are reshaping competitive dynamics and adding value beyond commodity vial supply.
- Sustainability trends are expanding the appeal of glass vials (with higher recycled-content, lower-carbon furnaces, and circular-supply commitments), especially among large pharmaceutical companies focused on Scope 3 emissions.
Latest Market Trends
Premiumization of Vial Formats
As injectable biologics and vaccines become more prevalent, the demand for higher-spec amber glass vials, particularly Type I, sterile, pre-sterilized, crimped-closure formats has risen. These premium formats command higher average selling prices and longer contract commitments, shifting the market away from commodity bulk vials. Vial manufacturers are increasingly offering services such as extractables/leachables documentation, container-closure integrity validation, and automated finishing, moving the product from pure glass containers toward integrated packaging solutions. This trend is not only increasing value per unit but also raising barriers to entry for smaller players who lack validation capabilities.
Supply-Chain Localization & Regional Manufacturing Growth
Pharmaceutical manufacturers and CMOs are placing greater emphasis on supply-chain resilience, shorter lead times, and local sourcing. As a result, vial manufacturers are investing in production capacity in Asia-Pacific (notably India and China) and Latin America to serve regional fill/finish hubs. Governments’ localization initiatives and export incentives support this trend. The result: faster time-to-fill, lower logistics cost, and greater flexibility in size/format changeover for regional buyers. This is particularly significant for high-volume biologics and vaccines, where agility in manufacturing and packaging is critical.
Amber Glass Vials Market Drivers
Rising Demand for Biologics and Vaccines
The growth of global biologics, vaccine campaigns, and injectable therapies is a primary driver of the amber glass vials market. These therapies often require protection from light degradation, chemical inertness, and reliable container-closure systems, points at which amber glass vials are optimally placed. With multiple vaccine booster programs, pandemic preparedness drives, and increasing biologic approvals, the volume of high-spec vials is rising significantly. The upstream need for validated vials with high-quality glass (Type I) and certified finishing further supports growth.
Shift toward Pre-Sterilized, Ready-to-Use Packaging
Pharma companies and CMOs are increasingly preferring pre-sterilized ready-to-fill vials because these reduce validation time, minimize contamination risk, and streamline fill/finish operations. This trend elevates the demand for amber glass vials supplied in sterilized trays or crates, with validated closures and finishing. Suppliers who can provide these formats capture higher margins and more stable contracts. This transition from non-sterile bulk supply to ready-to-use format is broadening the market and increasing average revenue per unit.
Technological & Quality Upgrades in Glass Vial Supply
Quality expectations for pharmaceutical packaging continue to rise, particularly for biologics and vaccines. Vial suppliers are adopting technologies such as improved annealing, surface treatments to reduce ion-exchange, siliconisation optimization, low extractables/leachables profiles, container closure integrity testing, and automated inspection. These upgrades add cost and capability but also create differentiation and justify premium pricing. The trajectory toward more advanced vials is bolstering market growth because customers are willing to pay for validated formats and risk-managed supply chains.
Market Restraints
Volatility in Raw Materials and Energy Costs
Glass vial manufacturing is energy-intensive and highly exposed to fluctuations in raw material (silica, soda ash, cullet) and energy (gas/electricity) costs. Sudden cost increases can compress margins, force price renegotiations with pharma customers, or delay new investments. This cost volatility creates risk for manufacturers of glass vials and may slow down capacity expansion or raise pricing that can dampen demand.
Regulatory Qualification & Entry Barriers for High-Spec Formats
While demand is strong for high-spec vials, the regulatory burden (extractables/leachables data, container closure integrity validation, sterilization assurance, documentation, and supply chain audits) is high, especially for biologics and vaccines. New entrants or smaller players may find it difficult to qualify for high-value contracts quickly. This barrier slows the pace at which low-cost suppliers can scale into premium segments and may limit competition in those high-growth areas.
Amber Glass Vials Market Opportunities
Expansion of Biologics Fill/Finish Capacity in Emerging Regions
As biologics and vaccine manufacturing expand, especially in emerging markets (India, China, Southeast Asia, Latin America), there is a strong opportunity for vial manufacturers to partner with local fill/finish providers or establish regional plants. Localized vial supply shortens lead times, reduces logistics and customs risk, and aligns with government incentives for on-shore manufacturing. Existing participants can secure long-term contracts with CMOs establishing new biologic lines; new entrants can target regional niche capacity with modular lines tailored for biologics.
Product Differentiation through Advanced Glass & Surface Technologies
There is growing demand for vials with enhanced performance: ultra-low extractables/leachables, special coatings (e.g., siliconisation control, de-nitrosation), surface treatments to avoid delamination, and enhanced traceability (2D codes, RFID). Manufacturers who invest in these technologies can charge higher premiums, reduce risk for pharma end-users, and lock in longer-term supply contracts. This is an opportunity to move up the value chain rather than compete purely on volume.
Sustainability and Circular-Economy Packaging Leadership
Glass already has strong sustainability credentials (fully recyclable, high inertness), but packaging buyers are increasingly demanding transparent supply-chain metrics, lower carbon-footprint furnaces, recycled-content glass, and closed-loop take-back programs. Vial manufacturers who proactively build sustainable production, obtain certifications (LCA, carbon-footprint disclosure), and market their vials as “green-pharma” can differentiate themselves. With pharma companies under pressure to reduce Scope 3 emissions, this is a growing strategic opportunity.
Product Type Insights
Within the amber glass vials market, the dominant product type is the 2.1–5.0 mL vial segment, widely used for single-dose injectables and lyophilized vaccine formats. This size offers optimal fill volume, fits common fill/finish equipment, and has achieved broad standardization in pharma manufacturing. Smaller formats (≤0.5 mL, 0.6–1.0 mL) are gaining traction for specialty biologics and micro-dose therapies, while larger formats (>10 mL) serve niche biologics and research applications but remain smaller in overall value. The shift toward sterile, Type I, crimp-sealed vials is lifting average selling prices, making these premium formats increasingly influential in market value growth.
Application Insights
The largest application by value in the amber glass vials market is liquid injectable formulations, driven by the high volume of parenteral drugs and biologics requiring light protection and stringent packaging integrity. Lyophilized powders and biologics/vaccine applications are the fastest-growing sub-segments, as more biologics require freeze-dry formats and ultra-high performance packaging. Diagnostic reagents, lab storage, and cosmetic serums represent smaller but meaningful adjacent applications that provide diversification beyond mainstream pharma. Each of these applications demands increasingly specialized vial features (e.g., low leachables, precision closures), which feed premium growth.
Distribution Channel Insights
The supply of amber glass vials is dominated by direct OEM (pharmaceutical & biotech manufacturers) contracts, which account for nearly half of the market value due to large volumes, long-term supply agreements, and high quality requirements. Contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs/CDMOs) represent a growing channel as more pharmaceutical firms outsource fill/finish. Distributors serve smaller buyers (diagnostics, cosmetics, labs) who purchase smaller volumes and standard formats. Vial manufacturers are increasingly offering value-added services (validation support, inventory management, just-in-time delivery) to strengthen OEM relationships and lock-in contracts, raising barriers to simple commoditization through distributors alone.
| By Product Type | By Capacity | By Application | By End User | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America is a major market for amber glass vials, accounting for an estimated 28% of global value (USD 725 million in 2024). The United States drives most of the demand, supported by a strong biologics pipeline, a large CMO network, and stringent regulatory regimes motivating high-spec vial adoption. Growth is steady, influenced by regional investments in fill/finish capacity and supply-chain localization strategies.
Europe
Europe holds a significant share (24% of global value, USD 622 million in 2024) with major hubs in Germany, France, Italy, and the UK. Demand is driven by established pharmaceutical clusters, regulatory focus on high-performance packaging, sustainability requirements, and advanced manufacturing adoption. Growth is moderate but stable.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is the largest regional share (32% or USD 829 million in 2024) and the fastest-growing region. Rapid expansion of pharma/biotech manufacturing in India and China, export-oriented fill/finish facilities, and government incentives for localization have created strong demand growth for amber glass vials. India is a standout country for double-digit volume growth as vaccines and generics expansion accelerate.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for around 8% of the global market (USD 207 million in 2024), with Brazil and Mexico being key countries. While demand is smaller relative to mature regions, local generic and vaccine manufacturing and increased import substitution are beginning to boost vial demand.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa (MEA) region also represents approximately 8% (USD 207 million in 2024). Demand is gradually growing as regional pharma manufacturing parks and vaccine fill/finish initiatives (notably in the GCC and South Africa) gain momentum, although infrastructure and regulatory hurdles remain.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Amber Glass Vials Market
- SCHOTT AG
- Corning Incorporated
- Gerresheimer AG
- Stevanato Group S.p.A.
- SGD Pharma
- Nipro Corporation
- Bormioli Pharma S.p.A.
- Owens-Illinois (O-I)
- DWK Life Sciences / Duran Group
- Piramal Glass
- AGC Inc. (pharma glass divisions)
- Vitro (pharmaceutical glass lines, Mexico)
- Hindusthan National Glass (regional pharma focus)
- Nanyang Glass / regional Chinese producers
- Nipro Pharma Packaging
Recent Developments
- In early 2025, Stevanato Group announced an acquisition aimed at expanding the amber glass vial capacity dedicated to biologics fill/finish customers.
- In mid-2024, Gerresheimer announced a strategic collaboration to co-develop next-generation amber glass vials with tamper-evident closures targeting cold-chain biologics.
- In late 2024, multiple vial manufacturers announced furnace upgrades and investment in automation & surface-treatment capabilities, aligning with sustainability drives and higher-spec product demand.