Hospitality Robots Market Size
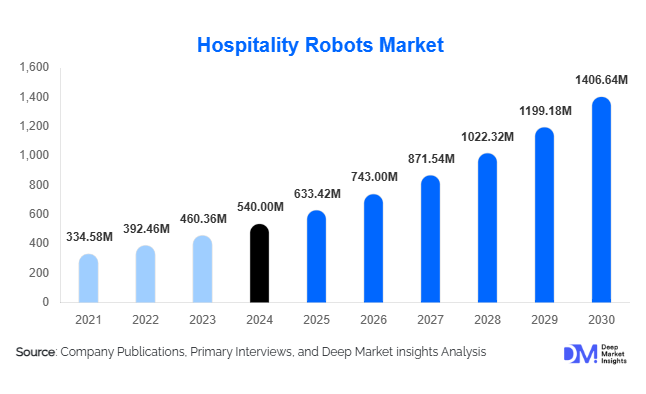
According to Deep Market Insights, the global hospitality robots market size was valued at USD 540 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 633.42 million in 2025 to reach USD 1,406.64 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 17.3% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The rapid adoption of robotics across hotels, restaurants, and tourism venues is driven by growing labor shortages, heightened hygiene requirements, and the integration of AI-enabled automation for superior guest experiences. With advances in autonomous navigation, natural language processing, and robot-as-a-service models, hospitality robots are moving from pilot installations to mainstream adoption worldwide.
Key Market Insights
- Hospitality robots are transforming guest interactions through contactless check-in, in-room delivery, and concierge services that enhance operational efficiency and brand differentiation.
- Hardware components dominate the market with over 60% share in 2024, as demand surges for delivery, cleaning, and service robots in commercial properties.
- Delivery robots lead by application, capturing nearly 40% of the 2024 market value, as hotels and restaurants adopt robotic logistics for room service and amenity transport.
- North America holds the largest regional share (38%), supported by high labor costs, advanced infrastructure, and a strong ecosystem of robotics providers.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by expanding tourism, smart-hotel projects, and local robotics manufacturing in China, Japan, and South Korea.
- Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) models are lowering capital costs and enabling scalable deployment across hotel chains and independent properties.
Latest Market Trends
AI-Powered Guest Interaction and Personalization
Hospitality robots are increasingly powered by artificial intelligence, enabling contextual conversations, multilingual support, and data-driven personalization. Front-desk robots integrated with natural language processing can respond to guest queries, offer recommendations, and streamline check-ins without human intervention. Machine learning algorithms are being used to predict guest preferences, automate concierge responses, and personalize service delivery. The combination of AI, facial recognition, and property management system integration is enhancing the overall guest experience while reducing staff workload and improving brand engagement.
Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) Adoption Accelerating
RaaS business models are transforming the economic feasibility of hospitality robotics. Instead of large upfront investments, hotels can now lease or subscribe to robot fleets with bundled maintenance and software upgrades. This pay-per-use model makes automation accessible for small and mid-sized operators and ensures technology updates without major capital costs. Vendors offering analytics dashboards and remote fleet management are creating recurring revenue streams while helping hotels optimize robot utilization and efficiency. The rise of RaaS is expected to double the number of properties deploying robots between 2025 and 2030.
Hospitality Robots Market Drivers
Severe Labor Shortages and Rising Wage Pressures
Hospitality sectors worldwide are experiencing acute staffing challenges and high turnover rates. Robots capable of performing repetitive, time-consuming tasks such as room deliveries, cleaning, and information assistance are helping to offset workforce gaps. Hotels deploying service robots report operational cost savings of 20–35% and improved turnaround times. This structural labor shortage, particularly acute in North America and Europe, is the single strongest catalyst for automation in hospitality operations.
Shift Toward Contactless and Hygienic Guest Experiences
Post-pandemic guest behavior has permanently shifted toward minimal-contact, high-hygiene service environments. Robots enable secure delivery of food, luggage, and amenities without human touchpoints, meeting safety expectations while enhancing brand trust. Cleaning and UV-C disinfection robots are now standard in many large hotel chains. This trend aligns with growing consumer preference for technology-driven, touch-free interactions that combine safety and novelty.
Technological Maturity and Cost Reduction
Rapid improvements in LiDAR navigation, SLAM mapping, IoT connectivity, and affordable AI modules have significantly reduced robot production costs. Integration with property management systems, cloud analytics, and voice-assistant interfaces has made modern robots more intelligent and user-friendly. This technological maturity is driving adoption across mid-scale hotels and restaurants that previously found robotics cost-prohibitive.
Market Restraints
High Initial Investment and ROI Uncertainty
Despite cost reductions, upfront investment in robotics hardware, integration, and staff training remains substantial. Many smaller hospitality operators hesitate due to long payback periods and uncertainty around consistent utilization. Maintenance contracts and software updates add to recurring expenses, creating adoption barriers for independent establishments.
Integration Complexity and Guest Acceptance
Integrating robots with existing IT systems and ensuring seamless operation in dynamic guest environments is challenging. Safety regulations, corridor navigation, and aesthetic acceptance play critical roles. Some guests still prefer human interaction, requiring operators to balance automation with personalized service. Poorly implemented robotics may risk guest satisfaction and brand perception.
Hospitality Robots Market Opportunities
Smart Tourism and Infrastructure Initiatives
National programs such as “Smart Dubai”, “Made in China 2025”, and “Japan Society 5.0” are promoting intelligent infrastructure and automation in hospitality. Government-backed tourism and urban innovation projects are integrating robotics into hotels, airports, and entertainment complexes. This creates strong opportunities for suppliers and investors to align with public–private partnerships and technology grants.
Advanced AI and Multimodal Integration
Next-generation hospitality robots are incorporating AI, voice recognition, facial analysis, and autonomous decision-making to deliver seamless service experiences. Vendors that develop interoperable ecosystems connecting robots with IoT-enabled rooms, property management software, and customer analytics can expand value creation beyond hardware sales. These integrations open new recurring revenue channels through data services and predictive maintenance.
Emerging Market Expansion
Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and parts of Latin America present enormous untapped potential. Tourism development projects and rising disposable incomes are accelerating hotel and resort construction, creating demand for robotic service solutions. Local assembly and regional distribution partnerships reduce import costs and make robots more accessible, particularly in China, India, and Saudi Arabia, which are expected to drive future market volume growth.
Product Type Insights
Delivery robots lead the market with approximately 40% of total revenue in 2024, owing to clear ROI and ease of integration into hotel and restaurant operations. Cleaning and disinfection robots follow, supported by hygiene mandates and efficiency needs. Front-desk and concierge robots are emerging rapidly in upscale and technology-forward hotels to improve brand differentiation. Security and surveillance robots remain niche but are gaining adoption in large resorts and casinos requiring 24/7 monitoring.
Component Insights
Hardware dominates with over 60% share in 2024, as most spending is directed toward robots, sensors, actuators, and navigation systems. However, software and services are the fastest-growing components, driven by upgrades, AI module integration, and fleet management systems. Vendors focusing on platform-agnostic software and analytics are expected to capture rising recurring revenues.
End-Use Insights
Hotels represent nearly 50% of the total market value, as they adopt robots for room service, cleaning, and front-desk tasks. Restaurants and bars are the fastest-growing end-use, leveraging robots for table service, delivery, and food-handling automation. Airports, cruise lines, and resorts are emerging secondary markets, driven by passenger-volume growth and demand for consistent guest service. Export-led demand from developing countries is also fueling imports of low-cost robotic solutions from China and Japan.
| By Product Type | By Component | By Application | By End-Use Industry | By Deployment Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America dominates the global market with a 38% share in 2024. The U.S. leads adoption due to labor shortages, high wage structures, and the presence of major robotics manufacturers. Hotels across Las Vegas, New York, and Florida have deployed fleets of delivery and cleaning robots to streamline operations. Canada is following similar trends, supported by a strong tourism recovery and government incentives for automation.
Europe
Europe shows steady growth with widespread adoption in the U.K., Germany, France, and Italy. The focus is on enhancing sustainability, energy efficiency, and staff optimization in mid- to high-end properties. European operators are experimenting with multilingual concierge robots and AI-driven guest analytics, supported by EU innovation grants for robotics and AI applications.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, projected to grow at over 25% CAGR through 2030. China, Japan, and South Korea lead the regional market with strong manufacturing ecosystems and government support for robotics innovation. India and Southeast Asia are emerging frontiers due to large hospitality construction pipelines and affordable technology imports. Increasing domestic tourism and smart-city initiatives further accelerate adoption.
Middle East & Africa
MEA is witnessing strong growth, particularly in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar. Robotics is a focal point of luxury hotel projects, smart airports, and mega-tourism developments such as NEOM. Africa’s luxury safari lodges and resort chains are also exploring cleaning and concierge robots to elevate guest service quality.
Latin America
Latin America remains in an early adoption phase, with Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina showing growing interest. The regional focus is on delivery and service robots for large hospitality complexes and urban restaurants. Tourism recovery and hotel refurbishments are expected to support moderate growth through 2030.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Hospitality Robots Market
- SoftBank Robotics
- LG Electronics
- Bear Robotics
- Keenon Robotics
- Pudu Robotics
- Ubtech Robotics
- Future Robot Co.
- Knightscope
- Aethon
- Robotemi
- Hyundai Robotics
- Miso Robotics
- Connected Robotics
- Xenex Disinfection Services
- Travelmate Robotics
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, LG Electronics unveiled its next-generation CLOi Service Robots line for hotel and airport applications, featuring advanced AI navigation and improved payload capacity.
- In March 2025, Keenon Robotics announced strategic expansion into the Middle East, partnering with regional distributors to supply delivery and cleaning robots to luxury hotel chains.
- In February 2025, Pudu Robotics launched the “HolaBot 2” delivery series with enhanced human–robot interaction and fleet optimization capabilities tailored for restaurants and resorts.