Bicycle Sharing Market Size
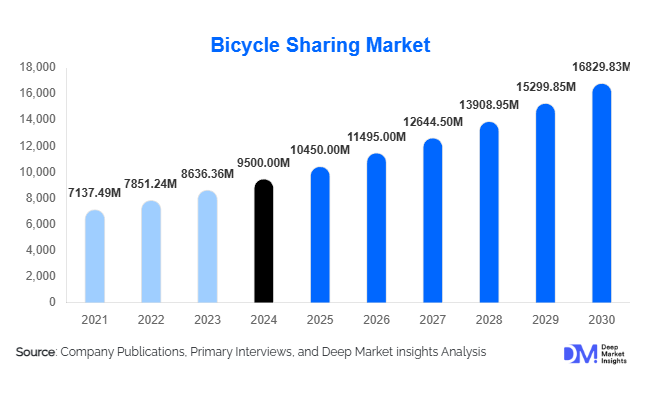
According to Deep Market Insights, the global bicycle sharing market size was valued at USD 9,500 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 10,450.0 million in 2025 to reach USD 16,829.83 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 10.0% during the forecast period (2025–2030). This growth is driven by rapid urbanization, government initiatives promoting sustainable mobility, and rising adoption of electric and dockless bikes that enhance accessibility and convenience for commuters worldwide.
Key Market Insights
- Asia Pacific dominates the bicycle sharing market, accounting for nearly half of global revenue in 2024, led by China’s extensive dockless bike networks and expanding programs in India and Southeast Asia.
- Traditional pedal bikes remain the largest segment, representing around 65% of the 2024 market, while e-bikes are the fastest-growing sub-segment with double-digit growth rates.
- Docked systems retain leadership globally due to well-established urban infrastructure in Europe and North America, although dockless and hybrid models are quickly gaining share.
- Subscription and membership payment models dominate recurring revenue streams, particularly in commuter-focused urban centers.
- Integration with smart-city transit networks and IoT-enabled fleet management is are key enabler of operational efficiency and user satisfaction.
- Corporate and institutional mobility programs, for campuses, logistics, and last-mile delivery, are emerging as new growth verticals for operators.
What are the latest trends in the bicycle sharing market?
Shift Toward Electric and Smart Fleets
The global transition toward electric mobility is reshaping the bicycle sharing industry. Operators are increasingly upgrading fleets to electric bikes (e-bikes), which extend range, reduce user fatigue, and attract new demographics. Smart lock technology, GPS tracking, and mobile app integration are becoming standard, allowing seamless user experiences and real-time fleet management. This trend also enhances safety and maintenance through predictive analytics and data-driven fleet optimization. E-bike sharing models generate higher revenue per ride and encourage longer-distance travel, broadening market reach beyond traditional urban cores.
Integration with Public Transit and Smart-City Ecosystems
Municipal governments worldwide are promoting micro-mobility as part of integrated urban transport networks. Bicycle sharing is being linked to metro, bus, and tram systems through unified ticketing and digital payment platforms. Cities are investing in dedicated bike lanes, smart docks, and multimodal transport hubs. This alignment supports congestion reduction and sustainability goals. Operators that align their business models with smart-city initiatives and public transit infrastructure are securing long-term contracts and improving utilization rates.
What are the key drivers in the bicycle sharing market?
Urbanization and Congestion Mitigation
Rapid urban growth is straining public transportation and road networks, leading cities to adopt shared bicycles as efficient, low-cost, and eco-friendly solutions for short-distance commuting. Governments are prioritizing non-motorized mobility infrastructure, offering tax incentives and grants for shared mobility projects, especially in congested metropolitan areas.
Sustainability and Environmental Awareness
Growing concern over climate change and air quality is accelerating the adoption of green transport solutions. Bicycle sharing aligns with net-zero emission targets, helping cities reduce carbon footprints. Consumers are increasingly drawn to low-impact commuting options, driving consistent growth in membership and ridership across eco-conscious markets in Europe and Asia.
Technological Innovation and Fleet Optimization
IoT sensors, GPS systems, and AI-driven analytics have revolutionized fleet management. Predictive maintenance and demand forecasting tools enhance operational efficiency, while digital payment systems and mobile apps streamline user engagement. These innovations are critical to lowering operational costs and improving customer retention.
What are the restraints for the global market?
High Infrastructure and Operational Costs
Bike-sharing systems require significant upfront investment in bikes, docking stations, maintenance facilities, and software platforms. Operating expenses, including rebalancing fleets, preventing theft or vandalism, and maintaining battery infrastructure for e-bikes, continue to pressure profitability, particularly for new entrants and municipal operators.
Regulatory and Infrastructure Limitations
Inconsistent local regulations regarding parking zones, safety compliance, and sidewalk usage often hinder the deployment of dockless systems. Lack of dedicated bike lanes and road safety infrastructure in developing cities also discourages ridership, limiting growth potential in certain markets.
What are the key opportunities in the bicycle sharing industry?
Integration into Smart-City Mobility Networks
The proliferation of smart-city programs offers opportunities for bicycle sharing operators to embed their services into wider urban mobility ecosystems. Collaborations with city councils and public transit agencies enable unified ticketing, real-time navigation, and shared data platforms that improve route efficiency and ridership.
Expansion of Electric Bike (E-Bike) Sharing Models
E-bike sharing represents the fastest-growing sub-segment, supported by advancements in battery technology and user demand for effortless long-distance rides. Premium pricing and value-added services, such as fast-charging docks and battery-swap systems, enhance revenue streams and attract wider consumer segments.
Corporate and Institutional Mobility Solutions
Enterprises, universities, and industrial campuses are adopting dedicated bicycle fleets for internal mobility and employee commuting. This institutional demand creates steady, contract-based revenue and supports operators’ expansion into private ecosystems beyond public road networks.
Product Type Insights
Traditional pedal bicycles continue to dominate the global bicycle sharing market, contributing approximately 65% of total revenue in 2024. Their leadership is attributed to widespread affordability, lower maintenance costs, and the simplicity of operation that makes them ideal for mass deployment in developing and emerging economies. Cities across Asia, Latin America, and parts of Europe rely heavily on pedal bikes to provide accessible, low-cost mobility solutions for daily commuting. However, the market is rapidly transitioning toward electrification. Electric bicycles (e-bikes) are projected to record a robust CAGR exceeding 15% through 2030, driven by advancements in battery efficiency, integration with smart mobility platforms, and consumer preference for faster and less labor-intensive commuting options. In addition, cargo and utility bikes are emerging as a niche yet high-potential subsegment, primarily adopted for last-mile delivery and logistics applications. Their growth is most visible in Europe and urban Asia, where e-commerce expansion and sustainability mandates are accelerating the adoption of electric cargo bike fleets by courier and logistics operators.
System Type Insights
Docked systems currently hold the largest market share, accounting for about 62% of the global total in 2024. These systems are favored for their operational stability, structured parking management, and strong alignment with municipal transport planning. Long-term public-private partnerships, especially in European and North American cities, have ensured consistent expansion of dock-based stations integrated with metro and bus networks. However, the rise of dockless and hybrid systems has significantly disrupted the market landscape. These models offer greater flexibility, lower deployment costs, and faster scalability, particularly in densely populated urban areas. Dockless systems are proving especially successful in rapidly urbanizing regions such as Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America, where traditional cycling infrastructure is still evolving. The hybrid approach, combining fixed docking for high-demand zones with dockless flexibility in outer districts, is becoming a preferred model among operators seeking operational efficiency and user convenience.
Application Insights
Daily commuting remains the dominant use case in the bicycle sharing market, accounting for nearly 50% of total rides in 2024. This segment benefits from predictable weekday demand, integration with office districts, and alignment with corporate and university sustainability programs. Rapid urbanization, traffic congestion, and rising fuel costs continue to drive commuters toward shared bicycles as a convenient and cost-effective alternative. Last-mile connectivity applications, linking commuters from public transport hubs to workplaces or residential areas, represent the second-largest share and are expanding steadily as cities upgrade their multimodal transport systems. Tourism-oriented usage follows closely, with strong uptake in cities such as Paris, Singapore, and Barcelona, where leisure cycling aligns with local tourism initiatives. Meanwhile, the logistics and delivery segment is emerging as an attractive new revenue stream, particularly for e-bike operators supporting short-distance e-commerce and food delivery services in congested urban centers.
Payment Model Insights
Subscription and membership-based models currently dominate revenue generation, accounting for a significant share of recurring income in 2024. These models attract frequent urban users seeking predictable, low-cost access and drive high customer retention through loyalty programs and integrated mobile applications. They also provide operators with stable, long-term cash flows, which are critical for system expansion and maintenance. Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) models, while smaller in share, remain vital for tourists and occasional users, offering flexibility and one-time payment convenience. A rapidly growing subsegment includes institutional and corporate partnerships, where companies and universities deploy shared bikes to promote sustainable mobility and employee wellness. As governments and private employers increasingly adopt carbon-neutral commuting targets, the demand for enterprise-level subscription contracts is expected to accelerate through 2030.
| By Bike Type | By Sharing Model | By User Type | By Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads the global bicycle sharing market, commanding nearly 50% of the total market share in 2024. The region’s dominance is driven by large-scale adoption in China, India, and Japan, underpinned by rapid urbanization, digital payment integration, and strong policy incentives for sustainable urban mobility. China remains the epicenter of innovation, with companies such as Mobike and Hellobike pioneering dockless and AI-enabled systems that set global benchmarks for scalability. India’s growth trajectory is supported by smart-city programs and rising demand for affordable last-mile connectivity in Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities. Japan, Singapore, and South Korea are witnessing an uptick in e-bike adoption due to supportive infrastructure and aging demographics. The region’s growth is further supported by government initiatives targeting carbon reduction and traffic decongestion, positioning Asia Pacific as both the largest and fastest-growing regional market through 2030.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 20–25% of global revenue and represents one of the most mature and sustainability-focused markets. Countries such as Germany, the U.K., France, and the Netherlands lead in market penetration due to robust cycling infrastructure, favorable regulations, and high public acceptance of green transport solutions. The European Green Deal and city-level carbon neutrality pledges are key growth drivers, encouraging local governments to subsidize e-bike sharing systems and expand dedicated bike lanes. The region is also witnessing accelerated adoption of electric and cargo bikes to support logistics and delivery services in low-emission zones. Moreover, digital integration with multimodal transit apps, enabling users to plan, pay, and navigate across buses, metros, and bike-sharing platforms, enhances accessibility and convenience. These factors, combined with stringent emission norms and strong ESG mandates, ensure steady market expansion in Europe through 2030.
North America
North America holds 15–20% of the global market, primarily driven by large-scale urban systems in New York, San Francisco, Chicago, and Washington D.C. The region’s growth is supported by rising commuter adoption, expanding corporate wellness initiatives, and strong municipal partnerships promoting low-carbon transportation. Programs like Citi Bike (Lyft) and Capital Bikeshare demonstrate successful integration with public transit networks. However, challenges such as urban sprawl, limited cycling lanes, and varying local regulations restrict full-scale expansion. Despite these hurdles, the increasing push for micromobility electrification, coupled with growing investments from private operators and technology firms, is expected to sustain steady growth. In Canada, government-backed clean transportation incentives and the popularity of e-bikes in cities like Toronto and Vancouver further bolster regional market prospects.
Latin America
Latin America holds a smaller but fast-growing market share of about 7–8% in 2024. The region’s expansion is led by Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia, where local governments are prioritizing shared mobility solutions to alleviate urban congestion and pollution. Affordable dockless systems are gaining popularity due to their adaptability to cities with limited cycling infrastructure. Public-private initiatives in São Paulo, Mexico City, and Bogotá are encouraging the deployment of low-cost e-bike fleets integrated with digital fare systems. Regional growth is further supported by the rising adoption of mobile payments, youth-oriented sustainability campaigns, and increased awareness of health and fitness benefits. Over the next decade, Latin America is projected to witness double-digit growth, positioning it as a promising emerging region in the global bicycle sharing landscape.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa (MEA) region currently holds a modest but rapidly expanding share of the global market. Leading countries such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are incorporating bicycle sharing programs into broader smart-city and tourism initiatives. The UAE’s Dubai and Abu Dhabi have introduced large-scale e-bike and dockless systems to promote healthy lifestyles and reduce traffic emissions, while Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 strategy includes extensive urban mobility reforms. In South Africa, private operators are collaborating with municipalities to expand access to shared bikes in business districts and tourist zones. The region’s growth is being accelerated by government investment in sustainable infrastructure, increasing urban fitness awareness, and the expansion of tourism-driven mobility ecosystems. As a result, MEA is projected to post a steady CAGR of over 10% through 2030, supported by both public funding and private partnerships.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the Bicycle Sharing Market
- Lime
- Bird Rides Inc.
- Nextbike GmbH
- Bolt Technology OÜ
- Spin (owned by Ford Mobility)
- Donkey Republic
- Mobike
- Hellobike
- Tembici
- Beryl Cycles
- JCDecaux SA
- Anywheel Pte Ltd.
- Call a Bike
- SG Bike
- Youon Technology Co., Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Lime expanded its electric bike fleet across 25 new European cities, integrating AI-based predictive maintenance to enhance uptime and reduce service costs.
- In May 2025, Bird Rides launched a hybrid docked-dockless system in major U.S. metropolitan areas, aiming to reduce clutter and improve city compliance.
- In February 2025, Nextbike GmbH partnered with Deutsche Bahn to introduce corporate mobility packages, allowing enterprises to deploy branded e-bike fleets for employees.
- In January 2025, Tembici announced a USD 80 million funding round to expand its Latin American operations and deploy 30,000 new e-bikes across Brazil and Mexico.