Alternative Sweeteners Market Size
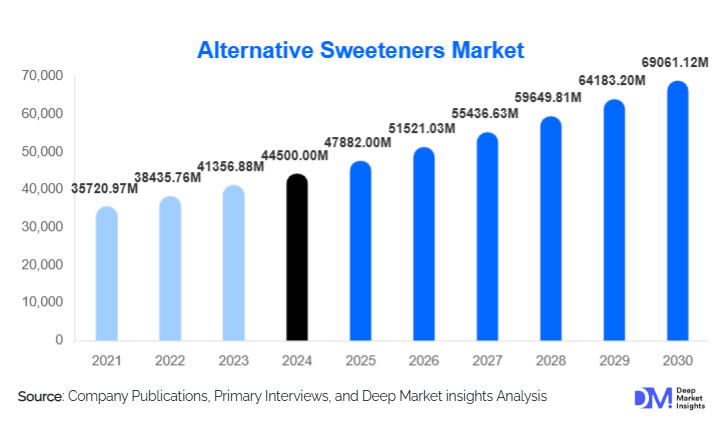
According to Deep Market Insights, the global alternative sweeteners market size was valued at USD 44,500 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 47,882 million in 2025 to reach USD 69,061.12 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period (2025–2030). Market growth is primarily driven by rising health consciousness, increasing global sugar-reduction regulations, rapid adoption of natural and low-calorie sweeteners, and continuous advancements in precision fermentation and rare-sugar technologies.
Key Market Insights
- High-intensity sweeteners remain the dominant product category, driven by their high potency, low cost, and widespread adoption in beverages and packaged foods.
- Natural sweeteners such as stevia and monk fruit are the fastest-growing segment, supported by clean-label consumer preferences and regulatory approvals across key markets.
- Asia-Pacific leads the global market, supported by rising disposable incomes, rapid urbanization, and increasing prevalence of diabetes and obesity.
- Precision fermentation and rare sugars (like allulose and tagatose) are transforming product development through improved taste profiles and sustainable production.
- Food & beverages represent over 60% of total demand, with beverage reformulation accelerating due to sugar taxes and consumer health shifts.
- Regulatory efforts to reduce caloric sugar intake across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are directly stimulating the adoption of alternative sweeteners.
What are the latest trends in the alternative sweeteners market?
Emergence of Precision-Fermented Sweeteners
Precision fermentation is reshaping the alternative sweeteners industry by enabling the production of high-purity sweet proteins and next-generation stevia glycosides without relying on agricultural raw materials. These sweeteners offer a cleaner taste, improved stability, and reduced environmental impact. Companies are leveraging engineered microbial strains to produce sweet proteins like brazzein and novel glycosides at scale. This trend supports manufacturers seeking alternatives with reduced bitterness, greater solubility, and more natural positioning. The technology is also helping reduce supply chain volatility associated with plant-derived sweeteners.
Rapid Expansion of Rare Sugars and Clean-Label Sweeteners
Rare sugars such as allulose and tagatose are gaining strong traction due to their sugar-like taste profiles and minimal caloric impact. These ingredients appeal to health-conscious consumers and manufacturers targeting keto, diabetic-friendly, and low-glycemic product lines. Clean-label demand is also accelerating the adoption of natural sweeteners such as stevia, monk fruit, and plant-derived polyols. Manufacturers are increasingly blending rare sugars with natural high-intensity sweeteners to enhance flavor profiles and reduce aftertaste. This trend aligns with rising global consumer preference for minimally processed, recognizable ingredients.
What are the key drivers in the alternative sweeteners market?
Rising Global Focus on Sugar Reduction
Governments across North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific are implementing sugar taxes, labeling mandates, and health guidelines to combat obesity and diabetes. These regulations are compelling beverage and food producers to reformulate existing products and develop new low-calorie offerings. As a result, demand for both natural and artificial sweeteners is rising significantly. Consumer awareness of sugar-related health risks is also boosting the adoption of alternative sweeteners in tabletop, beverage, supplement, and personal care applications.
Advancements in Sweetener Technology and Taste Optimization
Breakthroughs in enzymatic conversion, biotechnology, and rare-sugar synthesis are producing sweeteners that closely mimic the taste and functionality of sucrose. Improved sensory profiles, including reduced bitterness and enhanced sweetness onset, make these ingredients suitable for large-scale food & beverage reformulation. Precision fermentation enables consistent production quality and scalability, providing manufacturers with cost-effective, sustainable alternatives to traditional plant extraction. These innovations are expected to accelerate the adoption of next-generation sweeteners globally.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Production and Refinement Costs
Despite growing demand, many natural and novel sweeteners remain more expensive to produce than traditional sugar or synthetic sweeteners. Extraction for stevia and monk fruit requires significant raw material input, while rare-sugar production relies on advanced enzymatic or fermentation processes that raise costs. Price sensitivity in emerging markets can further slow adoption. Manufacturers also face challenges integrating new sweeteners into formulations without sacrificing taste or stability, often requiring additional investments in R&D.
Regulatory and Market Acceptance Barriers
Approval timelines for new sweeteners differ across regions, creating inconsistencies in global market rollout. Novel sweeteners such as allulose, certain sweet proteins, and some rare sugars may still require additional safety data in specific markets. Consumer skepticism about artificial sweeteners, especially concerning long-term health effects, continues to hinder adoption in some regions. Supply chain constraints and varying labeling requirements also limit international expansion and slow global standardization.
What are the key opportunities in the alternative sweeteners industry?
Expansion of Low-Calorie and Functional Food Categories
The growing popularity of functional beverages, sports nutrition products, zero-sugar snacks, and diabetic-friendly foods is opening new opportunities for ingredient manufacturers. Brands are increasingly incorporating sweeteners such as allulose, stevia, and polyols to meet nutritional and regulatory demands. As consumer interest in weight management and low-glycemic diets strengthens, alternative sweeteners will play a central role in product development across dairy, bakery, beverages, and nutraceuticals.
Scaling of Biotech-Enabled Sweeteners
Biotechnology-driven sweeteners represent a major growth frontier. Precision fermentation allows scalable production of sweet proteins and advanced stevia glycosides with improved sensory attributes. This unlocks new opportunities for partnerships between biotech startups and established food & beverage conglomerates. Biotech sweeteners also address environmental concerns by reducing dependence on agricultural land and water, aligning with sustainability initiatives among global food manufacturers.
Product Type Insights
High-intensity sweeteners (HIS) hold the largest market share due to their exceptionally high sweetness potency, cost efficiency, and widespread application in beverages, tabletop sweeteners, and processed foods. Low-intensity sweeteners (LIS) and sugar alcohols continue to gain momentum in bakery, confectionery, and nutraceutical applications. Rare sugars are emerging as premium options with strong growth potential due to their sugar-like taste experience. Novel sweet proteins, though still in an early phase, are expected to gain meaningful traction as fermentation costs decrease.
Application Insights
The food & beverage segment dominates the market, accounting for over 60% of global consumption. Beverage reformulation is the single largest application, driven by sugar taxes and demand for zero-calorie drinks. Bakery and confectionery manufacturers are increasingly adopting polyols and rare sugars to replicate sugar’s mouthfeel. Pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals represent one of the fastest-growing applications, with sweeteners used extensively in syrups, chewables, supplements, and oral-care products. Personal care applications, especially toothpaste and mouthwash, continue to expand as brands adopt non-cariogenic sweeteners like xylitol.
Distribution Channel Insights
Ingredient distributors and B2B supply chains remain the dominant channels for alternative sweeteners, given their extensive use in industrial food production. However, direct-to-consumer (D2C) sales via e-commerce platforms are rising as consumers seek tabletop sweeteners for home use. Food ingredient marketplaces and specialty distributors play key roles in supplying rare sugars and fermentation-derived sweeteners to niche manufacturers. Increasing digitalization of ingredient procurement is driving the adoption of online B2B marketplaces and direct manufacturer portals.
End-User Insights
Large-scale food & beverage manufacturers represent the primary end-users, leveraging alternative sweeteners to reformulate legacy products and develop zero-sugar variants. Nutraceutical and pharmaceutical companies are expanding sweetener usage to improve flavor masking and palatability in supplements and medications. SMEs and specialty food brands are showing strong interest in clean-label sweeteners as part of premium product positioning. Consumer households continue to adopt tabletop natural sweeteners due to rising health awareness.
Age Group Insights
Consumers aged 31–50 represent the largest demand group, driven by high health awareness and purchasing power. The 18–30 segment drives growth in natural and clean-label sweeteners, especially through fitness, keto, and low-sugar lifestyle trends. Older consumers (51–65) show strong adoption of diabetic-friendly sweeteners due to metabolic health considerations. The 65+ demographic increasingly relies on alternative sweeteners in medical nutrition products and low-glycemic dietary plans.
| By Product Type | By Form | By Application | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America accounts for a significant share of global demand, driven by high consumption of diet beverages, strong regulatory pressure to reduce sugar intake, and early adoption of rare sugars like allulose. The U.S. remains a major hub for biotech innovation in sweet proteins and fermentation-based sweeteners. Major food brands continue reformulating products to meet evolving consumer and regulatory demands.
Europe
Europe is a rapidly growing market driven by stringent sugar-reduction policies, high consumer preference for natural ingredients, and strong demand for clean-label products. Countries such as the U.K., Germany, and France lead adoption in the beverages, bakery, and confectionery sectors. European manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D to improve taste profiles and expand the usage of natural sweeteners.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the largest and fastest-growing region, driven by increasing diabetes prevalence, rising health consciousness, and expanding processed food consumption. China and India are key growth engines, with strong demand for both artificial and natural sweeteners. The region also serves as a major production hub for stevia, supporting global supply chains.
Latin America
Latin America is witnessing steady growth supported by rising adoption of low-calorie beverages, growing health awareness, and evolving food industry standards. Mexico and Brazil show strong demand for sugar-reduced beverages as obesity and diabetes rates rise. Local manufacturers are gradually increasing the usage of natural sweetener blends.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East is emerging as an important growth market with increasing preference for sugar-free beverages and premium health products. Africa shows potential for future expansion as awareness of metabolic health issues rises. Import reliance remains high due to limited local production capabilities, creating opportunities for suppliers.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Alternative Sweeteners Market
- Tate & Lyle
- Cargill
- Archer Daniels Midland (ADM)
- Ingredion
- Ajinomoto
- DuPont (IFF)
- PureCircle
- Roquette
- Amai Proteins
- Stevia Corp
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, a leading biotechnology company expanded its precision fermentation facility to increase production of sweet proteins used in low-calorie beverages.
- In March 2025, several global beverage brands announced reformulated, sugar-free product lines using rare sugars such as allulose and tagatose.
- In January 2025, multiple ingredient manufacturers introduced next-generation stevia blends designed to reduce bitterness and improve taste performance in carbonated drinks.