Air Treatment Products Market Size
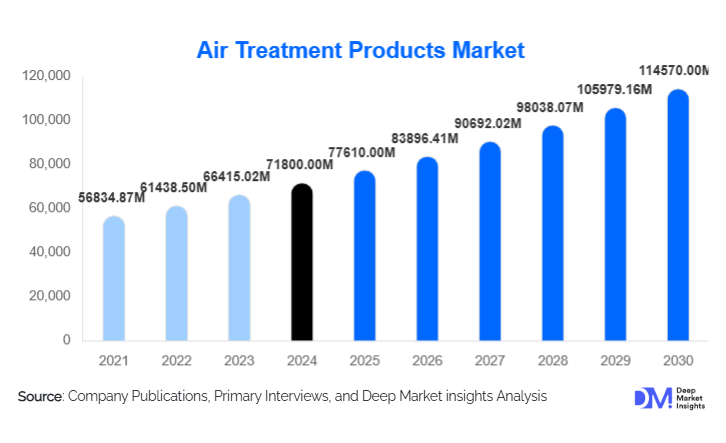
According to Deep Market Insights, the global air treatment products market size was valued at USD 71,800 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 77610 million in 2025 to USD 114570 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 8.1% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market growth is primarily attributed to increasing pollution levels, growing prevalence of respiratory diseases, rising demand for indoor air quality management, extensive adoption of HVAC-integrated systems, and strict government regulations targeting air emission control across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Key Market Insights
- AI- and IoT-enabled smart air treatment products are witnessing rapid adoption, offering real-time pollution detection, filter optimization, and energy-efficient air quality management.
- Asia-Pacific holds the largest market share and is the fastest-growing region, driven by urbanization, industrialization, and government-led air quality initiatives.
- HEPA filtration technology dominates market share due to its proven ability to eliminate 99.97% of airborne particles, including allergens, bacteria, and viruses.
- The residential air treatment market is expanding rapidly due to rising health awareness and increased online sales of portable air purifiers and smart humidifiers.
- Healthcare and semiconductor industries are driving high-value demand due to cleanroom and sterile air requirements.
- Industrial facilities are significantly investing in compliance-driven air treatment systems including scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and emission filtration units.
What are the latest trends in the Air Treatment Products Market?
Rising Adoption of Smart and Connected Air Purification Systems
Air treatment products are increasingly integrating IoT, AI, and advanced sensor technologies to deliver continuous monitoring, automated filtration, and data-driven optimization. Smart purifiers now come with Wi-Fi-enabled, multi-parameter sensors that detect PM2.5, PM10, VOCs, CO2, temperature, and humidity and automatically adjust fan speed, filtration intensity, and operating mode according to real-time air quality conditions. These systems are compatible with mobile apps and smart home ecosystems, enabling remote control, programmable schedules, filter life tracking, and voice-assistant integration through platforms such as Alexa and Google Home. In commercial buildings and industrial facilities, cloud-based dashboards are helping facility managers benchmark air quality across zones, monitor compliance with internal and regulatory standards, and optimize energy consumption by synchronizing air treatment with HVAC load, occupancy patterns, and outdoor pollution levels. The shift to AI-powered adaptive filtration, which learns from historical data and user preferences, is improving personalization, extending filter life, lowering maintenance frequency, and supporting predictive maintenance models that reduce unplanned downtime.
HEPA and Hybrid Filtration Becoming Industry Standard
HEPA filters remain the backbone of the global air treatment products market due to their proven capability to capture up to 99.97% of airborne particles as small as 0.3 microns, including dust, pollen, bacteria, and some viruses. To address the broader spectrum of pollutants found in residential, commercial, and industrial environments, manufacturers are increasingly adopting hybrid architectures that combine HEPA media with activated carbon layers, UV-C germicidal lamps, photocatalytic oxidation modules, and plasma sterilization components. These hybrid systems are designed to target particulate matter, gaseous contaminants, odors, and microbial loads in a single, compact configuration, making them suitable for hospitals, cleanrooms, laboratories, high-density office spaces, and premium residential units. New designs emphasize low-pressure-drop materials and optimized airflow channels, which reduce energy consumption and operational noise while maintaining high Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR). Additionally, the adoption of washable pre-filters, antimicrobial coatings on filter surfaces, and modular cartridges is lowering lifetime ownership costs and enabling easier servicing across residential and industrial deployments.
Industrial Air Treatment Systems Expanding in Emission Compliance Applications
Industrial sectors such as chemicals, cement, metals, power generation, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and oil & gas are scaling up their investments in air treatment infrastructure to comply with increasingly stringent emission and workplace safety regulations. Large-scale systems including electrostatic precipitators, baghouse filters, wet and dry scrubbers, and high-capacity HEPA-enabled HVAC units are being deployed to control particulate emissions, acid gases, fumes, and hazardous aerosols released during production processes. These solutions are often integrated with automated air quality monitoring networks that continuously track pollutant concentrations at stacks, shop-floor zones, and surrounding communities, triggering alarms and process adjustments when thresholds are exceeded. In many new industrial facilities in China, India, and parts of Europe, emission control systems are now embedded into plant design from the outset, rather than retrofitted later, which enhances efficiency and reduces long-term compliance costs. The expansion of clean manufacturing initiatives, along with corporate ESG commitments, is accelerating demand for high-performance industrial-grade air treatment technologies capable of delivering quantifiable reductions in emissions and occupational exposure.
What are the key drivers in the Air Treatment Products Market?
Increasing Prevalence of Respiratory and Airborne Diseases
The rising prevalence of asthma, allergic rhinitis, COPD, and other pollution-related respiratory disorders is a fundamental driver of the air treatment products market. Rapid urbanization, traffic congestion, industrial emissions, and indoor sources such as cooking fumes, tobacco smoke, and off-gassing from building materials have led to higher concentrations of PM2.5, VOCs, and bioaerosols in homes, offices, and public spaces. Urban populations in India, China, Southeast Asia, parts of Europe, and North America are especially exposed, prompting greater use of purifiers in bedrooms, living areas, classrooms, clinics, and transport hubs. Post-pandemic, the heightened awareness of airborne transmission risk has further increased adoption of HEPA and UV-C based solutions in hospitals, outpatient centers, diagnostic labs, schools, airports, and corporate offices, where maintaining clean air is now considered part of core health and safety protocols. This sustained shift in risk perception is translating into recurring demand for both portable and centralized air treatment systems.
Government Regulations and Compliance Requirements
National and regional regulatory frameworks are significantly shaping demand for air treatment solutions. Policies such as the U.S. Clean Air Act, the European Union’s Air Quality Directive, and India’s National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) set emission limits and indoor air quality expectations that manufacturers, industrial plants, and commercial buildings must meet. In practice, this translates into mandatory installation or upgrading of stack emission control systems, cleanroom-grade filtration in pharmaceuticals and electronics manufacturing, and enhanced ventilation and filtration in public buildings. Non-compliance can result in fines, operational restrictions, or reputational damage, reinforcing the business case for investing in modern air treatment infrastructure. In several jurisdictions, green building certifications and occupational safety standards also require specific filtration performance levels, driving upgrades of legacy HVAC systems with high-efficiency filters, demand-controlled ventilation, and integrated monitoring solutions.
Infrastructure Development and Smart Building Integration
Global growth in commercial real estate, public infrastructure, healthcare facilities, and data centers is directly contributing to higher installation rates of air treatment products. New office towers, shopping malls, airports, hotels, universities, and hospitals are increasingly designed as smart buildings, where HVAC, lighting, security, and energy management systems are interconnected. Within this context, air treatment is no longer an isolated add-on but a core component of building performance and occupant experience. Centralized HVAC systems with built-in filtration, humidification, dehumidification, and sterilization capabilities are being specified during the design phase, enabling more efficient lifecycle management. In smart homes, filtration units are being integrated into ducted systems and connected to home automation platforms that adjust ventilation based on occupancy, outdoor air quality, and indoor pollutant levels. This integration trend is driving volume growth not only in hardware but also in associated software, analytics, and after-sales service models.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Installation and Maintenance Costs
The upfront capital investment required for large-scale air treatment systems remains a key barrier, especially for small and mid-sized enterprises and cost-sensitive building projects. Industrial scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and high-capacity HEPA filtration units involve significant equipment costs, complex installation, and integration with existing process or HVAC systems. Even in the residential and small commercial segments, premium purifiers and advanced multi-stage filters can be perceived as expensive, particularly in price-sensitive markets. Ongoing expenses—such as periodic filter replacement, energy consumption for continuous operation, routine cleaning, and occasional component replacement—add to total cost of ownership. For many industrial facilities, these costs must be balanced against competing budget priorities, which can delay or limit upgrades to more advanced air treatment technologies.
Lack of Awareness and Standardization in Emerging Markets
In many developing economies, awareness of indoor air quality risks and the benefits of systematic air treatment remains limited outside of major urban centers and premium institutional settings. Consumers may not fully understand the differences between basic fans, simple filters, and certified HEPA or hybrid systems, leading to underinvestment or purchase of suboptimal solutions. Standardized performance labeling, testing protocols, and regulatory benchmarks for indoor air quality are still evolving in several regions, which makes it difficult for buyers to compare products and verify effectiveness claims. In smaller commercial and industrial establishments, the absence of stringent enforcement of air quality and worker-exposure norms often results in minimal spending on air treatment. This combination of low awareness, limited enforcement, and lack of clear standards slows market penetration, particularly in lower-tier cities and informal industrial clusters.
What are the key opportunities in the Air Treatment Products Market?
Expansion into Smart Homes, Healthcare, and Semiconductor Cleanrooms
Growing penetration of smart home ecosystems creates a favorable environment for manufacturers to position connected air purifiers, humidifiers, and integrated filtration modules as standard household appliances. Compatibility with voice assistants, home automation hubs, and energy management systems allows brands to bundle air treatment with broader comfort and security offerings. In parallel, the healthcare sector presents a high-value opportunity as hospitals, clinics, dental practices, and diagnostic labs upgrade to systems capable of controlling airborne pathogens and ensuring consistent air quality in critical care units, operating theaters, and isolation wards. Semiconductor fabrication plants, EV battery manufacturing facilities, and pharmaceutical cleanrooms require ultra-low particulate environments, making them premium customers for advanced HEPA and ULPA filtration, laminar airflow systems, and redundant sterilization technologies. Suppliers that can serve all three segments—smart homes, healthcare, and ultra-clean industrial environments—with differentiated product lines and service contracts stand to capture significant recurring revenue.
Government-Led Emission Monitoring and Public Infrastructure Upgrades
Many governments are rolling out clean air action plans that include funding for monitoring networks, retrofitting of public buildings, and modernization of legacy industrial assets. Projects covering schools, metro stations, airports, government offices, and public hospitals often require installation of centralized filtration, ventilation, and sterilization systems that can handle high foot traffic while maintaining regulatory compliance. Air treatment manufacturers can participate in these initiatives through public tenders, public–private partnerships, and long-term maintenance contracts. In addition, as authorities deploy fixed and mobile emission monitoring stations to track air quality at city and regional levels, there is growing scope for integrated solutions that combine sensors, filtration units, and software platforms. These projects not only generate direct equipment sales but also create long-term demand for upgrades, consumables, and technology refresh cycles.
Growth in Public Transportation, Automotive, and Cabin Air Filtration
Cabin air quality is becoming a priority differentiator in passenger vehicles, commercial fleets, and public transportation systems. Automakers are adding multi-stage filters, ionizers, and sometimes in-duct UV-C modules to maintain low particulate and odor levels in enclosed cabins, particularly in EVs where quiet operation allows occupants to perceive air comfort more acutely. Premium models and electric vehicles are increasingly marketed with advanced cabin air purification as a health and comfort feature. In aviation and rail transport, operators are upgrading filtration modules to high-efficiency standards to reassure passengers and comply with evolving health and safety expectations. Urban bus networks and ride-hailing fleets are also beginning to explore retrofit solutions to improve perceived and actual air quality. These trends create a sizable opportunity for specialized cabin filters, compact sterilization modules, and OEM partnerships that embed air treatment capabilities directly into vehicle and transport platform design.
Product Type Insights
Air purifiers represent the largest product category, accounting for more than 32% of the 2024 market, primarily driven by household adoption, healthcare deployments, and increased use in offices, schools, and hospitality venues. Within this category, portable room purifiers and wall-mounted units are preferred for flexibility and lower installation complexity, while centralized purification modules are increasingly embedded in ducted HVAC systems for larger buildings. HEPA-based purifiers dominate due to their high particle capture efficiency and widespread recognition among consumers and professionals. Dehumidifiers and UV sterilizers are showing strong growth in hospitals, laboratories, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food storage environments where microbial and moisture control is critical. On the industrial side, electrostatic precipitators, bag filters, and scrubbers are gaining traction as facilities respond to tighter emission norms and corporate ESG expectations, providing long-term, high-capacity solutions for dust and fume control in heavy industries.
Application Insights
Indoor air treatment holds more than 56% of overall market share, reflecting increased focus on indoor environments where people spend the majority of their time. Commercial buildings, schools, hospitals, retail centers, and residential properties are investing in systems that maintain particulate and microbial loads within recommended thresholds, often integrating sensors to ensure continuous compliance. The combination of indoor pollution sources—such as cleaning agents, building materials, and occupant-generated contaminants—with outdoor pollution ingress makes indoor air treatment a priority for building owners and facility managers. Vehicle cabin air treatment, while currently smaller in absolute value, is one of the fastest-growing applications. Automotive OEMs, airlines, and public transit agencies are differentiating their offerings by ensuring cabins remain low in allergens, dust, and odors, particularly for premium and electric models. This segment is expected to expand further as cabin air quality becomes a more visible component of passenger comfort and safety.
Distribution Channel Insights
Online retail channels account for more than 24% of global sales and continue to gain share as consumers increasingly research, compare, and purchase air treatment products via e-commerce marketplaces and brand-owned websites. Online platforms facilitate access to a wide variety of models, transparent pricing, user reviews, and convenient filter subscription services. For residential and small commercial buyers, this channel is often the first point of contact with air treatment brands. However, HVAC contractors, system integrators, and offline industrial suppliers remain dominant for large-scale installations in factories, data centers, hospitals, and office complexes. These projects typically require site assessment, system design, customization, and professional installation, which are best handled through direct or channel-partner-based B2B sales. Hybrid models are also emerging, where product research and lead generation occur online, while the final sale and implementation are executed through offline technical partners.
End-Use Insights
The residential sector leads with approximately 28% share of the market, underpinned by rising health awareness, growing concern about urban pollution, and increasing penetration of smart home ecosystems. Consumers in major cities are adopting purifiers for bedrooms, living rooms, and home offices, often purchasing multiple units per household. Industrial applications across pharmaceuticals, electronics, semiconductor manufacturing, and specialized cleanrooms are projected to grow at around 10% CAGR as these sectors adopt higher cleanliness classes and stricter particulate and microbial control standards. In these environments, air treatment systems are mission-critical and tightly integrated with process control and quality assurance. Healthcare remains a pivotal end-use segment, with spending estimated at about USD 14 billion in 2024 and growing near 9.5% annually, driven by the need to protect patients and staff from airborne infections, maintain sterile environments for surgeries and intensive care, and ensure regulatory compliance in hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
| By Product Type | By Filter Technology | By Application | By End-Use Sector |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for roughly 27% of the global market, reflecting high penetration of HVAC systems, strong healthcare infrastructure, and advanced industrial and commercial air quality standards. The U.S. drives the majority of regional demand, with widespread adoption of residential purifiers, building-integrated filtration, and industrial emission control systems. The presence of leading technology providers and a favorable regulatory landscape encourage early adoption of AI- and IoT-enabled air treatment solutions. Canada contributes additional demand in healthcare, industrial, and residential sectors, particularly in urban centers where pollution and allergy rates are rising.
Europe
Europe represents around 25% of global market share, with Germany, France, the U.K., Italy, and the Nordic countries leading consumption. Stringent EU directives on ambient and indoor air quality, combined with a strong sustainability focus, are driving adoption of high-efficiency filters, low-energy HVAC systems, and certified cleanroom technologies. Industrial users in automotive, pharmaceuticals, and advanced manufacturing rely heavily on air treatment systems to meet both regulatory requirements and stringent internal quality standards. In the commercial and residential sectors, there is growing demand for low-noise, energy-efficient purifiers and ventilation systems that align with green building certifications and carbon reduction targets.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the largest and fastest-growing region, holding about 34% market share and expanding rapidly as air quality concerns become central to public policy and consumer behavior. China is a key growth engine, driven by extensive urbanization, industrial activity, and government programs aimed at pollution control and indoor environment improvement. India is also seeing robust adoption in metropolitan areas and industrial clusters, supported by NCAP initiatives and rising health awareness among middle-class consumers. Japan and South Korea contribute significant demand for technologically advanced, compact, and energy-efficient systems that cater to space-constrained buildings and tech-centric consumers. Across the region, investments in new hospitals, semiconductor fabs, data centers, and commercial real estate further amplify demand for both centralized and portable air treatment solutions.
Latin America
Latin America holds approximately 7% of the global market, with Brazil and Mexico being the primary contributors. Industrial expansion in sectors such as food processing, automotive, and pharmaceuticals is supporting growth in emission control and process air treatment systems. Urban centers are beginning to see rising adoption of residential and commercial purifiers as awareness of pollution and indoor air quality increases. However, economic constraints and uneven regulatory enforcement mean that adoption is concentrated in higher-income segments and large industrial players. Over time, improvements in healthcare infrastructure and commercial real estate development are expected to broaden regional demand.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for about 7% of the market, with demand driven by rapid construction activity, infrastructure projects, and healthcare expansion in countries such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and South Africa. In the Gulf states, the combination of arid climate, dust storms, and high reliance on air-conditioned environments creates strong need for filtration and humidity management in both residential and commercial buildings. Hospitals, airports, shopping malls, and hospitality venues increasingly specify advanced air treatment systems to maintain comfort and hygiene standards. In Africa, demand is emerging from urban hospitals, mining operations, and industrial hubs, although overall penetration remains at an earlier stage compared with other regions.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Air Treatment Products Market
- Daikin Industries
- Honeywell International
- LG Electronics
- Panasonic Corporation
- Carrier Global
- Whirlpool Corporation
- Philips Electronics
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Trane Technologies
- 3M
- Sharp Corporation
- Camfil AB
- IQAir
- Blueair AB
- Lennox International
Recent Developments
- In April 2024, Daikin Industries launched its new AI-based smart air purification and HVAC-integrated system for hospitals and pharma cleanrooms.
- In January 2025, Honeywell introduced a cloud-based IoT platform to remotely control and optimize air treatment systems in commercial buildings.
- In March 2025, LG Electronics collaborated with Camfil AB to develop industrial sterilization air management solutions for semiconductor manufacturing environments.