Smart Trash Bin Market Size
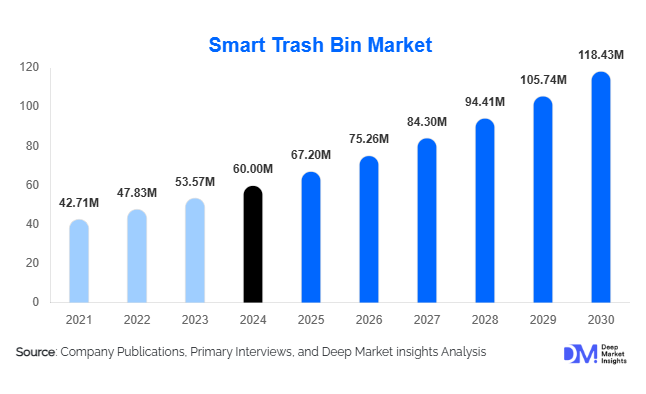
According to Deep Market Insights, the global smart trash bin market size was valued at USD 60 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 67.20 million in 2025 to reach USD 118.43 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 12.0% during the forecast period (2025–2030). Market growth is primarily driven by the adoption of IoT-enabled waste management systems, increasing hygiene concerns in public and commercial environments, and expanding smart-city infrastructure investments worldwide.
Key Market Insights
- Smart-city expansion and public infrastructure digitization are accelerating the adoption of connected waste-management solutions.
- Commercial applications dominate due to higher waste generation, strict hygiene standards, and facility automation initiatives.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, supported by urbanization, government smart-city projects, and lower sensor costs.
- IoT and AI integration are transforming waste collection efficiency and enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Multi-compartment bins lead demand, reflecting growing recycling mandates and environmental regulations.
- Falling sensor prices and maturing wireless infrastructure are enhancing affordability and scalability across end-users.
Latest Market Trends
IoT-Enabled Waste Optimization
Smart trash bins equipped with ultrasonic fill-level sensors, wireless communication modules, and data dashboards are redefining municipal and commercial waste collection. Real-time monitoring enables route optimization, fuel savings, and reduced collection frequency. Many city authorities are deploying networked bins to minimize overflow incidents, improve sanitation, and enhance resource utilization. Integration with cloud analytics platforms provides actionable insights, turning waste collection into a data-driven service.
Rising Adoption in Smart Homes and Offices
Touchless smart bins featuring motion sensors, voice control, and odor-control technology are increasingly popular in residential and office environments. These products enhance hygiene and convenience, aligning with the global post-pandemic focus on cleanliness. Integration with voice assistants and home-automation platforms such as Alexa and Google Home is becoming a differentiator, while corporate facilities embrace smart bins to improve sustainability reporting and waste segregation compliance.
Smart Trash Bin Market Drivers
Urbanization and Smart-City Initiatives
Rapid urban growth and government-backed smart-city programs are driving installations of connected bins across municipal zones, transport hubs, and public parks. Countries such as China, India, Saudi Arabia, and the U.S. are investing heavily in smart infrastructure to improve waste-collection efficiency and reduce environmental impact. These projects directly expand the market for networked waste-collection devices.
Increasing Hygiene and Operational Efficiency Needs
Post-COVID hygiene awareness, coupled with the desire to automate waste-handling processes, has boosted demand for touch-free and self-compacting bins. In airports, hospitals, and commercial offices, smart bins minimize manual contact, enhance cleanliness, and cut labor requirements. Businesses adopting ESG frameworks view these solutions as tangible steps toward sustainable operations.
Technological Advancements and Cost Declines
Continuous improvements in sensor accuracy, battery efficiency, and low-power connectivity (LoRaWAN, NB-IoT) are lowering production costs. Economies of scale and local manufacturing incentives such as “Make in India” further reduce end-user prices, increasing adoption among municipalities and building managers worldwide.
Market Restraints
High Upfront Cost and Limited ROI Awareness
Smart trash bins require higher capital investment compared with conventional alternatives. Many smaller municipalities and SMEs are hesitant due to uncertain return-on-investment calculations. Without awareness of long-term savings in fuel, labor, and maintenance, adoption remains slower in price-sensitive regions.
Integration and Standardization Challenges
The lack of unified IoT communication standards across municipal waste-management systems limits interoperability. Data fragmentation and inconsistent infrastructure, particularly in developing markets, restrict scalability and reduce the perceived benefits of smart-bin networks.
Smart Trash Bin Market Opportunities
Municipal Smart-Infrastructure Expansion
Governments worldwide are deploying large-scale smart-city projects that include digital waste-collection networks. These initiatives create long-term public procurement opportunities for manufacturers offering scalable IoT-enabled bin ecosystems, integrated monitoring dashboards, and analytics services. Partnerships with city councils and environmental agencies will generate recurring revenue from service contracts.
Integration with Analytics and Subscription Services
Beyond hardware sales, recurring software and maintenance models such as “waste-management-as-a-service” offer high-margin opportunities. Companies can leverage predictive analytics to forecast waste volume trends, enabling dynamic pricing and performance-based contracts. Subscription models for liner replacement, battery management, and sensor analytics are expected to boost recurring revenue streams.
Residential and Commercial Smart-Home Adoption
As smart homes and IoT-enabled offices proliferate, demand for compact, design-centric smart bins is surging. Integrating waste tracking with broader sustainability dashboards offers value to both consumers and corporations. This segment also presents opportunities for appliance brands to expand into waste-management accessories and connected ecosystems.
Product Type Insights
Automatic bins dominate the market, representing about 55–60% of global revenue in 2024. These models employ motion sensors for lid activation, built-in compaction, and IoT connectivity. Semi-automatic bins remain relevant in lower-income markets, offering affordability with limited automation. However, automatic variants are expanding fastest due to hygiene and labor-saving benefits across commercial and public installations.
Capacity Insights
The 14 – 23 gallon capacity segment leads globally with roughly 40% share in 2024. This category balances size and practicality for offices, malls, and hospitals, where moderate waste volumes require frequent disposal. Larger units above 23 gallons are primarily deployed outdoors or in municipal contexts, while smaller 8 – 13-gallon bins cater to residential kitchens and compact spaces.
End-User Insights
Commercial applications, including offices, airports, and healthcare facilities, account for about 60% of global revenue. The segment benefits from mandated hygiene protocols, sustainability initiatives, and centralized waste-management budgets. Residential adoption is growing steadily with smart-home proliferation, while municipal and public-infrastructure deployments are poised for rapid scale-up under smart-city programs in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East.
| By Product Type | By Capacity | By Power Source | By Connectivity | By End-Use Industry | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America leads the market with a 30–35% revenue share in 2024. The U.S. dominates regional demand due to advanced IoT infrastructure, high hygiene standards in commercial facilities, and government emphasis on sustainable waste solutions. Public-private partnerships and strong adoption in airports, universities, and tech campuses underpin continued growth.
Europe
Europe holds approximately a 25–30% share, driven by stringent recycling mandates and ESG regulations. Germany, the U.K., and France spearhead adoption through municipal sustainability programs and corporate waste-reduction goals. Retrofit opportunities in historic cities and expanding public funding for circular-economy initiatives further support market penetration.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for roughly 20–25% of 2024 revenue but is the fastest-growing region with an expected CAGR of 15–16%. China and India lead smart-city deployments, while Japan and South Korea focus on automation and robotics integration. Rapid urbanization and domestic manufacturing capabilities position APAC as the global growth engine for smart trash bins.
Middle East & Africa
This region contributes about 10–15% of 2024 revenue, led by the UAE and Saudi Arabia under national smart-city frameworks like Vision 2030 and Smart Dubai. African municipalities are beginning pilot programs in Kenya, South Africa, and Nigeria to modernize waste-collection efficiency through sensorized bins.
Latin America
Latin America represents around a 5–10% share, with Brazil and Mexico emerging as early adopters. Growing tourism, retail infrastructure, and sustainability awareness are expected to gradually expand the adoption of connected waste-management devices across metropolitan areas.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Top 15 Key Players
- Ecube Labs Co., Ltd.
- Big Belly Solar Inc.
- iTouchless Housewares & Products Inc.
- Simplehuman LLC
- EKO North America Inc.
- CleanRobotics Technologies Inc.
- Nine Stars Group Inc.
- Binology LLC
- Ausko Pte Ltd.
- Sensortec s.r.o.
- EvoEco Inc.
- Home Depot Inc. (Appliance Division)
- HANGSHAU Houseware Co., Ltd.
- TerraCycle Systems Ltd.
- SmartBin Solutions Ltd.
Recent Developments
- June 2025: Ecube Labs announced a partnership with the Seoul Metropolitan Government to deploy 5,000 IoT-enabled smart bins integrated with route-optimization software.
- April 2025: Big Belly Solar launched a new solar-powered compactor bin featuring AI-based fill-level prediction to reduce overflow incidents by 40%.
- February 2025: CleanRobotics Technologies introduced “TrashBot 2.0,” an AI-assisted waste-sorting bin aimed at commercial buildings and airports in North America.