B2B Continuing Education Market Size
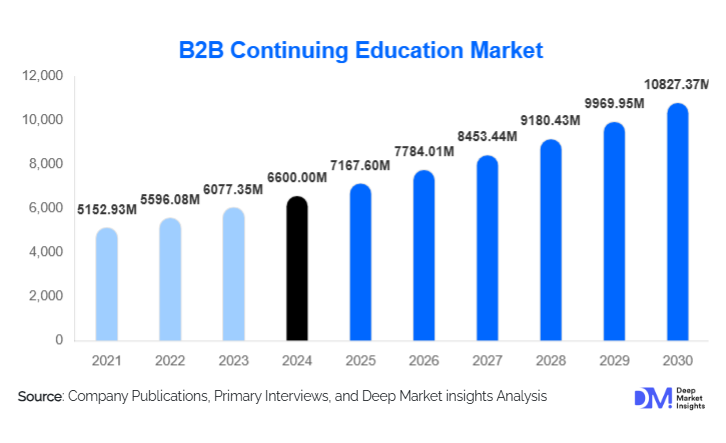
According to Deep Market Insights, the global B2B continuing education market size was valued at USD 6,600 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 7,167.60 million in 2025 to reach USD 10,827.37 million by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 8.6% during the forecast period (2025–2030). The market’s growth is primarily driven by the rising need for workforce reskilling and upskilling, growing regulatory and compliance training mandates, and increasing corporate investment in lifelong learning and credentialing programs. Organizations across industries are leveraging digital learning technologies, hybrid delivery models, and accredited certification programs to maintain competitiveness and compliance in a rapidly evolving business environment.
Key Market Insights
- Corporate digital transformation is reshaping the B2B continuing education landscape, creating demand for data-driven, AI-assisted, and adaptive learning platforms.
- Healthcare and IT industries lead global adoption, driven by stringent compliance requirements and continuous technological change.
- North America dominates the global market, accounting for around 37% of total revenues in 2024, supported by mature infrastructure and established accreditation systems.
- Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with India and China experiencing double-digit growth fueled by government-led skill development programs and rapid digital adoption.
- Micro-credentials and modular learning programs are emerging as key trends, providing enterprises with flexible, stackable, and cost-efficient solutions for employee development.
- Large enterprises account for over half of total spending, driven by ongoing corporate learning and leadership development initiatives.
Latest Market Trends
AI-Driven and Adaptive Learning Solutions
Artificial intelligence and analytics are transforming the continuing education ecosystem by enabling personalized learning paths, real-time performance feedback, and skill-gap mapping. Enterprises are increasingly adopting AI-driven learning management systems (LMS) that tailor content to individual learning styles and job requirements. Predictive analytics are being used to measure training ROI and forecast future skill needs. This technological integration enhances learning efficiency, reduces employee downtime, and supports targeted reskilling, making AI adoption one of the strongest emerging trends in the B2B continuing education market.
Micro-Credentials and Modular Learning Programs
Micro-credentialing is rapidly replacing traditional degree-based programs. Short, stackable courses allow employees to earn verified credentials that align with specific job roles or technologies. Employers value this flexibility as it enables agile workforce development. Online education providers and corporate learning platforms are collaborating with universities and professional associations to accredit modular learning paths, creating new revenue streams and expanding global recognition of alternative credentials. Subscription-based micro-learning platforms are expected to see strong growth through 2030.
B2B Continuing Education Market Drivers
Growing Corporate Investment in Workforce Upskilling
Corporations are increasing their learning and development budgets to maintain competitiveness amid digital transformation. Industries such as IT, finance, and healthcare are allocating higher shares of HR expenditure toward technical training, leadership development, and compliance education. Employers view continuous education as a strategic investment that reduces employee turnover, enhances productivity, and strengthens organizational resilience. The shift from one-time training events to ongoing learning ecosystems is a defining driver of market expansion.
Stringent Compliance and Licensing Regulations
In regulated industries, such as healthcare, finance, and legal services, continuing education is mandatory for maintaining professional licenses. Regulatory bodies are tightening requirements for certification renewals and audit compliance. This recurring need ensures a steady revenue stream for education providers offering accredited programs. The healthcare sector, particularly acute care and behavioral health, accounts for nearly 25% of total market revenues due to constant regulatory updates and patient safety mandates.
Hybrid and Remote Learning Adoption
The shift toward hybrid and remote learning models has expanded access to continuing education worldwide. Enterprises now prefer flexible, cost-efficient formats combining online asynchronous modules with live virtual sessions or in-person workshops. This model reduces travel and venue costs while maintaining engagement and interactivity. Hybrid formats accounted for nearly 30% of corporate learning investments in 2024 and are expected to be the dominant mode by 2030.
Market Restraints
Accreditation and Quality Assurance Challenges
The absence of standardized global accreditation frameworks limits the credibility of many online continuing education programs. Companies and professionals often hesitate to invest in unrecognized certifications, creating a trust deficit. Providers must continuously align their content with industry-recognized standards to maintain market relevance, which increases operational costs and regulatory complexity.
Infrastructure and Cost Constraints in Emerging Economies
High technology adoption costs and limited digital infrastructure in developing regions restrict market penetration. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) often lack the financial capacity to deploy enterprise-grade learning platforms. Although government initiatives aim to bridge these gaps, inconsistent internet access and digital literacy continue to slow adoption rates in regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Latin America.
B2B Continuing Education Market Opportunities
AI and Immersive Learning Integration
Emerging technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and AI-based simulation are redefining professional education. Immersive tools are particularly effective for sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and engineering that require hands-on experience. Providers who integrate these technologies can differentiate themselves, command premium pricing, and expand into high-skill training niches.
Government-Led Skill Development Programs
Public policy initiatives such as “Skill India,” “Made in China 2025,” and EU-wide workforce reskilling programs are opening opportunities for B2B education vendors. Governments are funding partnerships between private providers and public institutions to accelerate digital literacy and professional credentialing. Vendors aligning their offerings with national training frameworks stand to gain from long-term contracts and recurring revenue streams.
Regional Expansion and Localization
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are witnessing surging demand for affordable and culturally adapted training content. Localization, translating courses, aligning with local regulations, and customizing curricula for regional industries is a major growth lever. Providers establishing local partnerships and region-specific accreditation systems are expected to capture significant untapped market share.
Delivery Mode Insights
Offline and in-person formats currently account for approximately 52% of the 2024 market share, driven by sectors such as healthcare and engineering that demand practical, hands-on training. However, the online and hybrid segments are growing rapidly at a projected CAGR of over 10%, fueled by corporate cost optimization and scalable digital infrastructure. Asynchronous modules and blended learning are becoming standard components of enterprise training strategies.
Industry Vertical Insights
The healthcare and life sciences sector leads the global market, contributing roughly 28% of total revenues in 2024. Regulatory obligations for continuing medical education (CME), combined with constant technological advancements in diagnostics and patient care, sustain high spending levels. The IT and software sector follows closely, driven by rapid technological obsolescence and the need for continuous skill renewal in areas like AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
End-User Insights
Large enterprises represent the dominant customer segment, comprising over 55% of total market spending in 2024. They invest heavily in leadership development, compliance, and technical upskilling programs. The SME segment is projected to grow fastest through 2030, supported by SaaS-based learning management systems and cost-effective subscription platforms that lower barriers to entry for smaller firms.
| By Learning Format | By Course Type | By Enterprise Size | By End-Use Industry | By Delivery Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Regional Insights
North America
North America holds the largest market share, accounting for approximately 37% of global revenues in 2024. The U.S. dominates due to mature accreditation systems, advanced corporate learning cultures, and strong demand from the healthcare and finance sectors. Canada’s investments in workforce reskilling and remote learning infrastructure further enhance regional performance.
Europe
Europe represents around 23% of the global market, with the U.K., Germany, and France leading adoption. EU directives promoting lifelong learning and standardized credential frameworks are driving enterprise participation. Western Europe’s corporate learning budgets continue to expand, while Eastern Europe is emerging as a cost-competitive hub for digital course creation and export.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, projected to record a CAGR exceeding 11% through 2030. India and China are central to this growth, backed by government initiatives, expanding internet access, and a rising middle-class workforce seeking professional advancement. Southeast Asia is also emerging as a hotspot for localized, mobile-first training platforms.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for roughly 8% of global market revenues in 2024. Brazil, Mexico, and Chile lead adoption, primarily through regional training providers offering compliance and vocational programs. Government partnerships for digital workforce development and growing multinational investments are gradually improving market penetration.
Middle East & Africa
The region collectively represents about 7% of global market share but is expanding rapidly. The UAE and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in professional development initiatives tied to national transformation programs. Africa’s market remains nascent, though government-backed skill development schemes and mobile-based education models are showing promising results.
| North America | Europe | APAC | Middle East and Africa | LATAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Players in the B2B Continuing Education Market
- Skillsoft
- Coursera for Business
- Udemy Business
- LinkedIn Learning
- Pluralsight
- HealthStream Inc.
- RELIAS Learning
- Pearson PLC
- D2L Corporation
- SAP Litmos
- Cornerstone OnDemand
- CrossKnowledge
- NIIT Ltd.
- Simplilearn
- edX for Business
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Coursera for Business launched an AI-driven skill assessment dashboard enabling enterprises to map workforce competencies and recommend personalized learning paths.
- In March 2025, Skillsoft introduced immersive VR-based compliance simulations for healthcare and finance clients to enhance experiential learning outcomes.
- In January 2025, LinkedIn Learning expanded its credentialing partnership with major U.S. universities, enabling verified micro-certifications directly linked to professional profiles.