Sodium Reduction Ingredients Market Size
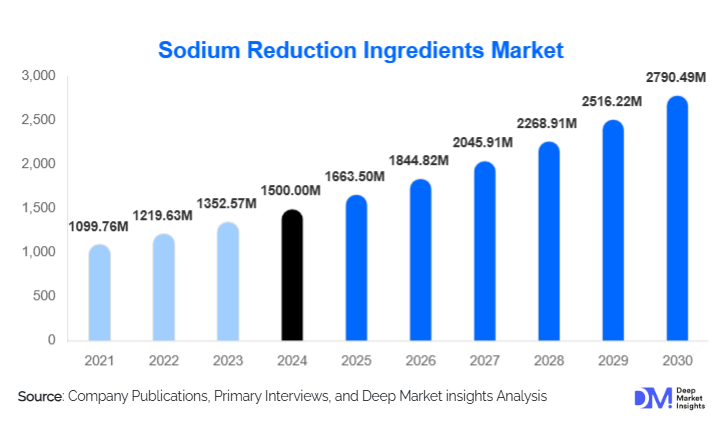
According to Deep Market Insights, the global sodium reduction ingredients market size was valued at USD 1,500 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 1,663.5 million in 2025 to reach USD 2,790.49 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 10.9% during the forecast period (2025–2030). This growth is primarily driven by increasing consumer health awareness, regulatory pressure to reduce sodium in processed foods, and strong innovation in natural and clean-label salt-reducing solutions.
Key Market Insights
- Regulatory momentum is accelerating sodium reduction reformulation, as governments and health agencies push processed food manufacturers to lower sodium content to mitigate hypertension risk.
- Clean-label innovation is reshaping the ingredients landscape, with demand rising for naturally derived sodium-reduction technologies such as yeast extracts, mineral salt blends, and amino acid–based enhancers.
- Processed meat products dominate the application side, since salt plays a key role in flavor, preservation, and texture, driving heavy use of potassium-based or yeast-derived substitutes.
- North America currently leads geographically, with the U.S. market especially strong due to regulatory and consumer health pressures.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, thanks to rising processed food consumption, greater health awareness, and high reformulation potential in markets like China and India.
- Technological adoption is rising, with companies investing in microbial fermentation, flavor-microbe systems, and other biotech-based salt substitutes to deliver effective low-sodium alternatives.
What are the latest trends in the sodium reduction ingredients market?
Clean-Label and Natural Sodium Substitutes Gaining Ground
One of the strongest trends in the market is the shift toward clean-label sodium reduction ingredients. Consumers are increasingly skeptical of synthetic additives, pushing manufacturers to adopt natural alternatives like yeast extracts and mineral salt blends. Ingredient companies are responding by developing formulations that are “label-friendly,” leveraging naturally occurring minerals (such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium salts) and fermentation-derived yeast extracts to deliver saltiness and umami without relying on traditional sodium chloride. These solutions help food makers market healthier products without compromising on taste or functionality.
Biotech & Microbial Innovation
Technological innovation is reshaping the landscape of sodium reduction. Biotech-driven approaches, including microbial fermentation and “flavor-microbe” systems, are being used to create novel salt substitutes that maintain flavor and mouthfeel while minimizing sodium content. These advanced systems allow ingredient companies to fine-tune taste profiles, mitigate off-notes (like bitterness from potassium), and scale production cost-effectively. Such solutions appeal strongly to both manufacturers targeting clean-label consumers and regulatory-compliant reformulation programs.
What are the key drivers in the sodium reduction ingredients market?
Health Awareness and Public Health Pressure
Growing global awareness of the health risks associated with high sodium intake, especially hypertension and cardiovascular disease, is a major driver of demand. Consumers are becoming more conscious of their salt intake, and public health organizations are actively campaigning for reduced sodium in processed foods. This dual push from consumers and regulators incentivizes food manufacturers to incorporate sodium-reducing ingredients into their formulations.
Regulatory Targets and Voluntary Programs
Many countries are implementing sodium reduction guidelines or targets, either via voluntary industry pledges or through regulatory frameworks. These initiatives compel manufacturers to reformulate, creating consistent demand for sodium-reduction ingredients. Ingredient companies are capitalizing on this by collaborating directly with food producers to design solutions that meet sodium targets while ensuring stability, safety, and consumer acceptance.
Advances in Ingredient Technology
The development of high-performance salt substitutes such as potassium chloride blends, yeast-derived flavor enhancers, and amino-acid-based compounds has enhanced the ability of food companies to reduce sodium without compromising taste or functionality. R&D investments have made these ingredients more effective and economical over time, enabling broader adoption across food categories.
What are the restraints for the global market?
Flavor and Sensory Challenges
A key restraint is the difficulty in replicating the taste and functionality of sodium chloride. Ingredients such as potassium chloride can impart metallic or bitter off-notes, which complicates formulation. Achieving an acceptable sensory profile often requires masking strategies or complex blends, raising formulation complexity and cost.
Cost Constraints and Production Scale
Sodium-reduction ingredients, especially novel ones, typically cost more than plain table salt due to complex manufacturing and R&D costs. For food producers, especially in cost-sensitive markets, this additional expense can be a barrier to adoption. Furthermore, scaling up production (especially for biotech-based solutions) demands considerable capital investment, which can slow growth for smaller ingredient players.
What are the key opportunities in the sodium reduction ingredients industry?
Regulatory-Driven Reformulation Partnerships
There is a growing opportunity for ingredient providers to partner directly with food manufacturers in regulatory-led reformulation initiatives. As governments and health agencies set sodium reduction targets, ingredient companies can offer tailored solutions that help food businesses meet those goals. Public-private collaborations and reformulation roadmaps present a robust opportunity for innovation-driven synergies.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Rapidly growing processed food consumption in regions such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America is creating untapped demand for sodium-reduction ingredients. Manufacturers and new entrants can capture this opportunity by providing locally tailored, cost-competitive salt-reducing solutions. Exporting advanced ingredients into these high-growth regions or establishing local manufacturing could unlock significant value.
Scaling Natural & Biotech-Based Solutions
Ingredient firms that invest in clean-label biotech innovation (e.g., microbial fermentation, flavor-microbe systems) will be ideally positioned. These technologies offer powerful, taste-optimized, and scalable alternatives to traditional sodium, such as potassium chloride. As demand for natural and low-sodium products increases, biotech-based ingredients could become a preferred choice, especially for health-conscious consumers and premium food brands.
Product Type Insights
Within the market, mineral salt substitutes, particularly potassium chloride, currently dominate due to their effectiveness in reducing sodium while retaining critical functional properties. Yeast extracts and amino acid–based enhancers are also gaining strong traction; they appeal to clean-label demands and help mask the undesirable tastes of mineral salts. Biotech-derived ingredients, including microbial-fermented flavor systems, are emerging and expected to become more significant as scale and cost efficiency improve.
Application Insights
The primary application driving demand is meat, poultry & seafood processing, because these products rely heavily on salt for flavor, preservation, and texture. Bakery and snacks also use sodium-reducing ingredients widely to cater to health-conscious consumers. Ready meals and soups are increasingly being reformulated for lower sodium, as are seasonings, dressings, and sauces, where flavor maintenance is critical. Additionally, there is growing interest in nutraceuticals and functional-food applications, particularly for health-oriented products targeting blood-pressure control.
Distribution Channel Insights
Ingredient manufacturers primarily sell to food processors through B2B channels. The partnership model is strong: ingredient companies often work directly with large food producers to co-develop reformulated products. In addition, specialty ingredient suppliers also engage via distributors, especially in regions where local food companies may not have direct supply relationships. There is limited direct-to-consumer (D2C) presence, because sodium-reduction ingredients are mostly used by food companies rather than sold directly to end consumers.
End-User / Buyer Insights
The major buyers are processed food manufacturers, including those in meat, snacks, bakery, ready meals, and sauces. These companies are reformulating to meet health and regulatory demands. Food service companies (restaurants, catering) are also increasingly interested, though their ingredient volumes are smaller compared to industrial food processors. A niche but growing segment is nutraceutical firms, which use sodium reduction ingredients in health-targeted supplements. Export-driven growth is notable: many food processors in fast-developing markets import advanced sodium-reduction ingredients from ingredient suppliers in North America and Europe.
| By Product Type | By Application | By Distribution Channel | By End-Use Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America is the largest regional market, driven by the U.S., which accounts for a significant share. High consumer awareness about hypertension, strong regulatory push to reduce sodium in food, and large-scale food manufacturing infrastructure all support ingredient adoption. Reformulation is widespread, especially in processed meats, snacks, and ready meals.
Europe
Europe holds a substantial share of the market. Countries like Germany, the U.K., and France are leading in reformulation efforts due to stringent sodium reduction guidelines, health-conscious consumers, and mature food processing industries. Clean-label solutions and natural sodium substitutes are particularly popular here.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region. In countries such as China and India, the demand for processed foods is rapidly rising, and reformulation is becoming a priority for global and local food companies. Increasing health awareness, especially in urban populations, is fueling the adoption of sodium-reduction ingredients. Ingredient providers are either exporting into these markets or setting up local production to tap this growth.
Latin America
Latin America, led by Brazil and Mexico, is emerging as an important region. Rising processed-food consumption, growing middle classes, and increasing health concerns are driving the demand. However, cost sensitivity remains a challenge, so competitive pricing of sodium-reduction ingredients is critical for penetration.
Middle East & Africa
In the Middle East & Africa, demand is growing gradually. Urbanisation, rising dietary health concerns, and increasing processed food consumption are driving interest. However, infrastructure constraints and lower purchasing power in some markets may limit near-term adoption. Still, multinational ingredient suppliers are seizing opportunities via regional food processing firms.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Sodium Reduction Ingredients Market
- Cargill, Inc.
- Royal DSM N.V.
- Kerry Group Plc
- Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
- Tate & Lyle Plc
- Innophos Holdings Inc.
- Angel Yeast Co. Ltd.
- Jungbunzlauer AG
- Sensient Technologies Corporation
- Givaudan SA
- DuPont (Food Ingredients)
- Biospringer
- Corbion NV
- Advanced Food Systems Inc.
- Dr. Paul Lohmann GmbH & Co. KGaA
Recent Developments
- In 2024–2025, several ingredient companies announced partnerships with major food manufacturers to co-develop potassium chloride–based salt blends tailored for processed meats, helping reduce sodium without compromising taste or safety.
- Royal DSM and biotech firms have accelerated investments in microbial fermentation platforms to develop next-generation flavor-microbe systems for sodium reduction, targeting clean-label and scalable solutions.
- Kerry Group expanded its yeast extract production capacity to meet growing demand from food companies seeking natural umami flavors that can mask the off-taste of mineral salt substitutes.