Commercial Microwave Ovens Market Size
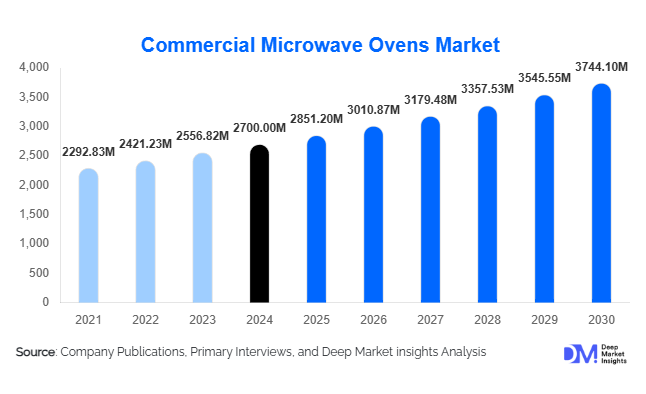
According to Deep Market Insights, the global commercial microwave ovens market size was valued at USD 2,700 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 2,851.20 million in 2025 to reach USD 3,744.10 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 5.6% during the forecast period (2025–2030). Market growth is primarily driven by the rising adoption of energy-efficient kitchen appliances, rapid expansion of quick-service restaurants (QSRs), and increasing demand for high-performance, smart microwave ovens that streamline operations and reduce labor dependency in commercial kitchens.
Key Market Insights
- Heavy-duty microwave ovens dominate the global market, accounting for approximately 44.5% of total 2024 revenue, owing to their use in high-volume kitchens and institutional catering.
- Countertop /freestanding units lead by product type, holding over 52% share due to portability and ease of installation.
- QSRs and fast-casual restaurants are the largest end-user segment, representing nearly 45% of market demand in 2024.
- North America leads the global market with around 35% share, while Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region with a projected CAGR of 8%+ through 2030.
- Technology innovation—including inverter, IoT connectivity, and energy-efficient magnetrons—is reshaping the competitive landscape.
- Replacement and retrofit demand for older magnetron-based ovens in mature markets is sustaining steady revenue streams.
Latest Market Trends
Smart and IoT-Enabled Commercial Microwave Ovens
Manufacturers are integrating smart sensors, cloud-based monitoring, and predictive-maintenance features into microwave ovens. IoT-enabled models allow remote diagnostics, firmware updates, and usage analytics, helping operators reduce downtime and optimize energy consumption. This technological leap is aligning with the broader “connected kitchen” trend, where commercial appliances communicate across platforms for menu automation and inventory efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Green Certification Focus
Energy-efficient models using inverter or solid-state technology are gaining traction as energy regulations tighten and operators seek to lower utility costs. Certification programs such as ENERGY STAR and EU EcoDesign are influencing purchasing decisions, with many large chains adopting sustainability-compliant appliances to meet corporate ESG targets.
Commercial Microwave Ovens Market Drivers
Expanding Food-Service Infrastructure
The surge in quick-service and fast-casual dining formats globally has substantially increased equipment demand. New outlets require high-throughput, durable appliances capable of consistent heating performance across large-scale operations, directly boosting heavy-duty oven sales.
Operational Efficiency and Labor Optimization
Rising labor costs and skill shortages in the food-service industry are driving automation adoption. Microwave ovens reduce food preparation times by 30–50%, streamline workflows, and help maintain consistent quality, making them essential for chain restaurants and institutional kitchens.
Technological Advancement and Premiumization
Innovation in magnetron design, inverter technology, and smart interfaces is enhancing product performance while reducing maintenance needs. Premium models with programmable controls and multi-stage cooking settings attract professional kitchens seeking precision and consistency.
Market Restraints
High Capital Cost and Budget Constraints
Premium heavy-duty or IoT-enabled ovens involve high upfront costs, limiting adoption among small restaurants and independent operators. Budgetary constraints in emerging markets slow replacement cycles and reduce market penetration for advanced models.
Infrastructure and Regulatory Challenges
Emerging economies often face inconsistent voltage standards, limited after-sales networks, and varying safety certifications, complicating large-scale deployment. These challenges can extend adoption timelines and limit high-performance equipment imports.
Commercial Microwave Ovens Market Opportunities
Emerging Regional Demand in Asia-Pacific and LATAM
Rapid expansion of food-service chains, institutional catering, and convenience retail across China, India, Brazil, and Mexico is unlocking high-growth opportunities. Localized manufacturing and region-specific product customization (power ratings, durability) can significantly increase market penetration.
Technological Integration and Retrofit Upgrades
Replacement of legacy magnetron systems with inverter-based models creates a recurring revenue stream for manufacturers. Upgrades focused on energy efficiency, digital controls, and connectivity offer opportunities for premium pricing and long-term service contracts.
Institutional and Non-traditional End-Uses
New segments such as hospitals, airports, schools, and cloud-kitchens require compact, fast, and durable ovens. Targeting these end-users with specialized, high-output models and robust service agreements provides substantial untapped potential.
Product Type Insights
Countertop /freestanding commercial microwave ovens dominate the global market with a 52.3% share in 2024. Their plug-and-play nature, portability, and low installation costs make them ideal for small and medium-sized food-service outlets. Built-in and high-speed combination units are gaining traction in premium kitchens, offering faster cooking cycles and compact integration. Over the forecast period, high-speed models are expected to register a CAGR of 7%+ as restaurants pursue throughput efficiency.
End-Use Insights
Quick-service restaurants (QSRs) and fast-casual dining outlets are the leading end-users, representing 44.7% of global revenue in 2024. Growth stems from expanding global franchise networks and the standardization of cooking equipment across outlets. Institutional catering (hospitals, schools, corporate canteens) is projected to be the fastest-growing sub-segment with 7% CAGR through 2030, driven by rising demand for high-capacity, hygienic food preparation appliances. Convenience retail and cloud-kitchen operators are also accelerating adoption, boosting replacement cycles and export-driven demand for compact professional ovens.
Distribution Channel Insights
Offline channels remain dominant, accounting for 61.5% of global sales in 2024 due to long-standing dealer networks, technical service offerings, and installation support. However, online sales channels are growing rapidly (CAGR 9%), driven by digitization and manufacturer-direct e-commerce models that offer transparent pricing and expanded product visibility for small operators.
| By Product Type | By Power Output | By Application | By Structure Type | By Technology Type | By Distribution Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America held 34.9% of global market value in 2024, led by the U.S., where equipment replacement cycles average 5–7 years. Stringent energy regulations, rebates for high-efficiency models, and mature QSR networks sustain consistent demand. Canada shows steady growth in institutional catering upgrades.
Europe
Europe represents 25–30% of global value, with high adoption in hospitality and institutional foodservice sectors. Energy-efficiency standards and sustainability mandates are spurring retrofits, particularly in the U.K., Germany, France, and Italy.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region (CAGR 8.4%) through 2030. China and India lead adoption with rapid QSR expansion and infrastructure investment. Japan and South Korea remain mature markets emphasizing technology and reliability. Rising urban populations and disposable incomes underpin sustained growth.
Latin America
Brazil and Mexico dominate regional demand, supported by expanding retail foodservice networks and quick-service restaurant franchises. Local manufacturing incentives and import substitution programs are aiding market penetration.
Middle East & Africa
Demand is concentrated in GCC countries, driven by hotel and airport catering growth. Africa’s market is smaller but expanding, aided by hospitality and institutional kitchen development in South Africa, Kenya, and Nigeria.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Commercial Microwave Ovens Market
- Panasonic Corporation
- Midea Group Co., Ltd.
- Sharp Corporation
- Whirlpool Corporation
- LG Electronics Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Bosch Siemens Home Appliances
- Electrolux AB
- Toshiba Corporation
- Haier Group Corporation
- Alto-Shaam Inc.
- The Middleby Corporation
- Amana Commercial (ACP Inc.)
- Hatco Corporation
- Vollrath Company LLC
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Panasonic Corporation introduced a new IoT-enabled commercial microwave oven line integrating real-time energy monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities for QSR operators.
- In May 2025, Midea Group announced the expansion of its commercial kitchen appliance manufacturing facility in Guangdong to meet surging Asia-Pacific demand.
- In February 2025, Sharp Corporation launched inverter-based heavy-duty ovens in Europe aimed at reducing energy consumption by 15–20% compared to conventional models.