Electric Ranges Market Size
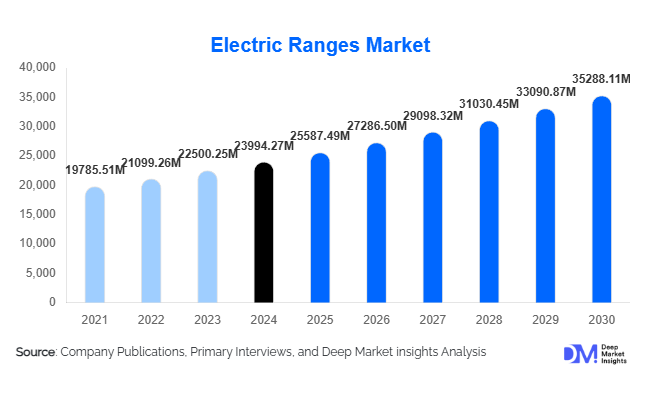
According to Deep Market Insights, the global electric ranges market size was valued at USD 23,994.27 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 25,587.49 million in 2025 to reach USD 35,288.11 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 6.64% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market growth is primarily driven by increasing household electrification, government incentives for energy-efficient appliances, and the rising adoption of smart, induction-based cooking technologies across residential and commercial applications.
Key Market Insights
- Induction and smart ranges are gaining rapid traction due to their superior energy efficiency and precise temperature control compared to gas alternatives.
- North America and Europe dominate the market, supported by strong consumer preference for sustainable and electric kitchen appliances.
- Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region, fueled by urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and government initiatives promoting all-electric homes.
- IoT-enabled cooking appliances are transforming user experiences through remote monitoring, automation, and integration with smart home ecosystems.
- Rising electricity access and infrastructure improvements in developing economies are expanding the addressable market for electric ranges.
- Manufacturers are investing in energy efficiency, design innovation, and connectivity features to align with evolving consumer lifestyles and sustainability goals.
What are the latest trends in the electric range market?
Smart and Connected Kitchen Appliances
The integration of IoT and AI in electric ranges is reshaping the cooking appliance landscape. Consumers can now remotely control temperature settings, cooking modes, and timers via mobile apps and voice assistants such as Alexa and Google Home. Predictive cooking algorithms and auto-shutoff features enhance both convenience and safety. Manufacturers are also offering over-the-air (OTA) software updates to add new functionalities and recipes, positioning electric ranges as intelligent kitchen hubs rather than static appliances.
Shift Toward Induction Cooking
Induction-based electric ranges are rapidly replacing traditional coil and radiant models due to their higher energy efficiency, faster cooking times, and improved safety. With global efforts to phase out natural gas appliances, induction cooking is becoming the preferred solution in modern households. Governments in the U.S., Canada, and Europe are promoting induction technology through rebate programs and efficiency labeling standards. Major brands are responding with expanded product lines featuring sleek designs, touch controls, and multi-zone cooking surfaces.
What are the key drivers in the electric range market?
Growing Electrification and Energy Efficiency Regulations
Policies aimed at decarbonizing residential energy consumption are accelerating the transition from gas to electric cooking solutions. Initiatives such as “electrify everything” campaigns in North America and Europe are propelling the adoption of electric ranges. Additionally, the rise in renewable energy generation supports clean electricity use, making electric ranges more sustainable. Compliance with energy labeling standards (such as ENERGY STAR) further boosts consumer confidence in electric models.
Rising Urbanization and Lifestyle Modernization
Rapid urbanization, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region, is increasing the number of modern households equipped with electric cooking systems. As consumers prioritize convenience, aesthetics, and smart functionality, demand for premium electric ranges with advanced features like self-cleaning, digital displays, and Wi-Fi connectivity is surging. The growing popularity of home cooking and renovation trends post-pandemic continues to sustain market momentum.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Upfront Cost and Energy Price Volatility
Although operationally efficient, electric ranges have higher initial costs compared to traditional gas stoves. Premium smart or induction models often require dedicated electrical wiring, adding installation expenses. Additionally, fluctuations in electricity prices can affect running costs, particularly in developing regions, limiting adoption among cost-sensitive consumers.
Limited Awareness and Compatibility Challenges
In emerging markets, consumer awareness about the long-term benefits of electric cooking remains limited. Furthermore, older housing infrastructure may lack sufficient electrical capacity or compatible outlets for high-power ranges. These compatibility and infrastructural barriers pose adoption challenges, especially in rural and low-income regions.
What are the key opportunities in the electric range industry?
Integration with Smart Home Ecosystems
The rise of connected living offers substantial opportunities for manufacturers to integrate electric ranges with home automation systems. Future models are expected to include interoperability with energy management platforms, enabling consumers to optimize electricity use based on real-time grid data. Partnerships with smart home players like Amazon, Google, and Samsung are likely to expand feature sets and drive market differentiation.
Emergence of Sustainable Materials and Designs
Eco-friendly manufacturing and recyclable materials are emerging as key differentiators. Companies adopting sustainable production practices, such as using low-impact metals and minimizing carbon footprints, are appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, compact and modular range designs suited for small urban kitchens are expanding addressable demand in high-density cities.
Product Type Insights
Induction electric ranges dominate the market segment, driven by efficiency and safety advantages. Radiant electric ranges maintain a steady share due to affordability and reliability in conventional households. Coil-based electric ranges continue to decline as consumers shift toward modern, glass-top models. The integration of dual-fuel hybrids, offering both induction and radiant zones, is also emerging as a premium category trend catering to culinary flexibility.
Application Insights
The residential sector accounts for the majority of global sales, supported by urban housing expansion, energy-efficient building standards, and rising smart home penetration. The commercial segment, including restaurants, hotels, and catering facilities, is adopting high-performance induction ranges for faster cooking and lower heat emissions. Growing emphasis on sustainable foodservice operations is also driving commercial adoption across developed markets.
Distribution Channel Insights
Online retail channels are rapidly expanding, supported by digital marketplaces such as Amazon, Best Buy, and regional e-commerce platforms offering a wide selection of models and transparent pricing. Offline channels, including specialty appliance stores and home improvement retailers, remain significant, especially for premium and professional-grade models that require in-person consultation. Direct-to-consumer (D2C) sales through brand websites are also growing, driven by customization options and promotional offers.
| By Product Type | By Application | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America leads the global market, underpinned by strong electrification trends, government incentives for energy-efficient appliances, and widespread smart home adoption. The U.S. and Canada are witnessing rising consumer preference for induction ranges as part of building decarbonization initiatives. The region also hosts major manufacturers such as GE Appliances, Whirlpool, and Electrolux, enhancing market competitiveness and innovation.
Europe
Europe represents a mature market with strong regulatory backing for electric appliances. The EU’s focus on reducing household carbon emissions and the “Fit for 55” initiative are encouraging transitions away from fossil fuel–based cooking. Countries such as Germany, France, and the U.K. are seeing accelerated demand for induction and smart electric ranges, supported by subsidies for energy-efficient home upgrades.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with China, India, Japan, and South Korea driving adoption. Rapid urbanization, growing disposable incomes, and expanding retail distribution networks are propelling demand. Local manufacturers are introducing cost-effective induction models to capture middle-income households, while smart and luxury ranges are gaining popularity in urban centers. Government electrification programs in India and Southeast Asia further enhance growth prospects.
Latin America
Latin America is experiencing steady growth led by Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. Increasing electricity access, modernization of household infrastructure, and urban apartment developments are supporting market expansion. Regional consumers are gradually shifting from gas to electric ranges due to safety concerns and improved grid reliability.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa market is still in the early adoption stage, but it shows strong potential. The growing construction of residential and hospitality projects, especially in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa, is boosting demand for modern kitchen appliances. Government-led electrification programs and renewable energy initiatives are expected to accelerate long-term growth.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Electric Ranges Market
- Whirlpool Corporation
- GE Appliances (Haier Group)
- Electrolux AB
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- LG Electronics Inc.
- BSH Home Appliances Group
- Midea Group
- Haier Smart Home Co., Ltd.
- Fisher & Paykel Appliances
- Viking Range, LLC
Recent Developments
- In August 2025, LG Electronics launched its new AI-integrated induction range lineup with real-time recipe assistance and adaptive heat control across global markets.
- In June 2025, Whirlpool introduced a new series of ENERGY STAR-certified electric ranges featuring recycled steel and advanced connectivity options for home energy management systems.
- In March 2025, Samsung announced a partnership with SmartThings Energy to integrate power monitoring and usage optimization for all its premium induction range models.