Wearable Inertial Sensors Market Size
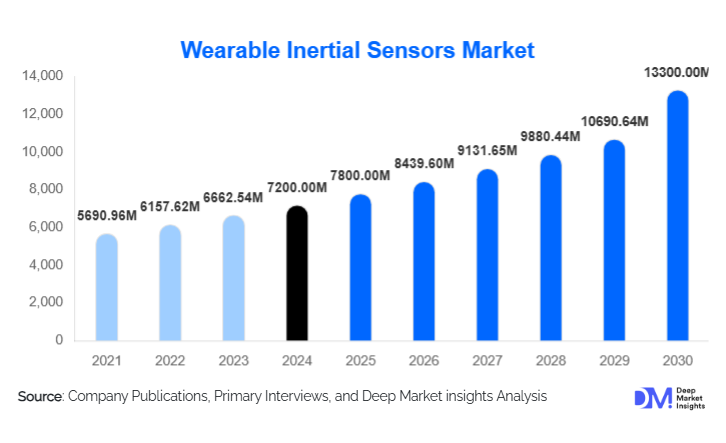
According to Deep Market Insights, the global wearable inertial sensors market was valued at approximately USD 7,200 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from about USD 7,800 million in 2025 to reach nearly USD 13,300 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8.2% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market expansion is underpinned by rising demand for embedded motion sensing in consumer wearables, growth of remote health monitoring, and increasing integration of inertial sensors into industrial, safety, and AR/VR systems.
Key Market Insights
- Accelerometers continue to dominate sensor type share, being the most deployed and cost-efficient sensor in wearables, especially in fitness and consumer electronics products.
- 3-axis sensor configurations lead among axis types, offering the right balance of functionality vs cost and power consumption for mainstream wearable designs.
- Wearable bands and watches represent the highest revenue among form factors owing to their mass adoption in fitness, health tracking, and consumer electronics.
- Wireless connectivity (Bluetooth/BLE, WiFi, ANT+) captures a major share, enabling seamless data offload from devices to smartphones or cloud platforms.
- Sports & fitness tracking is the largest application segment, driven by consumer interest in activity monitoring, performance analytics, and quantified health metrics.
- Consumer electronics is the dominant end-use sector, integrating inertial sensors into smartwatches, fitness bands, gaming devices, and AR/VR hardware.
Latest Market Trends
Sensor Fusion & Edge Intelligence
Wearable devices increasingly combine accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers, and complementary sensors (e.g., optical, environmental) with on-device machine learning to reduce drift, improve orientation estimation, and deliver smarter motion insights. Embedding lightweight AI at the sensor level helps filter noise, calibrate sensor biases dynamically, and provide actionable analytics locally, reducing reliance on continuous cloud connectivity. This trend is helping wearable inertial sensors move from raw data providers to embedded smart motion subsystems.
Textile & Flexible Sensor Integration
Miniaturization and advances in flexible electronics have paved the way for inertial sensors being embedded directly into fabrics, patches, or garment fibers. Smart clothing with motion-sensing capability is gaining traction in sports, posture monitoring, rehabilitation, and posture correction domains. This allows more natural, unobtrusive wearables that track full-body movement with less user friction than rigid devices.
Market Drivers
Growing Health & Wellness Awareness
Consumers are increasingly adopting wearable devices to monitor activity, fall risk, gait, posture, and mobility trends. Governments and healthcare systems are promoting preventive and remote care models, which encourage the use of motion wearables. The awareness of chronic diseases, obesity, and aging populations further fuels demand for continuous motion monitoring.
Advances in MEMS & Low-Power Innovations
Progress in MEMS fabrication, power management, packaging, and materials allows sensors to become smaller, more sensitive, and more energy efficient. This enables embedding inertial sensors into limited form factors (patches, textiles, watches) without excessive power draw. The cost per unit is also falling, helping expansion into lower-cost wearables and emerging markets.
IoT / Connectivity & Data Ecosystems
Seamless wireless integration through BLE, WiFi, and edge/cloud ecosystems allows inertial sensor data to feed into analytics, health apps, coaching platforms, and safety systems. The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) accelerates demand for motion sensing as part of interconnected devices in fitness, smart homes, safety, and industrial monitoring.
Market Restraints
Battery & Power Limitations
Wearable devices must balance continuous motion sampling with battery life constraints. High sampling rates, multi-axis sensing, and wireless transmission consume energy. This power tradeoff limits the complexity or duration of usable sensing and requires additional innovations in ultra-low power design.
Sensor Drift, Calibration & Regulatory Compliance
Inertial sensors suffer from drift and require calibration, especially for long-term accuracy. Maintaining reliability in varied temperature, motion, and user contexts is challenging. Additionally, in medical or industrial domains, devices must meet stringent regulatory standards (FDA, CE, ISO), which increase development time, validation cost, and compliance burden.
Market Opportunities
Wearable Motion for Healthcare & Rehabilitation
There remains a large untapped potential in integrating inertial sensors into medical devices for gait analysis, fall detection, post-operative rehabilitation, Parkinson’s monitoring, and home physiotherapy. Partnerships with hospitals, insurers, telemedicine providers, and regulatory incentives can pave adoption in this domain. Wearables that can reliably demonstrate clinical value may qualify for reimbursement and institutional adoption.
Industrial Safety, Ergonomics & Occupational Monitoring
Employers and regulators are increasingly requiring monitoring of worker movement, posture, fatigue, and fall risks in hazardous or repetitive tasks (construction, mining, logistics). Embedded inertial sensors in helmets, vests, and wearables can provide real-time alerts for unsafe postures or motion anomalies, reduce injury risk, and feed data to safety analytics platforms.
Emerging & Under-penetrated Geographies
Regions such as India, Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa present growth opportunities due to rising disposable incomes, increasing health awareness, smartphone penetration, and lower starting baselines of wearable adoption. Local manufacturing policies (e.g., “Make in India”) can reduce import costs, encourage domestic OEMs, and unlock new markets. Early movers in these markets can capture share before saturation sets in.
Segmental Insights
From the segmentation established, here are insights into the leading sub-segments in 2024 and their approximate shares:
Accelerometers (Sensor Type): 45 % – Because of their lower cost, small size, and essential role in basic motion detection across nearly all wearables, accelerometers remain the dominant contributor to revenue and volume.
3-Axis configuration (Axis): 40 % – Most wearable devices adopt 3-axis accelerometers (and often 3-axis gyros) for orientation and motion sensing, making 3-axis the standard choice, balancing performance and complexity.
Wearable Bands & Watches (Form Factor): 35 % – Smartwatches and fitness wristbands are broadly adopted by consumers and represent the largest slice of wearable inertial sensor usage.
Wireless Connectivity (Bluetooth/BLE etc.): 55 % – The wireless interface is dominant as wearables are expected to be wire-free and interact with phones / IoT ecosystems.
Sports & Fitness Tracking (Application): 30 % – Many motion sensor deployments begin in sports/fitness (step counting, activity metrics, motion analytics), securing this as a foundational application.
Consumer Electronics (End Use): 35 % – Devices like smartwatches, AR/VR units, and gaming wearables absorb a large share of sensor demand by volume and revenue.
North America (Region): 40 % – The region leads due to high technology adoption, strong consumer base, and high R&D and health infrastructure investment.
Each of these segments reflects both historical dominance and ongoing trends: cost efficiency, scale in consumer wearables, and growing applications in health, AR/VR, and industrial safety.
End-Use Demand Analysis
The demand for wearable inertial sensors is strongest in the consumer electronics and fitness sectors, but the fastest growth lies in healthcare and industrial safety segments. In healthcare, the push for remote patient monitoring, fall detection for elderly populations, gait analysis, and rehabilitation wearable systems is fueling new demand. In industrial settings, companies are increasingly deploying wearables to monitor posture, fatigue, motion abnormalities, and compliance with occupational safety standards. Beyond these, emerging applications in smart clothing, gesture control in AR/VR, esports motion mapping, and full-body motion capture are creating new use cases. Because many wearables are manufactured in Asia and exported globally, parts suppliers and sensor manufacturers benefit from export-driven demand. As wearable device shipments in fitness, smartwatches, AR/VR, and industrial safety grow (often double-digit growth annually), the inertial sensor component demand scales proportionally. The correlation between the growth of end-use sectors and inertial sensor demand is strong, making expansion in large verticals (healthcare, industrial) key to scaling the market.
| By Sensor Type | By Axis Configuration | By Form Factor | By Connectivity | By End-Use Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America leads the global wearable inertial sensors market, accounting for roughly 40 % of the market value in 2024. The U.S. is the primary driver, given its mature consumer electronics market, healthcare system openness to digital health, strong R&D presence, and major wearable device firms. High incomes, early adoption of health/performance monitoring, and supportive regulation make this region a mature, high-margin market. Growth remains solid but somewhat moderating as saturation in consumer wearables increases.
Europe
Europe holds about 20–25 % of the global share in 2024, driven by demand in Germany, the UK, France, and Italy. The region emphasizes regulatory compliance (medical wearables), data privacy, and industrial applications (safety, ergonomics). Adoption is strong in fitness, medical monitoring, and AR/VR, though growth is more moderate due to higher cost sensitivity and regulatory barriers.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is one of the fastest-growing regions, with perhaps a 25–30 % share in 2024 and projected higher CAGR ahead. China leads due to domestic manufacturing capacity and a large consumer base. India, Southeast Asia, and South Korea are growth engines as wearable adoption increases. Lower costs, high population, rising health awareness, and supportive manufacturing policies help accelerate this region’s expansion. India may see double-digit growth rates given the low base effect.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for a smaller share ( 5–10 %) in 2024, with Brazil and Mexico as the primary markets. Growth is moderate, driven by rising smartphone penetration, health & fitness awareness, and remote care adoption. The affordability challenge remains, but niche premium wearables, sports & health segments offer pockets of opportunity.
Middle East & Africa
This region commands the smallest share ( 5 %) in 2024. UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are leaders within the region, with demand from luxury consumer devices, health/fitness markets, and government health initiatives. Growth is steady as infrastructure improves and awareness rises. Intra-African adoption, local import/export dynamics, and health monitoring needs in remote areas also drive niche demand.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Wearable Inertial Sensors Market
- Bosch Sensortec
- STMicroelectronics
- TDK / InvenSense
- Analog Devices
- Texas Instruments
- NXP Semiconductors
- Qualcomm
- Samsung Electronics
- Sensirion
- Xsens
- MEMSIC
- Honeywell
- Kionix
- Sony
- Apple
Recent Developments
- In 2024, several MEMS sensor firms announced next-generation low-drift IMU chips for wearable applications, targeting smaller footprints and lower power budgets.
- In early 2025, a major wearable device manufacturer released a smart textile line embedding inertial sensors for posture and gait tracking, highlighting integration trends.
- In mid-2025, a large semiconductor company acquired a motion-sensor IP startup to boost its sensor fusion and embedded AI capabilities.