Shredding Equipment Market Size
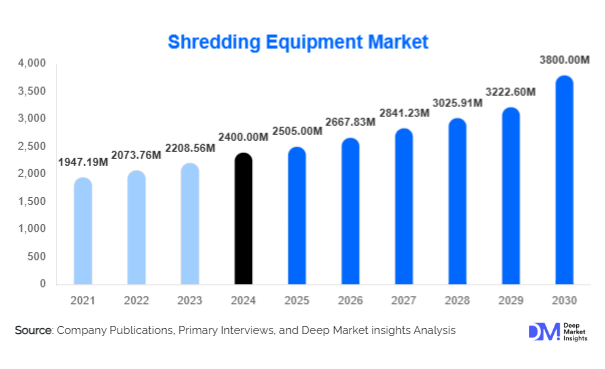
According to Deep Market Insights, the global shredding equipment market size was valued at USD 2,400 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 2,550 million in 2025 to reach USD 3,800 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market growth is primarily driven by increasing volumes of municipal and industrial waste, stringent environmental regulations, growing demand for recycling and secure document destruction, and rising adoption of advanced, energy-efficient, and automated shredding technologies.
Key Market Insights
- Twin-shaft shredders dominate globally, offering an optimal balance of throughput, cost-efficiency, and versatility in handling diverse waste materials, including plastics, wood, and municipal solid waste.
- Municipal solid waste and recycling applications lead the demand, reflecting increasing regulatory pressures for landfill diversion and recycling targets across Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific.
- Waste management and recycling companies remain the largest end-users, particularly in developed regions where investments in high-capacity, high-efficiency shredders are prioritized.
- North America and Europe account for nearly half of the global market share, driven by mature regulatory frameworks, advanced infrastructure, and high adoption of automated, smart shredding solutions.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with rapid urbanization, industrialization, and government initiatives in India, China, and Southeast Asia boosting equipment demand.
- Technological integration, including IoT-enabled monitoring, predictive maintenance, energy-efficient drives, and mobile shredders, is enhancing operational efficiency and attracting new industrial users.
Latest trends in Shredding Equipment Market
Integration of Smart and IoT-Enabled Shredders
Manufacturers are increasingly embedding sensors, IoT monitoring, and predictive maintenance systems into shredding equipment. These features allow operators to remotely monitor load, detect jams, optimize energy consumption, and schedule maintenance proactively. The trend is particularly significant in industrial and municipal applications, where downtime is costly, and efficiency is critical. Smart shredders also support real-time reporting, enabling compliance with environmental and safety regulations while reducing operational costs.
Adoption of Mobile and Modular Shredding Units
Mobile shredding units are gaining traction for on-site applications in construction, demolition, e-waste processing, and disaster debris management. Modular designs are enabling easy maintenance and scalability, while also reducing downtime. The portability of these units allows for flexible deployment, meeting the increasing demand for decentralized shredding operations and catering to regions with emerging infrastructure. driver market
Rising Waste Generation and Regulatory Pressure
The rapid increase in municipal solid waste, industrial scrap, plastics, and electronic waste worldwide is driving the adoption of shredding equipment. Governments in North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific are imposing stricter regulations on waste management, recycling targets, and e-waste handling, incentivizing municipalities and industries to invest in efficient shredding solutions. This trend is expected to continue as urbanization and industrial growth accelerate.
Technological Advancements and Energy Efficiency
Innovations such as slow-speed high-torque shredders, energy-efficient electric drives, hybrid systems, and automation have improved machine reliability and reduced operational costs. Industrial operators prefer machines with lower total cost of ownership, which includes energy savings, minimal maintenance downtime, and longer component lifespans. Adoption of these advanced technologies is a significant growth driver for the market.
Shredding Equipment Market Restraints
High Capital and Maintenance Costs
Industrial shredders require significant upfront investment, particularly for high-capacity, multi-shaft, and smart equipment. Ongoing maintenance, blade replacements, and energy costs can be substantial, limiting adoption among small-to-medium enterprises and budget-constrained municipalities. Financing challenges and long payback periods act as barriers to market expansion.
Fragmented Standards and Material Heterogeneity
Shredding equipment must handle diverse waste types with varying moisture content, hardness, and contamination. Differences in regulatory standards across regions complicate machine design, increasing production costs and reducing standardization. Additionally, supply chain volatility for steel, motors, and wear parts impacts pricing and profitability, restricting rapid market growth.
Shredding Equipment Market Opportunities
Expansion through Environmental Regulations and Public Policy
Governments worldwide are promoting recycling, landfill diversion, and e-waste processing. Public funding, subsidies, and mandates provide opportunities for manufacturers to supply high-efficiency shredders to municipalities and industrial recyclers. Companies that align their equipment with environmental compliance requirements can capitalize on growing demand.
Technological Differentiation and Product Innovation
Integration of automation, IoT-enabled monitoring, modular design, and energy-efficient drives presents an opportunity to differentiate products. High-tech shredders that reduce operational costs and improve safety appeal to industrial and municipal clients, creating avenues for premium pricing and stronger market positioning.
Untapped Regional Markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America
Developing regions are witnessing rapid urbanization, industrialization, and rising waste generation. Countries such as India, China, Brazil, and Southeast Asian nations represent high-growth markets with increasing investment in waste infrastructure. Localized manufacturing, partnerships, and flexible solutions for diverse materials can help new entrants and existing players expand their footprint.
Product Type Insights
Twin-shaft shredders lead the market due to their versatility, reliability, and cost-efficiency in processing diverse materials. Single-shaft shredders are used for low-to-medium capacity operations, while granulators cater to specialized recycling applications like plastics and rubber. Slow-speed high-torque designs are gaining traction for heavy-duty industrial and municipal waste applications due to energy efficiency and low maintenance. Mobile shredders are emerging for on-site processing of construction, demolition, and e-waste.
Application Insights
Municipal solid waste and recycling dominate applications, followed by paper/document shredding, plastic and metal recycling, and e-waste processing. Construction and demolition waste management, biomass processing, and secure document destruction are emerging applications driving incremental growth. Demand is increasing for shredders capable of handling mixed and contaminated materials efficiently, aligning with circular economy initiatives.
End-Use Insights
Waste management and recycling companies are the largest end-users, accounting for roughly 30–35% of global demand. Automotive recycling, electronics/e-waste processing, construction & demolition, and government/municipalities are growing rapidly, driven by regulatory mandates and industrial expansion. Secure document destruction and biomass processing are niche but fast-growing segments, especially in regions prioritizing data security and renewable energy.
| By Product Type | By Application | By End-Use | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America remains the largest market, with the U.S. and Canada accounting for approximately 35–40% of the global 2024 market. Mature regulatory frameworks, high waste processing capacity, and adoption of advanced shredding technologies drive demand. Municipal, industrial, and e-waste processing are key contributors.
Europe
Europe accounts for about 20–30% of the global market in 2024, led by Germany, the U.K., and France. Strong environmental regulations, recycling infrastructure, and a focus on energy-efficient equipment drive adoption. Eastern Europe is the fastest-growing subregion due to the modernization of waste management systems.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, led by India, China, and Southeast Asia. Rapid urbanization, industrialization, and rising waste generation are fueling demand. Governments are investing heavily in waste processing infrastructure, presenting opportunities for local and international equipment suppliers.
Latin America
Latin America, primarily Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina, is gradually adopting shredding equipment, driven by urbanization and industrial growth. Outbound imports of high-capacity shredders are rising to support municipal and industrial recycling initiatives.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa hold a smaller share (~5–7%) but are witnessing rising demand, particularly in GCC countries and South Africa. Investments in municipal solid waste management, e-waste recycling, and infrastructure development are driving growth.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Shredding Equipment Market
- SSI Shredding Systems, Inc.
- Vecoplan LLC
- UNTHA Shredding Technology GmbH
- Weima Maschinenbau GmbH
- Lindner Recyclingtech GmbH
- Komptech GmbH
- Shred-Tech Corporation
- Harden Machinery Ltd
- BCA Industries
- Genox Recycling Tech Co., Ltd.
- Allegheny Shredders, Inc.
- Brentwood Recycling Systems
- Granutech-Saturn Systems
- Zerma Machinery & Recycling Technology
- Williams Patent Crusher and Pulverizer Co., Inc.
Recent Developments
- In 2025, SSI Shredding Systems launched an IoT-enabled twin-shaft shredder line for high-capacity municipal waste processing, improving operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities.
- In 2025, UNTHA Shredding Technology introduced modular shredders for e-waste and plastics, enabling flexible deployment and easy maintenance in Asia-Pacific and Latin America.
- In 2025, Vecoplan LLC expanded its mobile shredding equipment portfolio for construction and demolition applications, focusing on on-site processing and reducing transportation costs.